
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Do not copy Please.
The pendulum is suspended from point O and consists of two bars, each weighing 10 lb. Determine the moment of inertia of the pendulum about the axis that passes through a) bolt
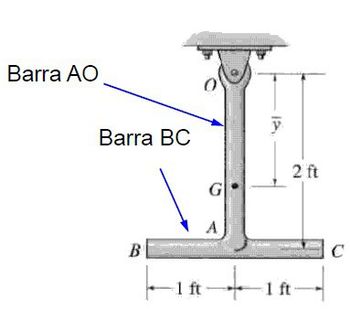
Transcribed Image Text:Barra AO
Barra BC
B
G
A
2 ft
-1 ft-1 ft
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q.1) Determine the radius of gyration of the area below. Assume t = 20 mm. units: mm 200 300 Xarrow_forwardSuppose that aaa = 5.29 in. and b = 2.3 in. Determine the moment of inertia for the shaded area about the x axis.arrow_forwardAt the instant shown, the uniform slender rod with mass m = 32 kg is pin-supported at point O. It has dimensions a = 0.24 m and b = 0.70 m. Determine its mass moment of inertia lo (in kg•m2) about the axis that passes point O and is perpendicular to the screen. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 3 places after the decimal point. a b M Your Answer: Answerarrow_forward
- A composite pendulum is made of a uniform slender rod and a uniform disk. If the rod has length of 1.1 m and mass of 12.2 kg, and the disk has radius of 0.35 m and mass of 9.7 kg, determine the mass moment of inertia (in kg • m) about the centroidal x axis that passes through its center of gravity (seen from the profile view). Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. y G G R Profile view Your Answer: Answerarrow_forward3. Consider the following shape with a = 1 ft and b = 3 ft. a. Determine the centroid. b. Determine the moment of inertia about the horizontal centroidal axis Determine the moment of inertia about the vertical centroidal axis. c. a barrow_forwardThe uniform rod of length 4b and mass m is bent into the shape shown. The diameter of the rod is small compared with its length. Determine the moments of inertia of the rod about the three coordinate axes. Use the values m = 9.7 kg and b = 650 mm. Answers: Ixx = i lyy= Izz i i kg-m² kg.m² kg.m²arrow_forward
- Calculate the center of mass of the 6 lb right angle bar assuming constant density.arrow_forwardSOLVE IN DIGITAL FORMAT STEP BY STEParrow_forward1. A circular disk has a density p(r) which varies as a function of distance from the center of the disk. The disk has a radius R and a thickness t. Assuming p(r) = Po(1-r/R): Calculate the total mass of the disk. a. b. Calculate the moment of inertia of the disk about an axis out of the plane of the page and passing through Point G. C. Calculate the moment of inertia of the disk about an axis out of the plane of the page and passing through Point O. G Rarrow_forward
- 6 Given the system of points A,B,C with A(1,-1,1), B(2,0,2), C(-1,1,0) and masses m₁= 2,m₂=1,m3=4 respectively. Determine the moments and events inertia of the system with respect to the system of axes Oxyz. Then find the moments of inertia with respect to the primary axis system with origin O and to define the addresses of these axes.arrow_forward2arrow_forwardThe slender rod in the figure has a mass 10 kg. Find mass moment of inertia (MMI) about an axis perpendicular to the screen and passing through point O. 500 mm A A. 0.833 kg.m2 B. 5.27 kg.m2 0.675 kg.m2 C. 4.598 kg.m2 D.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY