
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
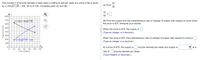
Transcribed Image Text:The number x of bicycle helmets a retail chain is willing to sell per week at a price of $p is given
by x = 80/p + 25 – 350, 20<ps 100. Complete parts (A) and (B).
dx
(A) Find
dp
dx
800-
dp
700-
(B) Find the supply and the instantaneous rate of change of supply with respect to price when
the price is $75. Interpret your results.
x= 1000– 55/p+ 25
600–
500-
When the price is $75, the supply is
400-
(Type an integer or a decimal.)
300-
When the price is $75, the instantaneous rate of change of supply with respect to price is
200-
/지= 80시p+ 25 -350
(Type an integer or a decimal.)
100-
p.
0-
At a price of $75, the supply is
bicycle helmets per week and supply is
at a
20
40
60
80
100 120
rate of bicycle helmets per dollar.
(Type integers or decimals.)
Price (Dollars)
Supply/Demand
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Let 10p + x = 100 be the demand equation, where p is the price per item when x items are demanded. (a) Find the total revenue when the level of production is: (i) 40; (ii) 41; (b) Find the exact revenue derived from the 41st item. (c) Find the approximate revenue derived from the 41st item. (d) What is the error if the derivative is used to approximate the marginal revenue?arrow_forwardThe marginal revenue (in thousands of dollars) from the sale of x handheld gaming devices is given by the following function. )= 4x (x² +27,000) 4x R'(x) = 2 (a) Find the total revenue function if the revenue from 130 devices is $21,660. (b) How many devices must be sold for a revenue of at least $38,000? BECED (a) The total revenue function is R(x)=, given that the revenue from 130 devices is $21,660. (Round to the nearest integer as needed.) (b) devices must be sold to generate a revenue of at least $38,000. (Type a whole number.)arrow_forwardONLY TYPED SOLUTIONarrow_forward
- A manufacturing company produces ACME Standard Widgets having a fixed cost of $50 and variable cost of $8 per unit. Sales history indicates that the sales price in dollars, P, varies with the demand, D, by the function: P = 200 - 0.1D Determine the following: Optimum demand for the widgets. Maximum profit that can be made. Determine the range of demands for which the company is profitable.arrow_forwardSuppose the demand for a product is given by D(p) = -2p+230. A) Calculate the elasticity of demand at a price of $28. Elasticity = (Round to three decimal places.) B) At what price do you have unit elasticity? (Round your answer to the nearest penny.) Price = $arrow_forwarda) The demand function for a product is p = 60 3-9/15) where q is the number of units and p is the price of one unit. At what price will the demand be 15 units? How many units will be demanded if the price is $41.60?arrow_forward
- Suppose the demand for a product is given by D(p)=-8p+227. A) Calculate the elasticity of demand at a price of $18. Elasticity = (Round to three decimal places.) B) At what price do you have unit elasticity? (Round your answer to the nearest penny.) Price = $arrow_forwardFor the cost and price functions below, find a) the number, q, of units that produces maximum profit; b) the price, p, per unit that produces maximum profit; and c) the maximum profit, P. C(q) = 90+12q; p= 64-2q a) The number, q, of units that produces maximum profit is q = b) The price, p, per unit that produces maximum profit is p=$ c) The maximum profit is P = $.arrow_forwardFor the cost and price functions below, find a) the number, q, of units that produces maximum profit; b) the price, p, per unit that produces maximum profit; and c) the maximum profit, P. C(q) = 70+ 14q; p = 70-2q a) The number, q, of units that produces maximum profit is q = b) The price, p, per unit that produces maximum profit is p = $ c) The maximum profit is P = $arrow_forward
- 4x+200 A garden shop determines the demand function q = D(x) = 30x+9 during early summer for tomato plants where q is the number of plants sold per day when the price is x dollars per plant. (a) Find the elasticity. (b) Find the elasticity when x = 2. (c) At $2 per plant, will a small increase in price cause the total revenue to increase or decrease? (a) The elasticity isarrow_forwardThe daily demand function for x LED lights sold by a major retailer is p = 1112.5 0.75x dollars, and the average cost of sales is C = 250 + 3x dollars. Find the quantity that will maximum profit, the selling price at that quantity and the maximum profit. a) Selling LED lights will maximum profit. b) The selling price at the answer in part (a) is $ c) The maximum profit is $arrow_forwardThe HAC at Humberview has decided to sell Gatorade to raise money. The demand function is described by px=-4x+340 , where x is the number of bottles, in hundreds, and px is in dollars. The cost function, in dollars, is described by Cx=300x-275. Determine the number of Gatorade bottles they must sell so that they maximize their profit.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education