
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
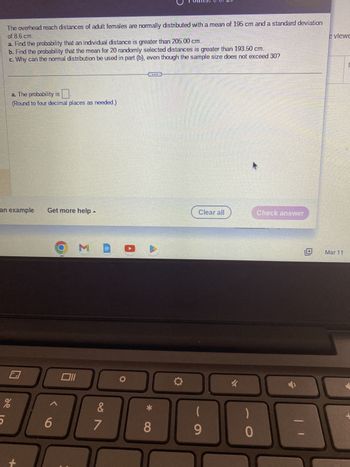
Transcribed Image Text:The overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 195 cm and a standard deviation
of 8.6 cm.
a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 205.00 cm.
b. Find the probability that the mean for 20 randomly selected distances is greater than 193.50 cm.
c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30?
5
a. The probability is
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
an example
%
+
Get more help
6
O M
Oll
&
3
7
ELE
8
O
Clear all
9
k
-
0
Check answer
11
e viewe
Mar 11
|
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 195 cm and a standard deviation of 7.8 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 204.30 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 25 randomly selected distances is greater than 193.20 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30? a. The probability is- (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. The probability is- (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Choose the correct answer below. A. The normal distribution can be used because the finite population correction factor is small. B. The normal distribution can be used because the original population has a normal distribution. C. The normal distribution can be used because the mean is large. D. The normal distribution can be used because the probability is less than 0.5arrow_forwardThe overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 195 cm and a standard deviation of 8.9 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 207.50 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 15 randomly selected distances is greater than 193.70 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30? a. The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardThe overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 202.5 cm and a standard deviation of 8 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 215.00 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 15 randomly selected distances is greater than 200.30 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30?arrow_forward
- The overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 197.5 cm and a standard deviation of 8.9 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 210.90 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 15 randomly selected distances is greater than 195.70 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30?arrow_forwardThe overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 202.5 cm and a standard deviation of 8.9 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 211.80 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 15 randomly selected distances is greater than 200.30 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30? a. The probability is. (Round to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardThe overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 205.5 cm and a standard deviation of 7.8 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 218.90 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 15 randomly selected distances is greater than 203.30 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30?arrow_forward
- The overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 197.5 cm197.5 cm and a standard deviation of 8.3 cm8.3 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 210.90210.90 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 1515 randomly selected distances is greater than 196.00 cm.196.00 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30?arrow_forwardThe overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 202.5 cm and a standard deviation of 8 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 211.80 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 15 randomly selected distances is greater than 200.70 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 307 a. The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Choose the correct answer below. O A. The normal distribution can be used because the probability is less than 0.5 O B. The normal distribution can be used because the original population has a normal distribution. O C. The normal distribution can be used because the finite population correction factor is small. O D. The normal distribution can be used because the mean is large. Click to select your answer(s). Us / SAMSUNGarrow_forwardThe overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 197.5 cm and a standard deviation of 8.6 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 206.80 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 25 randomly selected distances is greater than 195.30 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30? a. The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. The probability is. (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Choose the correct answer below. O A. The normal distribution can be used because the probability is less than 0.5 O B. The normal distribution can be used because the mean is large. Oc. The normal distribution can be used because the finite population correction factor is small. O D. The normal distribution can be used because the original population has a normal distribution.arrow_forward
- The overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 202.5 cm and a standard deviation of 8.3 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 212.50 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 20 randomly selected distances is greater than 200.70 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30?arrow_forwardThe overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 197.5 cm and a standard deviation of 8.3 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 210.90 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 15 randomly selected distances is greater than 195.70 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30?arrow_forwardThe overhead reach distances of adult females are normally distributed with a mean of 195 cm and a standard deviation of 7.8 cm. a. Find the probability that an individual distance is greater than 205.00 cm. b. Find the probability that the mean for 20 randomly selected distances is greater than 192.80 cm. c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30? a. The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Choose the correct answer below. A. The normal distribution can be used because the probability is less than 0.5 B. The normal distribution can be used because the finite population correction factor is small. O C. The normal distribution can be used because the original population has a normal distribution. D. The normal distribution can be used because the mean is large.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman