
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The homogeneous bar shown in Fig. P-106 is supported by a smooth pin at C and a cable that runs from A to B around the smooth peg at D. Find the stress in the cable if the bar weighs 19000 lb.
Area= 19 sq.in. Bar Length=10meters
Solve this:
#1. 1. Solve the reaction @ A
#1. 2. Find the horizontal reaction @ C
#1. 3Solve the angle between the cable and the bar @ A
#1. 4 Find the Reaction @D
#1. 5 Determine the angle of resultant at D with respect to the horizontal bar.
#1. 6 Determine the stress develop in the cable caused by the homogeneous bar.
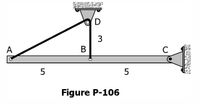
Transcribed Image Text:D
3
A
В
5
Figure P-106
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A horizontal L=1.2 m long mb=14 kg uniform bar is hinged on the left end and pulled at the right end by a cable. The cable makes 23° angle with horizontal. A 24 kg store sign is suspended below the bar at d=0.18 m from the right end. Find the magnitude of horizontal hinge force.arrow_forwardFor the truss shown below, use symmetry to determine the displacement of the nodes and the stresses in each element. E=30E6 psi, Elements 1, 2, 4 and 5 have Area=10 in? and element 3 has Area = 20 in?, Use i hand calculations. 6 ft 2 8 ft 8 ft- 20,000 lbarrow_forwardA two-story building has steel columns AB in the first floor and BC in the second floor, as shown in the figure. The roof load P₁ equals 400 kN, and the second-floor load P2 equals 720 kN. Each column has a length L = 3.75 m. Find internal axial forces in each column, then plot the axial force diagram. Ignore the self-weight of the columns. P₁= 400 KN C F P₂=720 kN B L=3.75 m L = 3.75 marrow_forward
- x = A cylindrical rod is made of three segments and is subjected to axial loads as indicated in the figure. The diameters of the segments are : 0.5 in, y = 1 in, and z = 0.5 in. Find the average normal stress at points A, B, and C. Remember that the sign convention is tension positive, and compression is negative. 3 kip A 9 kip у Z BY NO SA B 2021 Cathy Zuple C 8 kip 2 kip The average normal stress at A is σ A = The average normal stress at B is σ = The average normal stress at C is σc = ksi. ksi. ksi.arrow_forwardParvinbhaiarrow_forwardA picture frame is hung using the ropes 3 mm in diameter as shown in the figure. The maximum stress in the rope is not to exceed 900 kPa. What is the maximum weight of the frame that can be hung? Assume 0-20°.arrow_forward
- PLEASE EXPLAINarrow_forwardHey please help me here 1) calculate the magnitude of the force at the smooth surface support at A in Newtons. 2) calculate the magnitude of the vertical and horizontal components of the reaction force at the pin connection C in Newtons.arrow_forwardThe figure shown belowarrow_forward
- A brass pipe has an internal diameter of 400mm and a metal thickness of 6mm. A single layer of high tensile wire of diameter 3mm is wound closely around it at a tension of 500N. Find the stress in the pipe when there is no internal pressure. (b) the maximum permissible internal pressure in the pipe if the working tensile stress in the brass is 60MN/m^2. (c)) The stress in the steel wire under condition b. Treat the pipe as thin cylinder and neglect longitudinal stresses and strains. Young mudulus of steel=200GN/m^2 and for brass =100GN/m^2arrow_forwardI am struggling with this questionarrow_forwardI am struggling with this questionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY