
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
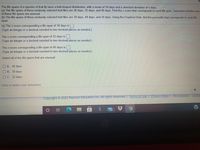
Transcribed Image Text:The life spans of a species of fruit fly have a bell-shaped distribution, with a mean of 34 days and a standard deviation of 5 days.
(a) The life spans of three randomly selected fruit flies are 38 days, 32 days, and 46 days. Find the z-score that corresponds to each life span. Determine whether any
of these life spans are unusual.
(b) The life spans of three randomly selected fruit flies are 39 days, 44 days, and 24 days. Using the Empirical Rule, find the percentile that corresponds to each life
span.
(a) The z-score corresponding a life span of 38 days is
(Type an integer or a decimal rounded to two decimal places as needed.)
The z-score corresponding a life span of 32 days is
(Type an integer or a decimal rounded to two decimal places as needed.)
The z-score corresponding a life span of 46 days is
(Type an integer or a decimal rounded to two decimal places as needed.)
Select all of the life spans that are unusual.
O A. 46 days
O B. 38 days
O C. 32 days
Click to select your answer(s).
Copyright © 2020 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Policy Permissions | Conta
99
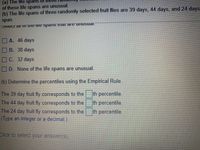
Transcribed Image Text:(a) The lite spans
of these life spans are unusual.
(b) The life spans of three randomly selected fruit flies are 39 days, 44 days, and 24 days
span.
A. 46 days
B. 38 days
C. 32 days
D. None of the life spans are unusual.
(b) Determine the percentiles using the Empirical Rule.
The 39 day fruit fly corresponds to the
The 44 day fruit fly corresponds to the
The 24 day fruit fly corresponds to the
(Type an integer or a decimal.)
th percentile.
th percentile.
th percentile.
Click to select your answer(s).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Five students took a self-confidence test. Their deviation scores were –4, +3, +1, –2, and +2. Assuming that these scores com form a normaldistribution, which deviation represents the highest raw score?arrow_forwardYou may need to use the appropriate technology to answer this question. Data were collected on the top 1,000 financial advisers. Company A had 239 people on the list and another company, Company B, had 121 people on the list. A sample of 16 of the advisers from Company A and 10 of the advisers from Company B showed that the advisers managed many very large accounts with a large variance in the total amount of funds managed. The standard deviation of the amount managed by advisers from Company A was s₁ = $583 million. The standard deviation of the amount managed by advisers from Company B was s₂ = $484 million. Conduct a hypothesis test at a = 0.10 to determine if there is a significant difference in the population variances for the amounts managed by the two companies. What is your conclusion about the variability in the amount of funds managed by advisers from the two firms? State the null and alternative hypotheses. 2 2 H₂:0 2 Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer…arrow_forwardA taxi company operates in two different regions, and it is analyzing the prices of rides in those regions. It has compiled the prices (in dollars) of 101 rides in each of the two regions during the last week. The histograms below show the distributions of the two data sets. Each histogram shows price (in dollars) on the horizontal axis and the number of taxi rides on the vertical axis. The means and standard deviations for the data sets are also given. Region A 25- 20+ 15+ 10+ 5+ 1₂ 0.5 5.5 10.5 15.5 20.5 25.5 30.5 35.5 40.5 45.5 50.5 Region A mean: $25.28 Region A standard deviation: $7.95 25 Expl 20- 15+ 10+ neck 5+ 0A 0.5 5.5 5.5 10.5 15.5 20.5 25.5 30.5 35.5 40.5 45.5 50.5 (a) Identify the data set for which it is appropriate to use the Empirical Rule. It is appropriate to use the Empirical Rule for the (Choose one) data set. The company wants to use the Empirical Rule to make some approximations about both data sets. Unfortunately, it is appropriate to use the Empirical Rule on…arrow_forward
- A company conducted a survey on the number of hours employees spend on a particular task per week. The data collected from a sample of 10 employees are as follows: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 10, 11, 12, 13. Calculate the standard deviation of the hours spent on the task per week.arrow_forwardFran is training for her first marathon, and she wants to know if there is a significant difference between the mean number of miles run each week by group runners and individual runners who are training for marathons. She interviews 42 randomly selected people who train in groups and finds that they run a mean of 47.1 miles per week. Assume that the population standard deviation for group runners is known to be 4.4 miles per week. She also interviews a random sample of 47 people who train on their own and finds that they run a mean of 48.5 miles per week. Assume that the population standard deviation for people who run by themselves is 1.8 miles per week. Test the claim at the 0.01 level of significance. Let group runners training for marathons be Population 1 and let individual runners training for marathons be Population 2. Step 2 of 3 : Compute the value of the test statistic. Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardA company produces steel rods. The lengths of the steel rods are normally distributed with a mean of 99.3-cm and a standard deviation of 1.5-cm. For shipment, 25 steel rods are bundled together.Find P27, which is the average length separating the smallest 27% bundles from the largest 73% bundles. P27 =arrow_forward
- A company produces steel rods. The lengths of the steel rods are normally distributed with a mean of 119.5-cm and a standard deviation of 2.2-cm. For shipment, 24 steel rods are bundled together.Find P75, which is the average length separating the smallest 75% bundles from the largest 25% bundles.P75 = -cmarrow_forwardThe daily number of bad checks received by a large department store in a random sample of 5 days out of the past year was 67, 76, 72, 84, and 76. Find the Standard deviation.arrow_forwardThe salaries of professional baseball players are heavily skewed right with a mean of $3.2 million and a standard deviation of $2 million. The salaries of professional football players are also heavily skewed right with a mean of $1.9 million and a standard deviation of $1.5 million. A random sample of 40 baseball players’ salaries and 35 football players’ salaries is selected. The mean salary is determined for both samples. Let represent the difference in the mean salaries for baseball and football players. Which of the following represents the shape of the sampling distribution for ? skewed right since the populations are both right skewed skewed right since the differences in salaries cannot be negative approximately Normal since both sample sizes are greater than 30 approximately Normal since the sum of the sample sizes is greater than 30arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman