
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
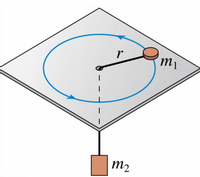
The mass m1 is free to rotate on a frictionless table. Mass m1 rotates at a constant speed in a circle of radius r and is connected by a string through a hole in the table to a hanging mass m2 . Mass m2 is at rest.
a. Draw and label a free-body diagram for the each of the two masses. You should have two separate free-body diagrams and clearly distinguish to which mass each applies.
b. Using variables, write Newton’s 2nd law in the x- and y- direction for mass m1.
Transcribed Image Text:m2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. A block of mass m accelerates up a slope that has friction. a. Draw a free-body diagram for the block indicating all the forces acting on it. (Note that there must be a force acting on the block in order for it to accelerate up the slope.) b. Write down the equations for Newton's 2nd law for both x and y directions. c. Solve for the applied force Fap in terms of the angle of incline 0, mass m, acceleration of the block a, kinetic friction force fr, and acceleration of gravity g.arrow_forwardA 60 kg student rides on a roller coaster that makes a vertical loop. a. Draw a free-body diagram for when the student is at the bottom of the loop. B.if the radius of the loop is 30m,and the roller coaster is traveling at 20 m/s at the bottom of the loop,what is the net force acting on the student in the vertical direction? C.What force does the seat apply to the student when at the bottom of the loop?arrow_forwardA very dedicated physics student decides to ride the elevator in Strode while standing on a scale. The student weighs 700 N. Determine the apparent weight the student reads on the scale for the following 3 situations:a. The elevator is accelerating upwards at 3 m/s^2.b. The elevator is moving upwards at 7 m/s. c. The elevator is accelerating downwards at 4 m/s^2. Please include known values, a diagram, and implied values so I can better understand.arrow_forward
- Which of the following is true? a. Earth exerts a force due to gravity on your body, and your body exerts a smaller force on the Earth, because your mass is smaller than the mass of the Earth. b. The Moon orbits the Earth because the Earth exerts a force on the Moon and the Moon exerts a force equal in magnitude and direction on the Earth. c. A rocket taking off exerts a force on the Earth equal to the force the Earth exerts on the rocket. d. An airplane cruising at a constant speed is not affected by gravity.arrow_forwardA person exerts a force of 120 NN on a rope that pulls a sled across a very smooth horizontal surface. The rope is oriented 37⁰0 above the horizontal. The sled has a total mass of 50 kgkg. The sled starts at rest and moves for 10 mm. Select all the quantities that can be determined using the given information. A. Determine the acceleration of the sled. B. Determine the normal force exerted by the surface on the sled. C. Determine the time taken for the sled to move 10 m. D. Determine the speed of the sled after moving for 10 m. F. Check all that apply. acceleration of the sled normal force exerted by the surface on the sled mass of the person time taken for the sled to move 10 mm speed of the sled after moving 10 mmarrow_forwardChoose the correct answer ( A / B / equal / can’t tell ).a) A book rests on a table with friction. We apply a force to the book. Which is larger?A – The force required to start moving the bookB – The force required to move the book at a constant speedb) Two blocks are on a table. Block A has double the mass of block B. Is the center of mass of the systemcloser to block A or block B?c) Two blocks slide a distance d on a surface without friction, starting from rest. Both blocks have thesame applied force F, acting parallel to the motion. Block A has twice the mass of block B. Which blockhas more Kinetic Energy when it has traveled the distance d?d) Two blocks slide a distance d on a surface without friction, starting from rest. Both blocks have thesame applied force F, acting parallel to the motion. Block A has twice the mass of block B. In whichcase did the applied force F do the most work?e) The earth orbits around the sun. Which force has a larger magnitude?A – force of the sun on the…arrow_forward
- A 10 N force is applied to a 4.0 kg block at rest on a table. The block experiences a frictional force. Draw a free-body diagram of the block. What is the weight of the block? What is the normal force on the block? If the coefficient of kinetic friction is µk = 0.20, what is the kinetic frictional force on the block? What is the net force on the block? What is the acceleration of the block from the net force? Just 1, 2, and 3 please!arrow_forwardA string, 0.750 m in length, is attached to a hook in the ceiling. A 0.600 kg mass is rotating around the vertical axis and the angle between the vertical axis and the string is 18°. a) Draw the free body diagram and kinetic diagram of the mass. b) Determine the tension in the string. c) Determine the velocity of the massarrow_forward3. Consider an inclined plane with two balls suspended as shown below. The pulley has negligible mass and both the pulley and the surface of the incline are frictionless.a. If one of your classmates calculated that, once released, the acceleration of the blocks would be 43?, without doing any calculations, say whether or not this could be a reasonable value for the acceleration.b. Draw and label a free body diagram (FBD) for each ball. (Don’t break any forces into components for the FBDs—save that work for the next question. Be sure your drawings show clearly any information you know about the directions and relative magnitudes of the forces.) Rank the relative magnitudes of all forces in your FBDs. (I’m looking for a single ranking that includes every different force in both FBDs, separated by <, >, or =.)Ball A: Ball B:relative sizes of the magnitudes of all forces in FBDs:__________________________________________________________________c. Use the FBDs from the previous…arrow_forward
- 3. a. Explain, with a free body diagram, how an object can experience a zero net force when at least three forces are acting on it.arrow_forward3.2.2 Represent and reason Two blocks are connected with a light string that runs over two light pulleys.arrow_forwardResearchers often use force plates to measure the forces that people exert against the floor during movement. A force plate works like a bathroom scale, but it keeps a record of how the reading changes with time. Shown is the data from a force plate as a woman jumps straight up and then lands.a. What was the vertical component of her acceleration during push-off?b. What was the vertical component of her acceleration while in the air?c. What was the vertical component of her acceleration during the landing?d. What was her speed as her feet left the force plate?e. How high did she jump?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON