
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
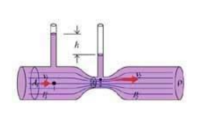
The internal diameters of the horizontal pipe shown in the figure are 2.50 cm in both extremes. A stream of water runs to the right at a rate of 1.80 x 10-4 m3/s.
Determine the internal diameter of the pipe reduction if the liquid level drops 5.00cm at that point.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A water line with an internal radius of 5.48 x 10-3 m is connected to a shower head that has 19 holes. The speed of the water in the line is 2.09 m/s. (a) What is the volume flow rate in the line? (b) At what speed does the water leave one of the holes (effective hole radius= 5.67 x 10-4 m) in the head? (a) Number (b) Number Units Units >arrow_forwardA large storage tank, open to the atmosphere at the top and filled with water, develops a small hole in its side at a point 18.7 m below the water level. If the rate of flow from the leak is 2.80 ✕ 10−3 m3/min, determine the following. (a) Determine the speed at which the water leaves the hole. m/s(b) Determine the diameter of the hole. mmarrow_forwardA horizontal pipe narrows from a radius of 0.250 m to 0.100 m. If the speed of the water in the pipeis1.00m/sinthe larger-radius pipe, what is the speed in the smaller pipe?arrow_forward
- A horizontal pipe line has different area of cross-section at two points P1 and P2. The diameter at P1 is 0.015m and at P2 is 0.005m. The difference of pressure between P1 and P2 is 0.3m of liquid column. Calculate the rate of flow of water and volume of liquid flowing through the pipe in 10s.arrow_forwardWater flows through the vertical pipe such that when it is at A, it is subjected to a pressure of 150 kPa and a velocity of 3 m/s. Determine the velocity and pressure at B as a function of the pipe diameter d. Plot the pressure and velocity versus the diameter for the range of values 25mm ≤ d ≤ 100 mm with a step of 25 mm increment. C -100 mmarrow_forwardFluid with the viscosity of 5X10-4 m2/s, is flowing in a pipe with the diameter of 35 cm and velocity of 2.5 cm/s. Calculate the head loss (m) for 100 m of the pipearrow_forward
- A water line with an internal radius of 6.89 x 103 m is connected to a shower head that has 12 holes. The speed of the water in the line is 0.982 m/s. (a) What is the volume flow rate in the line? (b) At what speed does the water leave one of the holes (effective hole radius = 3.14 x 104 m) in the head? (a) Number i (b) Number i Units Unitsarrow_forwardrn=0.17 cm (nozzle radius)rh=0.95 cm (garden hose radius)Q=0.65 L/s (flow rate through the hose) Calculate the maximum height to which water could be squirted with the hose if it emerges from the nozzle in meters.arrow_forwardWater is moving at a velocity of 2.50 m/s through a hose with an internal diameter of 1.60 cm. (a) What is the flow rate in liters per second? (b) The fluid velocity in this hose's nozzle is 14.0 m/s. What is the nozzle's inside diameter (in cm)?arrow_forward
- (a) The pressure inside an alveolus with a 2.00×10-4-m radius is 1.40×103 Pa , due to its fluid-lined walls. Assuming the alveolus acts like a spherical bubble, what is the surface tension of the fluid? (b) Identify the likely fluid.arrow_forwardWhat is the pressure at the bottom of a 5 m tall column of fluid with atmospheric pressure 101 kPa on the top surface if the fluid is water at 20◦C?arrow_forwardWater is flowing in the pipe shown in the figure below, with the 8.10-cm diameter at point 1 tapering to 3.05 cm at point 2, located y = 11.0 cm below point 1. The water pressure at point 1 is 3.20 x 104 Pa and decreases by 50% at point 2. Assume steady, ideal flow. What is the speed of the water at the following points? (a) point 1 (b) point 2 m/s m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON