The mean yield from process A is estimated to be 80 ± 5, where the units are percent of a theoretical maximum. The mean yield from process B is estimated to be 90 ± 3. The relative increase obtained from process B is therefore estimated to be (90 − 80)/80 = 0.125. Find the uncertainty in this estimate.
The
The mean yield from process A is estimated to be A= 80±5 and the mean yield from process B is estimated to be B= 90±3.
The form of the measurements of a process is,
Measured value(μ)± Standard deviation(σ).
Here, for a random sample the measured value will be sample mean and the population standard deviation will be sample standard deviation.
The form of the measurements of mean yield from process A is A= 80±5.
Here, the measured value of mean yield from process A is A= 80 and the uncertainty in the mean yield from process A is σA=5.
The form of the measurements of mean yield from process B is B= 90±3
Here, the measured value of mean yield from process B is B= 90 and the uncertainty in the mean yield from process B is σB=3.
Uncertainty:
The uncertainty of a process is determined by the standard deviation of the measurements. In other words, it can be said that the measure of the variability of a process is known as the uncertainty of the process.
Therefore, it can be said that uncertainty is simply (σ).
Standard deviation:
The standard deviation is based on how much each observation deviates from a central point represented by the mean. In general, the greater the distances between the individual observations and the mean, the greater the variability of the data set.
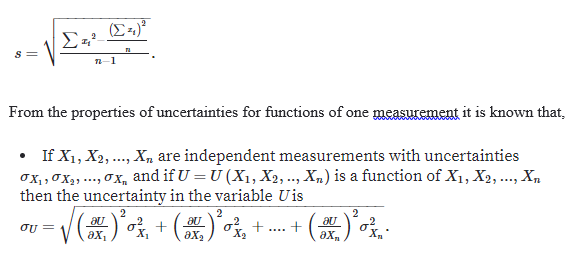
The general formula for standard deviation is,
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









