
Modern Physics
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781111794378
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
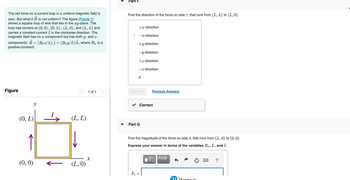
Transcribed Image Text:The net force on a current loop in a uniform magnetic field is
zero. But what if B is not uniform? The figure (Figure 1)
shows a square loop of wire that lies in the xy-plane. The
loop has corners at (0, 0), (0, L), (L, 0), and (L, L) and
carries a constant current I in the clockwise direction. The
magnetic field has no x-component but has both y- and z-
components: B = (Boz/L) j+ (Boy/L) Ê, where Bo is a
positive constant.
Figure
(0, L)
y
(0, 0)
(L, L)
(L, 0)
1 of 1
X
Part F
Find the direction of the force on side 1, that runs from (L, L) to (L, 0).
O
OOOO
+x-direction
-x-direction
+y-direction
-y-direction
+z-direction
-z-direction
O
Submit Previous Answers
Correct
▼ Part G
Find the magnitude of the force on side 4, that runs from (L, 0) to (0,0).
Express your answer in terms of the variables Bo, L, and I.
Π ΑΣΦ
F4 =
Doarson
****
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A superconducting wire of diameter 0.25 cm carries a current of 1000 A. What is the magnetic field just outside the wire?arrow_forwardCan a constant magnetic field set into motion an electron initially at test? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardA strip of copper is placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 2.5 T. The Hall electric field is measured to be 1.5103V/m (a) What is the drift speed of the conduction electrons? (b) Assuming that n =8.01028 elections per cubic meter and that the cross-sectional area of the strip is 5.0106m2 , calculate the current in the ship, (c) What is the Hall coefficient 1/nq?arrow_forward
- A long, straight, cylindrical conductor contains a cylindrical cavity whose axis is displaced by n from the axis of the conductor, as shown in the accompanying figure. The current density in the conductor is given by J=J0k, where J0 is a constant and k is along the axis of the conductor. Calculate the magnetic field at an arbitrary point P in the cavity by superimposing the field of a solid cylindrical conductor with radius R1and current density Jonto the field of a solid cylindrical conductor with radius R2and current density J . Then use the fact that the appropriate azimuthal unit vectors can be expressed as 1=kr1and 2=kr2 to show that everywhere inside the cavity the magnetic field is given by the constant B=120J0ka , where a=r1r2 and r1=r1r1 is the position of P relative to the center of the conductor and r2=r2r2 is the position of P relative to the center of the cavity.arrow_forwardConsider a right circular cylinder of radius R, with mass M uniformly distributed throughout the cylinder volume. The cylinder is set into rotation with angular speed ω about its longitudinal axis. (a) Obtain an expression for the angular momentum L of the rotating cylinder. (b) If charge Q is distributed uniformly over the curved surface only, find the magnetic moment µ of the rotating cylinder. Compare your expressions for µ and L to deduce the g factor for this object.arrow_forwardThe potential difference V(t) between parallel plates shown above is instantaneously increasing at a rate of 107V/s. What is the displacement current between the plates if the separation of the plates is 1.00 cm and they have an area of 0.200m2?arrow_forward
- At a particular instant an electron is traveling west to east with a kinetic energy of 10 keV. Earth's magnetic field has a horizontal component of 1.8105 T north and a vertical component of 5.0105 T down. (a) What is the path of the election? (b) What is the radius of curvature of the path?arrow_forwardAn electron in a TV CRT moves with a speed of 6.0107 m/s, in a direction perpendicular to Earth's field, which has a strength of 5.0105 T. (a) What strength electric field must be applied perpendicular to the Earth’s field to make the election moves in a straight line? (b) If this is done between plates separated by 1.00 cm, what is the voltage applied? (Note that TVs are usually surrounded by a ferromagnetic material to shield against external magnetic fields and avoid the need for such a collection,)arrow_forwardThe force on a magnetic moment z in a nonuniform magnetic field Bz is given by Fz=zdBzdz If a beam of silver atoms travels a horizontal distance of 1 m through such a field and each atom has a speed of 100 m/s, how strong must the field gradient dBz/dz be in order to deflect the beam 1 mm?arrow_forward
- The magnetic dipole moment of the iron atom is about 2.11023Am2 . (a) Calculate the maximum magnetic dipole moment of a domain consisting of 1019 iron atoms, (b) What current would have to flow through a single circular loop of wire of diameter 1.0 cm to produce this magnetic dipole moment?arrow_forwardA 40-cm by 6.0-cm rectangular current loop carries a current of 10 A. What Is the magnetic dipole moment of the loop?arrow_forwardThe Hall effect is to be used to find the density of charge carriers in an unknown material. A Hall voltage 40 V for 3-A current is observed in a 3-T magnetic field far a rectangular sample with length 2 cm, width 1.5 cm, and height 0.4 cm, Determine the density of the charge carriers.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill