
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
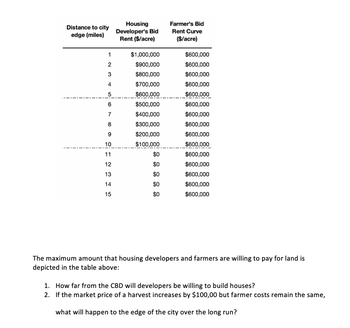
Transcribed Image Text:Distance to city
edge (miles)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Housing
Developer's Bid
Rent ($/acre)
$1,000,000
$900,000
$800,000
$700,000
$600,000
$500,000
$400,000
$300,000
$200,000
$100,000
$0
$0
$0
$0
$0
Farmer's Bid
Rent Curve
($/acre)
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
$600,000
The maximum amount that housing developers and farmers are willing to pay for land is
depicted in the table above:
1. How far from the CBD will developers be willing to build houses?
2. If the market price of a harvest increases by $100,00 but farmer costs remain the same,
what will happen to the edge of the city over the long run?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Define bid rent curve
A bid rent curve is a graphical representation of the variation in the amount that individuals or businesses are willing to pay (bid) for a specific piece of land or location at different distances from a central point or area, typically the central business district (CBD) of a city or town. It is a fundamental concept in urban economics and geography and helps explain how land use patterns develop within cities.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain different types of competition and also state why is competition good for the consumer from an economics perspectivearrow_forward1. Why is water, which is essential to life, so cheap, while diamonds, which are not essential to life, so expensive? Explain your answer using total utility (TU) and marginal utility (MU). 2. Discuss the advantages of perfect competition. 3. What is the shape and elasticity of the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm? Why? 4. How does the firm determine how much to produce in the short run?arrow_forwardThe world exists for one year. The Farmer seeks to maximize her profits. The farmer must choose whether to grown beans or berries. Here are some data about the two products. The farmer owns 1 acre of land and 0 gallons of water. Crop Beans Berries Price per unit of output (in $) 4 X Output put acre of land 24 28 Gallons of water used per unit of output 1 2 Labor cost per unit of output (in $) .2 .2 The profit maximizing farmer will; A. Grow beans if the price of purchasing water is less than $2 per gallon B. Earn equal profits growing Beans or Berries regardless of the price of water C. Seek to sell his water and thus will grow beans. D. Grow berries if X>=8 The farmer would sell this farm for any offer greater than $340 dollarsarrow_forward
- 1. Suppose you are the owner of a burger restaurant that has a cost of production given by C = 400 + 0.02q^2 where q is the number of burgers produced per day. Assume that the market for burgers is perfectly competitive. a. If the market price for a burger is $10, how many burgers should the manager plan to produce in a day? b. What is the profit level? Is this the maximum profit that the restaurant can make per day? c. What output will the firm produce if the price of a burger goes down to $8?arrow_forwardDiscuss in detail the short and long run laws of production.arrow_forwardYour uncle has just purchased a wheat farm and wants your advice on how he should price his product. Explain to your uncle the characteristics of the market structure under which his farm falls and how this will help him to determine the price and quantity of the wheat he will produce.arrow_forward
- In the long run, in a competitive economy, companies use resources until the extra or marginal production costs are: 1. Less than the price of the product 2. Greater than the price of the product 3. Equal to the price of the product 4. Equal to your earningsarrow_forwardSee image for question with sub-parts.arrow_forwardHow did the lauch of Apple's ipad effect the competitive market environment? High prices and high profits in a competitive generally lead to new suppliers entering the market, prices sliding down the market demand curve, the market supply curve shifting to the right, and significant product and technological innovation.arrow_forward
- I really need help with this question!arrow_forwardUse the graph below to answer the questions. Price $7 $6 $4 $2.50 Loss MC ATC MR₁ MR₂ 100 125 140 Firm's quantity (q) Suppose a firm in a competitive market faces a market price of $6. If the firm produces a level of output to maximize profit, how much profit does the firm earn? ✪ $ 840 If the market price drops to $4, the firm starts losing money. How much money does it lose? $ 280arrow_forwardHow do price controls affect the workings of a perfectly competitive market? Use a supply demand diagram as part of your answer.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education