
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
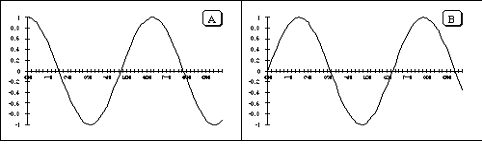
The graphs below may represent either a picture of the shape of a wave on a string at a particular instant in time, t1, or the transverse (up and down) velocity of the mass points of that string at that time. Depending on what they are, the wave on the string may be:
- a right going traveling wave
- a left going traveling wave
- a part of a standing wave growing in amplitude at time t1
- a part of a standing wave shrinking in amplitude at time t1
For each of the following cases, decide what the wave is doing and choose one of the four number (1)-(4) or none (N).
- Graph A is a graph of the string's shape and graph B is a graph of the string's velocity.
---Select--- 1 2 3 4 N - Graph A is a graph of both the string's shape and the string's velocity.
---Select--- 1 2 3 4 N - Graph B is a graph of the string's shape and graph A is a graph of the string's velocity.
---Select--- 1 2 3 4 N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 3 - (a) The plot below represents a snapshot of a wave in space taken a time t = 0s. Draw the history graph for this wave at x = 6m for t = 0s to t = 6s. y (cm) 1 -1 -1 1 m/s T 1 2 3 4 5 6 x (m) (b) The plot below represents the history graph of a wave at x = 0m. If the wave was moving with a speed of 1 m/s to the right. Draw a snapshot graph of this wave a t = 1s. y (cm) -1 2 В 4 5 6 t(s) -1-arrow_forwardA rubber ducky (located at x = 0 m) floats on a lake and bobs up and down due to one dimensional water waves. Shown to the right are a y(t) graph that depicts the vertical displacement of rubber ducky as a function of time and a y(x) graph that depicts the water wave as a function of position at the time t = 0 s. a. Explain how both graphs tells you whether this wave is moving to the right or to the left. Which parameter does this information help you find in the equation of motion in part b)? 3 2 AAAAA 1 3 -2 y (in cm) -2 y (in cm) at x=0 b. Write out the equation of motion y(x,t) = Asin[2ë specify the values for A, T, 2, 0, ±, and D. (27=-=-=27= + 9 ) +1 at t=0 t (in s) Am x (in m) o+D for this wave. Make sure youarrow_forwardA string is stretched so that it is under tension and is tied at both ends so that the endpoints don't move. A mechanical oscillator then vibrates the string so that a standing wave is created. The dark line in each diagram represents a snapshot of a string at an instant in time when the amplitude of the standing wave is a maximum. The lighter lines represent the string at other times during a complete cycle. All of the strings are identical except for their lengths, and all strings have the same tension. The number of nodes and antinodes in each standing wave is different. The lengths of the strings (L) and the amplitudes at the antinodes (A) are given in each figure. A B A = 12 cm L= 25 cm A= 12 cm L= 28 cm C A = 24 cm L= 20 cm A = 36 cm L= 30 cm Rank the wavelengths of the waves. OR All All the same Cannot determine Greatest Least zero Explain your reasoning. A string is stretched so that it is under tension and is tied at both ends so that the endpoints don't move. A mechanical…arrow_forward
- A standing wave is established on a 1.7 m length of string. This wave has 9 antinodes. What is the wavelength (in meters) of this wave?arrow_forwardA standing wave is established on a 2.4 m length of string. This wave has 9 antinodes. What is the wavelength (in meters) of this wave?arrow_forwarduse the wave shown above to answer the question. The wave is travelling to the right with a speed of 1.5m/s. this history graph was taken at x = 2.0m. A) what is the frequency of this wave? B) what is the wave number of this wave? C) what is the phase constant of this wave?arrow_forward
- A jetskier is moving at 8.3 m/s in the direction in which the waves on a lake are moving. Each time he passes over a crest, he feels a bump. The bumping frequency is 0.95 Hz, and the crests are separated by 5.8 m. What is the wave speed? Note: Answer in 3rd significant digit with unitarrow_forwardA string is stretched so that it is under tension and is tied at both ends so that the endpoints don't move. A mechanical oscillator then vibrates the string so that a standing wave is created. The dark line in each diagram represents a snapshot of a string at an instant in time when the amplitude of the standing wave is a maximum. The lighter lines represent the string at other times during a complete cycle. All of the strings are identical except for their lengths, and all strings have the same tension. The number of nodes and antinodes in each standing wave is different. the lengths of the strings (L) and the amplitudes at the antinodes (A) are given in each figure. Rank the speed of the wave in the strings. Enter in the form A > B = C . Hint: v=(T/μ)0.5.arrow_forwardA pipe closed at one end has two standing wave lengths of 0.667 meters and 0.4 meter with no standing wave between these values. What is the length of the tube?Group of answer choices 4 m 1 m 2 m 1/2 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON