
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
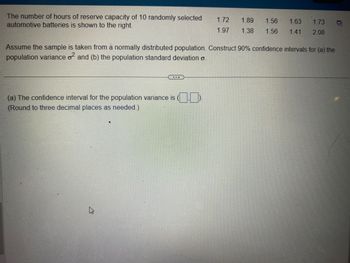
Transcribed Image Text:The number of hours of reserve capacity of 10 randomly selected 1.72
automotive batteries is shown to the right.
1.97
(a) The confidence interval for the population variance is (
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
1.89 1.56
1.38 1.56
Assume the sample is taken from a normally distributed population. Construct 90% confidence intervals for (a) the
population variance o² and (b) the population standard deviation o
4
1.63 1.73
1.41 2.08
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Determine the given variables
VIEW Step 2: Find the sample standard deviation using the given data
VIEW Step 3: Find the critical value for given confidence level
VIEW Step 4: Find the confidence interval for population variance
VIEW Step 5: Find the confidence interval for population standard deviation
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 22 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Times for a surgical procedure are normally distributed. There are two methods. Method A has a mean of 35 minutes and a standard deviation of 3 minutes, while method B has a mean of 39 minutes and a standard deviation of 1.5 minutes. (a) Which procedure is preferred if the procedure must be completed within 34 minutes? O Method A O Method B O Either Method (b) Which procedure is preferred if the procedure must be completed within 40.0 minutes? O Either Method O Method A O Method B (c) Which procedure is preferred if the procedure must be completed within 43 minutes? OMethod A O Method B O Either Method Prev 19 of 19 Next e to search hparrow_forwardThe grade point averages (GPA) for 12 randomly selected college students are shown on the right. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. Assume the population is normally distributed (a) Find the sample mean. x= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) X (b) Find the sample standard deviation. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) (c) Construct a 90% confidence interval for the population mean μ. A 90% confidence interval for the population mean is (Round to two decimal places as needed.) 2.3 3.1 2.9 1.9 0.6 4.0 2.5 1.1 3.7 0.1 2.3 3.3arrow_forwardWorkers at a certain soda drink factory collected data on the volumes (in ounces) of a simple random sample of 21 cans of the soda drink. Those volumes have a mean of 12.19 oz and a standard deviation of 0.14 oz, and they appear to be from a normally distributed population. Use the sample data to test the claim that the population of volumes has a standard deviation less than 0.15 oz. Use a 0.01 significance level. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. a. Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Ho: o0.15 oz H,: o0.15 oz H:o=0.15 oz O C. Ho: o=0.15 oz H,: o<0.15 oz O D. Ho: o =0.15 oz H:o#0.15 oz b. Compute the test statistic. x² = ] (Round to three decimal places as needed.) c. Find the P-value. P-value= (Round to four decimal places as needed.) O Time Remaining: 00:15:21 Nextarrow_forward
- Can you please check my workarrow_forwardUse technology to construct the confidence intervals for the population variance o2 and the population standard deviation o. Assume the sample is taken from a normally distributed population. c= 0.95, s= 34, n= 17 ..... The confidence interval for the population variance is (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardUse technology to construct the confidence intervals for the population variance o² and the population standard deviation a. Assume the sample is taken from a normally distributed population. c=0.99, s= 33, n= 16 The confidence interval for the population variance is ( ). (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The confidence interval for the population standard deviation is ( ). (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- A math teacher claims that she has developed a review course that increases the scores of students on the math portion of a college entrance exam. Based on data from the administrator of the exam, scores are normally distributed with H = 525. The teacher obtains a random sample of 2200 students, puts them through the review class, and finds that the mean math score of the 2200 students is 530 with a standard deviation of 119. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. C. Yes, because every increase in score is practically significant. D. No, because the score became only 0.95% greater. (d) Test the hypothesis at the a = 0.10 level of significance with n= 400 students. Assume that the sample mean is still 530 and the sample standard deviation is still 119. Is a sample mean of 530 significantly more than 525? Conduct a hypothesis test using the P-value approach. Find the test statistic. to =0 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) %3D Find the P-value. The P-value is (Round to three decimal…arrow_forwardThe mean score on a driving exam for a group of driver’s education students is 76 points, with a standard deviation of 6 points. Apply chebychev’s theorem to the data using K=2. Interpret, At least ___% of the exam score falls between ___and ____arrow_forwardPart Variability is critical in the manufacturing of the ball bearings. Large variances in the size of the ball bearings cause bearing failure and rapid wear out. Production standards call for a maximum variance of .0001 when the bearing sizes are measured in inches. A sample of 15 bearings shows a sample standard deviation of .014. a. Compute the 90% confidence interval estimate of the variance of the ball bearings in the population. b. Use a= 0.10 to determine whether the sample indicates that the maximum acceptable variance is being exceeded. Use critical value approach. ( Note: You must state null and alternative hypotheses, compute the test statistic, Report the critical Value, and draw a conclusion.arrow_forward
- Use technology to construct the confidence intervals for the population variance o and the population standard deviation o. Assume the sample is taken from a normally distributed population. c= 0.90, s = 5.76, n = 26 The confidence interval for the population variance is ( ). (Round to two decimal places as needed.) The confidence interval for the population standard deviation is ( ). (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardUse the data to calculate the sample variance, s. (Round your answer to five decimal places.) n = 7: 1.6, 3.5, 1.6, 2.1, 3.1, 2.9, 3.0 %3D Construct a 95% confidence interval for the population variance, of. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) to Test Ho: = 0.8 versus H: of + 0.8 using a = 0.05. State the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) x2 State the rejection region. (If the test is one-tailed, enter NONE for the unused region. Round your answers to two decimal places.) x2 > x² State the conclusion. H, is rejected. There is sufficient evidence to indicate that the population variance is different from 0.8. H, is rejected. There is insufficient evidence to indicate that the population variance is different from 0.8. H, is not rejected. There is sufficient evidence to indicate that the population variance is different from 0.8. O Ho is not rejected. There is insufficient evidence to indicate that the population variance is different from 0.8.arrow_forwardIn a random sample of 28 people, the mean commute time to work was 32.1 minutes and the standard deviation was 7.2 minutes. Assume the population is normally distributed and use a t-distribution to construct a 99% confidence interval for the population mean μ. What is the margin of error of μ? Interpret the results. The confidence interval for the population mean μ (_____,______) (Round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman