
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
PARTS A and B
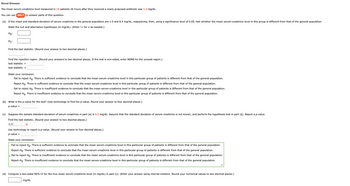
Transcribed Image Text:Renal Disease
The mean serum-creatinine level measured in 15 patients 24 hours after they received a newly proposed antibiotic was 1.2 mg/dL.
You can use SALT to answer parts of this question.
(a) If the mean and standard deviation of serum creatinine in the general population are 1.0 and 0.4 mg/dL, respectively, then, using a significance level of 0.05, test whether the mean serum-creatinine level in this group is different from that of the general population.
State the null and alternative hypotheses (in mg/dL). (Enter != for * as needed.)
Ho:
H₁:
Find the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Find the rejection region. (Round your answers to two decimal places. If the test is one-sided, enter NONE for the unused region.)
test statistic >
test statistic <
State your conclusion.
Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean serum-creatinine level in this particular group of patients is different from that of the general population.
Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean serum-creatinine level in this particular group of patients is different from that of the general population.
Fail to reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the mean serum-creatinine level in this particular group of patients is different from that of the general population.
Reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the mean serum-creatinine level in this particular group of patients is different from that of the general population.
(b) What is the p-value for the test? (Use technology to find the p-value. Round your answer to four decimal places.)
p-value=
(c) Suppose the sample standard deviation of serum creatinine in part (a) is 0.5 mg/dL. Assume that the standard deviation of serum creatinine is not known, and perform the hypothesis test in part (a). Report a p-value.
Find the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
0.72
*
Use technology to report a p-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
p-value=
State your conclusion.
Fail to reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean serum-creatinine level in this particular group of patients is different from that of the general population.
Reject Ho. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean serum-creatinine level in this particular group of patients is different from that of the general population.
• Fail to reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the mean serum-creatinine level in this particular group of patients is different from that of the general population.
Reject Ho. There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the mean serum-creatinine level in this particular group of patients is different from that of the general population.
(d) Compute a two-sided 95% CI for the true mean serum-creatinine level (in mg/dL) in part (c). (Enter your answer using interval notation. Round your numerical values to two decimal places.)
mg/dL
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2. Simply. "a) -5v45 - V52 3V125arrow_forwardCoal is carried from a mine in West Virginia to a power plant in New York in hopper cars on a long train. The automatic hopper car loader is set to put 86 tons of coal into each car. The actual weights of coal loaded into each car are normally distributed, with mean μ = 86 tons and standard deviation σ = 1.1 ton.(a) What is the probability that one car chosen at random will have less than 85.5 tons of coal? (Round your answer to four decimal places.) (b) What is the probability that 29 cars chosen at random will have a mean load weight x of less than 85.5 tons of coal? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)arrow_forwardCompute.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman