
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
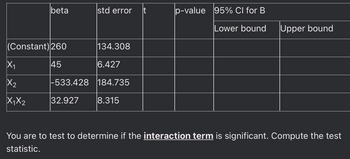
Transcribed Image Text:beta
(Constant) 260
45
X₁
X₂
X₁X2
std error
134.308
6.427
-533.428
32.927 8.315
184.735
It
p-value 95% CI for B
Lower bound
Upper bound
You are to test to determine if the interaction term is significant. Compute the test
statistic.

Transcribed Image Text:The management of a large firm would like to know something about employee
morale and the other variables to which it may be related. To study these
relationships, each employee in a simple random sample of 27 employees is
interviewed and tested to obtain information concerning morale level and the
average number of satisfying extra work social contacts experienced during a
week. Whether or not the duties the employee usually performs are appropriate to
the job title is also determined.
The dependent variable Y is measure of morale, the quantitative independent
variable, X1 is average number of social contacts, and the following dummy
variable coding is used to quantify the qualitative variable:
X₂ = 1 if yes,
X₂ = 0 if no.
The model including dummy variable and the interaction term was being estimated
and a part of computer outputs is below:
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In one of its Spring catalogs, L.L. Bean advertised footwear on 29 of its 192 catalog pages. Suppose we randomly surgery 20 pages. We are interested in the number of pages that advertise footwear. Each page may be picked at most once. Calculate the standard deviationarrow_forwardHow do we use these FOCs to show that (wtNt)/Yt =(1-α) if Yt = At Ktα Nt1-αarrow_forwardIn your own words, describe what the difference is between an error term and a residual. How does sample size affect the variance of each?arrow_forward
- Find the coefficient of x2y3z3 in the expansion of(x + y + z)8.arrow_forward5.arrow_forwardA large milling machine produces steel rods to certain specifications. The machine is considered to be running normally if the standard deviation of the diameter of the rods is at most 0.42 millimeters. The line supervisor needs to test the machine is for normal functionality. The quality inspector takes a sample of 45 rods and finds that the sample standard deviation is 0.49. What is the test statistic? Select one: а. 59.89 b. 48.63 с. 50.50 d. 52.45arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education