
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
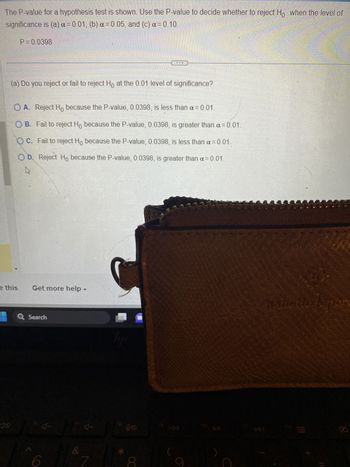
Transcribed Image Text:The P-value for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to reject Ho when the level of
significance is (a) x=0.01, (b) a= 0.05, and (c) α = 0.10.
40
P=0.0398
e this
(a) Do you reject or fail to reject Ho at the 0.01 level of significance?
O A. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than α=0.01.
OB. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than α=0.01.
OC. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than α=0.01.
OD. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than α=0.01.
ņ
Get more help -
Q Search
16
4-
6
17 1+
L
18
go
FE
CO
KAA
9
DII
(11
DDI
hanette lepore
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
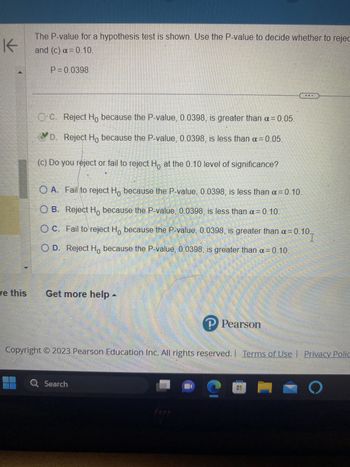
Transcribed Image Text:K
ve this
The P-value for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to rejec
and (c) a = 0.10.
P = 0.0398
OC. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than α = 0.05.
P
Get more help.
CHARIT
D. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.05.
(c) Do you reject or fail to reject H at the 0.10 level of significance?
PERS
OA. Fail to reject H because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.10.
OB. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.10.
OC. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than a = 0.10
O D. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than a = 0.10.
I
Q Search
n
Copyright © 2023 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Polic
P Pearson
!!!!
C
O
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
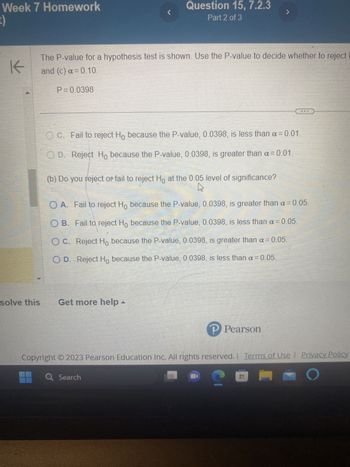
Transcribed Image Text:Week 7 Homework
K
solve this
The P-value for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to reject I
and (c) a=0.10.
P=0.0398
Question 15, 7.2.3
Part 2 of 3
OC. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.01.
OD. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than a = 0.01
(b) Do you reject or fail to reject Hō at the 0.05 level of significance?
h
OA. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than a = 0.05.
OB. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.05.
O C. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than α = 0.05.
O D. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.05.
Get more help -
Q Search
P Pearson
Copyright © 2023 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy.
(
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:K
ve this
The P-value for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to rejec
and (c) a = 0.10.
P = 0.0398
OC. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than α = 0.05.
P
Get more help.
CHARIT
D. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.05.
(c) Do you reject or fail to reject H at the 0.10 level of significance?
PERS
OA. Fail to reject H because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.10.
OB. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.10.
OC. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than a = 0.10
O D. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than a = 0.10.
I
Q Search
n
Copyright © 2023 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Polic
P Pearson
!!!!
C
O
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Week 7 Homework
K
solve this
The P-value for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to reject I
and (c) a=0.10.
P=0.0398
Question 15, 7.2.3
Part 2 of 3
OC. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.01.
OD. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than a = 0.01
(b) Do you reject or fail to reject Hō at the 0.05 level of significance?
h
OA. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than a = 0.05.
OB. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.05.
O C. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is greater than α = 0.05.
O D. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0398, is less than a = 0.05.
Get more help -
Q Search
P Pearson
Copyright © 2023 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy.
(
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Perform the test of hypothesis on the following scenarios. A brand of powdered milk is advertised as having a net weight of 250 grams. A curious consumer obtained the net weight of 10 randomly selected cans. The values obtained are 256, 248, 242, 245, 246, 248, 250, 255, 243, and 249 grams. Is there reason to believe that the average net weight of the powdered milk cans is less than 250 grams at 10% level of significance? Assume the net weight is normally distributed with unknown population variance. Note: pls follow the given steps in the photo attachedarrow_forwardA researcher conducts a hypothesis test on a population proportion. Her null and alternative hypothesis are H0:p = 0.4 and Ha: p < 0.4. The test statistic and p-value for the test are z = -3.01 and p-value = 0.0013. For asignificance level of a= 0.05, choose the correct conclusion regarding the null hypothesis.H0:________________________ Ha:_______________________Compare the p-value and a:_______________Decision:_________________________Conclusion:___________________________________________________________arrow_forwardThe P-value for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to reject Ho when the level of significance is (a) α = 0.01, (b) α = 0.05, and (c) α = 0.10. P = 0.0176 (a) Do you reject or fail to reject Ho at the 0.01 level of significance? A. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0176, is less than α = 0.01. B. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0176, is greater than α = 0.01. C. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0176, is greater than α = 0.01. D. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0176, is less than α = 0.01. (b) Do you reject or fail to reject Ho at the 0.05 level of significance? A. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0176, is less than α = 0.05. B. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0176, is greater than α = 0.05. C. Reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0176, is less than α = 0.05. D. Fail to reject Ho because the P-value, 0.0176, is greater than α = 0.05. (c) Do you reject or fail to reject Ho at the 0.10 level of significance? A. Fail to reject Ho because the…arrow_forward
- Test the claim that the mean GPA of night students is larger than the mean GPA of day students at the 0.005 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Họ: PN 2 pp Họ:N 2 D Ho: PN PD H1 : UN + UD Hị:PN + PD H1: N > uD The test is: right-tailed two-tailed left-tailed The sample consisted of 30 night students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.18 and a standard deviation of 0.07, and 30 day students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.14 and a standard deviation of 0.08. The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals) The p-value is: (to 2 decimals) Based on this we: Fail to reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardUse the calculator displays to the right to make a decision to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis at a significance level of α = 0.10. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Since the P-value is less than a, fail to reject the null hypothesis. O B. Since the P-value is greater than x, reject the null hypothesis. O C. Since the P-value is greater than x, fail to reject the null hypothesis. O D. Since the P-value is less than a, reject the null hypothesis. -C Z-Test Z-Test Inpt: Data Statsu #80 Ho:80 0:5.75 x:78.75 n:35 #μο μο Calculate Draw z 1.2861043 p=0.19840666 x = 78.75 n=35arrow_forwardA null and alternative hypothesis are given. Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. H0: p ≥ 0.2 Ha: p < 0.2 What type of test is being conducted in this problem?arrow_forward
- Find the value of the standard score, z, and determine whether to reject the null hypothesis at a 0.10 significance level. Is the alternative hypothesis supported? Ho: p= 19.6 seconds, H: p> 19.6 seconds, n = 121, x=20 5 seconds, o = 2.0 seconds a The value of the standard score is (Round to two.decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardAnswer all these questions A, B and C questions.arrow_forwardThe P-value for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to reject Upper H 0 when the level of significance is (a) alpha equals0.01 , (b) alpha equals0.05 , and (c) alpha equals0.10 . Pequals 0.0683 (a) Do you reject or fail to reject Upper H 0 at the 0.01 level of significance? A. Fail to reject Upper H 0 because the P-value, 0.0683 , is less than alpha equals0.01 . B. Fail to reject Upper H 0 because the P-value, 0.0683 , is greater than alpha equals0.01 . C. Reject Upper H 0 because the P-value, 0.0683 , is less than alpha equals0.01 . D. Reject Upper H 0 because the P-value, 0.0683 , is greater than alpha equals0.01 . (b) Do you reject or fail to reject Upper H 0 at the 0.05 level of significance? A. Fail to reject Upper H 0 because the P-value, 0.0683 , is less than alpha equals0.05 .…arrow_forward
- The P-value for a hypothesis test is shown. Use the P-value to decide whether to reject Upper H 0 when the level of significance is (a) alpha equals0.01 , (b) alpha equals0.05 , and (c) alpha equals0.10 . Pequals 0.0943 (a) Do you reject or fail to reject Upper H 0 at the 0.01 level of significance? A. Reject Upper H 0 because the P-value, 0.0943 , is greater than alpha equals0.01 . B. Fail to reject Upper H 0 because the P-value, 0.0943 , is less than alpha equals0.01 . C. Reject Upper H 0 because the P-value, 0.0943 , is less than alpha equals0.01 . D. Fail to reject Upper H 0 because the P-value, 0.0943 , is greater than alpha equals0.01 . (b) Do you reject or fail to reject Upper H 0 at the 0.05 level of significance? A. Reject Upper H 0 because the P-value, 0.0943 , is less than alpha equals0.05 . B. Fail…arrow_forwardTest the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is significantly different than the proportion of women who own cats at the 0.02 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho: M = μF Ho: PM = PF H₁ μM μF H₁:PM > PF The test is: left-tailed right-tailed two-tailed Based on a sample of 60 men, 30% owned cats Based on a sample of 40 women, 45% owned cats The test statistic is: Ho: PM = PF H₁: PM μF (to 2 decimals) (to 2 decimals) Ho: PM = PF Ho: M = μF H₁:PM ‡ PF H₁: μM < MFarrow_forwardThe following table contains the number of successes and failures for three categories of a variable. Test whether the proportions are equal for each category at the α=0.1 level of significance. Category 1 Category 2 Category 3 Failures 32 51 57 Successes 39 54 73 State the hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. A. H0: The categories of the variable and success and failure are independent. H1: The categories of the variable and success and failure are dependent. B. H0: The categories of the variable and success and failure are dependent. H1: The categories of the variable and success and failure are independent. C. H0: p1=p2=p3 H1: At least one of the proportions is different from the others. D. H0: μ1=E1 and μ2=E2 and μ3=E3 H1: At least one mean is different from what is expected. What is the P-value? nothing (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What conclusion can be…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman