
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
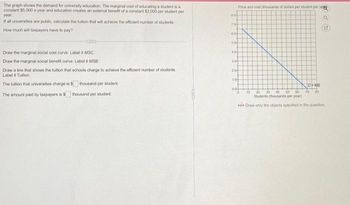
Transcribed Image Text:The graph shows the demand for university education. The marginal cost of educating a student is a
constant $5,000 a year and education creates an external benefit of a constant $2,000 per student per
year.
If all universities are public, calculate the tuition that will achieve the efficient number of students.
How much will taxpayers have to pay?
COC
Draw the marginal social cost curve. Label it MSC.
Draw the marginal social benefit curve. Label it MSB.
Draw a line that shows the tuition that schools charge to achieve the efficient number of students.
Label it Tuition.
The
tuition that universities charge is $thousand per student.
The amount paid by taxpayers is $thousand per student
1804
704
60
504
404
30
20
10
Price and cost (thousands of dollars per student per ye
00
DEMB
79 20
880
10 20 30 40 50 60
Students (thousands per year)
>>> Draw only the objects specified in the question
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Explain why there are no markets for public goods briefly.arrow_forwardMost countries today have subsidised the provision of education. Consider an imaginary country, Gondolin. Gondolin pays a subsidy of $10 000 per year to each student enrolled in tertiary education. ADDITIONAL INFO - DONT NEED THIS ANSWERED - Depict, with the help of a figure, the initial market for tertiary education in Gondolin, assume that: 1) education was left to the competitive free market; 2) the marginal private benefit is equal to the marginal social benefit; 3) the marginal private cost is equal to the marginal social cost. Now describe, using the help of the figure, the effect of the government subsidy on the price and quantity traded of tertiary education, where the X axis of the figure should be the quantity of students enrolled in tertiary education. You do not need to use actual numbers – focus on the direction of change in price and quantity traded caused by the subsidy. QUESTION Identify the area of the figure you drew in (a) that depicts the total size of the…arrow_forwardWhat exactly is a Pigovian tax? Give some instances of how the Pigovian tax can be used to tackle environmental issues.arrow_forward
- subject:ecoarrow_forwardThe diagram below represents the market for education. Assume that education provides several external benefits. a. Using the diagram, show the social demand curve for this market. Instructions: Use the tool provided 'Social value' to plot this line on the graph. Plot only the endpoints of the line. Tools Supply Private Social value Demand Private Pricearrow_forwardMost countries today have subsidised the provision of education. Consider an imaginary country, Gondolin. Gondolin pays a subsidy of $10 000 per year to each student enrolled in tertiary education.(a) Depict, with the help of a figure, the initial market for tertiary education in Gondolin, assume that: 1) education was left to the competitive free market; 2) the marginal private benefit is equal to the marginal social benefit; 3) the marginal private cost is equal to the marginal social cost. Now describe, using the help of the figure, the effect of the government subsidy on the price and quantity traded of tertiary education, where the X axis of the figure should be the quantity of students enrolled in tertiary education. You do not need to use actual numbers – focus on the direction of change in price and quantity traded caused by the subsidy.(b) Identify the area of the figure you drew in (a) that depicts the total size of the subsidy paid by the government to the students enrolled…arrow_forward
- Lets say a government decided they wanted to internalize the externality caused by the use of gasoline by putting a tax on gasoline. Carefully argue who the government should apply the tax to: the buyers or the sellers of the gasoline.arrow_forwardThe following graph shows market equilibrium of paper production. There are negative externalities in production and the Marginal External Cost is $5 per unit. We need to find the efficient allocation point. P 0 i. Do we correct the Marginal Social Benefit or Marginal Social Cost, and how? ii. Draw the corrected curve of MSB or MSC and mark the efficient point e. (Draw on paper. Take a photo and attach or send via email.) S D Q Attempt 4 Minu Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardProblem 05-01 (algo) On the basis of the three Individual demand schedules in the following table, and assuming these are the only three people in the society, determine a. the market demand schedule on the assumption that the good is a private good and b. the collective demand schedule on the assumption that the good is a public good. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. Individual 1 Individual 2 Individual 3 (a) Private Demand (b) Public Demand Price Qd Price Qd Price Qd Price Qd Price Qd $8 0 $8 1 $8 0 $8 1 1 7 0 7 2 7 0 7 2 2 6 0 6 3 6 1 в 4 3 5 1 5 4 5 2 5 7 4 4 2 4 5 4 3 4 10 5 3 3 3 в 3 4 3 13 в 2 4 2 7 2 5 2 16 7 1 5 1 8 1 6 1 19 8arrow_forward
- Please answer parts e and f below.arrow_forwardRefer to Table 3. How large would a subsidy need to be in this market to move the market from the equilibrium level of output to the socially-optimal level of output?arrow_forwardWhen does a subsidy that benefits consumers result in a more efficient allocation of a resource? A when the good being produced or consumed is not scarce B when the good being produced or consumed generates a negative externality when the good being produced or consumed generates a positive externality D when the equilibrium price of the good is one that consumers don't likearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education