
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
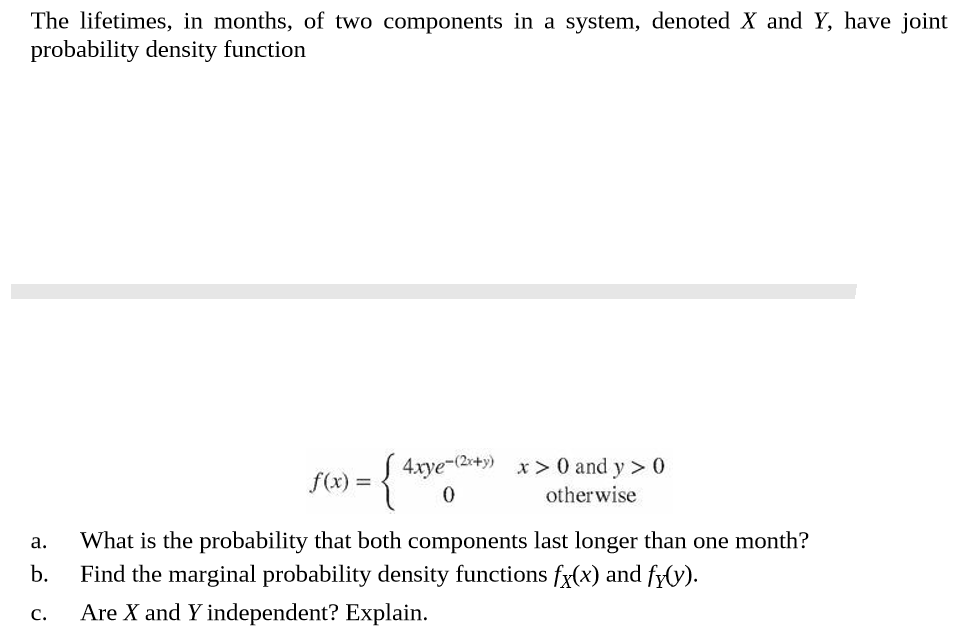
Transcribed Image Text:The lifetimes, in months, of two components in a system, denoted X and Y, have joint
probability density function
S 4xye-(2x+y) x > 0 and y > 0
f(x) =
otherwise
What is the probability that both components last longer than one month?
a.
b.
Find the marginal probability density functions fx(x) and fy(y).
Are X and Y independent? Explain.
C.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The estimated life of an electronic component (measured in months) follows the probability density function below: .x.e x > 0 f(x) = {4 elsewhere 1. Find the probability that estimated life is greater than 5. 2. Find the mean of the estimated lifearrow_forwardDirections: The amount of time required to serve a customer at a bank has an exponential density function with mean 4 minutes. 1. Find the probability that a customer is served in less than 3 minutes. Probability = 2. Find the probability that serving a customer will require more than 6 minutes. Probability =arrow_forwardThe Gamma distribution is often used to describe the wait time until a certain number of events occurs. Assume x1, . . . , xn ∼iid Gamma(α, β), where α is shape and β is rate. Calculate the maximum likelihood estimator of β either by hand or via R, but not both. The probability density function (PDF) for the Gamma distribution is: Calculate the log-likelihood function of the function below. I t doesnt have to be on r studi you can do by your handarrow_forward
- Section: Probabilty Density Functionsarrow_forward2. Consider a gas station's daily sales. Let Y be the volume of gas sold per day in 1000s of gallons. Assume the distribution of Y follows this pdf: 1sxs 2 S (v) . else What value of k is required for the above function to be a valid pdf? b. Verify that the function given is a valid probability density а. function c. Determine the cumulative distribution function (cdf) of the random variable d. Compute the probability that there is exactly 1500 gallons of sales on a given day (Hint: Find?(r - 1.5)) = 1 CO0arrow_forward1 Given the probability density function f(x) = over the interval [3,6], find the expected value, the mean, 3 the variance and the standard deviation. Expected value: Mean: Variance: Standard Deviation: > Next Questionarrow_forward
- A density curve consists of the line segment connecting the points (0,1) and (0.5,1) and the segment connecting(0.5, 1) to the x-axis.a. Determine the coordinate point where the second segment crosses the x-axis.b. Determine the slope of that segmentc. Determine the equation of the line containing this segment (y = mx + b)d. Calculate the probability P(X > 1)arrow_forwardLet X be the total amount saved in dollars at the cash register. The pdf of X is given by: Value of X 20 28 40 50 58 70 probability 0.36 0.21 0.24 0.1225 0.0175 0.03 .0175 0.0025 Before I make the purchase, you would place my chance of saving $20 at 24%. Suppose you approach me after I pay for my items and ask: "Did you save any money?" If I answer "no", then you know I didn't save $20 and thus the chance of saving $20 changes from the unconditional chance 24% to the conditional chance 0%. However, if I answer "yes" my chance of saving $20 would get higher. What would be the conditional chance of saving $20 if you knew I got a discount? Mathematically, we seek: P(X = 20|X > 0 ). Even though it looks weird, it is just a conditional probability. Find it. P(X = 20|X > 0) = P(X = 20 and X > 0) / P(X > 0) = Hint: P(X = 20 and X > 0) be read off the table by identifying possible values where the event (X = 20 and X > 0) is true, don't use the multiplication rule. Do not round, express your…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman