
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
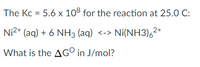
Transcribed Image Text:The Kc = 5.6 x 108 for the reaction at 25.0 C:
Ni2+ (aq) + 6 NH3 (aq) <-> Ni(NH3),2*
What is the AG° in J/mol?
![For the reaction in question 3, what will be the free energy under the
following conditions?
[Ni2*] = 0.0010M
[NH3] = 0.0050 M
[Ni(NH3),2*] = 0.010 M
Give me AG in J/mol?](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/fd47ee59-8c02-4471-82b7-8a3c00daed6e/459a8113-2b3b-459b-8598-01c5ed4ea414/4m5agt6_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:For the reaction in question 3, what will be the free energy under the
following conditions?
[Ni2*] = 0.0010M
[NH3] = 0.0050 M
[Ni(NH3),2*] = 0.010 M
Give me AG in J/mol?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Give correct detailed Solution (don't give Handwritten answer)arrow_forwardment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator3Dassignment-take Review Topical Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Consider the following system at equilibrium where AH° =-87.9 kJ, and K. = 83.3 , at 500 K: PCI3 (g) + Cl2 (g) PCI5 (g) If the TEMPERATURE on the equilibrium system is suddenly increased: The value ofK. A. Increases B. Decreases C. Remains the same The value of Qe A. Is greater than K. B. Is equal to K. C. Is less than K. The reaction must: A. Run in the forward direction to restablish equilibrium. B. Run in the reverse direction to restablish equilibrium. C. Remain the same. Already at equilibrium. The concentration of Cl, will: A. Increase. B. Decrease. C. Remain the same. Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 8 more group attempts remaining Pre 50 hparrow_forwardWhen 0.00258 mol of KI are dissolved into 40.0g solution, the temperzture of solution decreased by 1.57 oC. Assuming the container did not absorb or lose any hear, Cp(solution) = 4.184 J/g oC. What is the deltaHo (in kJ/mol) for the reaction: KI(s) -> K+(aq) + I-(aq)arrow_forward
- A positive value of ΔG°f for a solid compound at 25°C means the compound cannot exist at 25°C and 1 atm. process of forming the compound from the stable elements at 25°C and 1 atm is nonspontaneous. process of forming the compound from the elements is exothermic. compound must be a liquid or a gas at 25°C and 1 atm.arrow_forward2. Calculate AH for the following reaction at 25.0 °C: 30 Fe₂O4(s) + CO(g) 3FeO(s) + AH (kJ/mol)-1118 -110.5 -272 CO₂(g) -393.5arrow_forwardWhat is Sº for B in the reaction 3A 2B if AS (rxn) =-221.8 J/mol K? [S° (A) = (205.0 J/mol ·K)]arrow_forward
- In system IV, you are given the following:arrow_forwardWhich aqueous solution has the highest ΔTf value? Kf = 0.51 °C m-1. a.0.200 m KCl(aq) b. 0.200 m C3H8O3 (aq), glycerolarrow_forwardThe value of K, for this reaction is 0.44 at 50.0°C and 0.66 at 100.0°C. What is AH® for the reaction? kJ/molarrow_forward
- The following equilibrium constants have been determined for hydrosulfuric acid at 25°C: H2S(aq) = H*(aq) + HS (aq) K¸' = 9.5 × 10-8 HS (aq) = H*(aq) + S²¯(aq) K¸" = 1.0 × 10-19 es Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at the same temperature: H,S(aq) = 2H*(aq) + s²¯(aq) K = x 10arrow_forward5 [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Consider the following system at equilibrium where AH = -198 kJ, and Kc = 34.5, at 1.15 × 10³ K: 2SO2(g) + O2(g) = 2SO3(g) If the temperature on the equilibrium system is suddenly decreased: The value of Ke O increases Odecreases O remains the same T The value of Q O is less than Ke O is greater than K O is equal to Kc The reaction must O run in the forward direction to reestablish equilibrium Orun in the reverse direction to reestablish equilibrium O remain in the current position, since it is already at equilibrium The concentration of O2 will O increase O decrease O remain the same O F5 Show Hint A 6 F6 & 7 U K F7 * 8 DII F8 ( 9 F9 ) O F10 P Previous F11 + Next Save and Exit F12 deletearrow_forwardUse data to compute AG° at 82.0°C for the following reaction. 4FECI3(s) + 302(g) → 2FE203(s) + 6CI2(3) AH°t (FeCl3(s)) = -399.5 kJ mol-1 AH°t (Fe2O3(s) = -824.2 kJ mol-1 AS° (FeCl3(s)) = 142.3 J mol 1 K-1 AS° (Fe2O3(s)) = 87.4 J mol-1 K-1 AS° (Cl2(g)) = 223.1 J mol-1 K-1 AS° (O2(g)) = 205.152 J mol-1 K1 AG° = i kJ eTextbook and Media Save for Later Attempts: 0 of 3 used Submit Answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY