
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The graph below is for a firm with market power. Place point A at the firm's output and
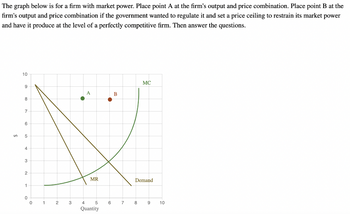
Transcribed Image Text:The graph below is for a firm with market power. Place point A at the firm's output and price combination. Place point B at the
firm's output and price combination if the government wanted to regulate it and set a price ceiling to restrain its market power
and have it produce at the level of a perfectly competitive firm. Then answer the questions.
10
B
X
MR
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0
1
2
5
3 4
Quantity
6
7
MC
Demand
8
9 10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose the government imposes the following production tax on one perfectly competitive firm in an industry: For each unit the firm produces, it must pay $1 to the government. Will consumers in this market end up paying higher prices because of the tax? Why or why not?arrow_forwardAvocados have been proven to bring many health benefits if consumed regularly. Many others including Gavin are huge fans of avocados and have plans to start a new business selling avocados. Assume the market for avocados to be perfectly competitive. Answer the following questions: a. If these firms are able to continue entering the market for avocados, it is likely that they are earning an economic profit. In order to earn an economic profit, firms must ensure that the price is above its Type ATC for Average Total Cost, AVC for Average Variable Cost, TC for Total Cost or VC for Variable Cost. b. Gavin decided to build an avocado farm in Brisbane. It is estimated that Gavin will need to spend $14.55 thousand on farming equipment costs. Gavin will also need to spend $20.95 thousand on labour and overhead costs. However, it is expected that Gavin will be able to sell 5 tonnes of avocados and gain revenue of $47.66 thousand from selling these avocados. Calculate the thousand. Answer to the…arrow_forwardIf the Peaches Fruit Company operates in a perfectly competitive industry, then The demand for individual consumers buying peaches from the Peaches Fruit Company should be horizontal. the demand for the Peaches Fruit Company should be perfectly elastic. The market demand for peaches should be horizontal. The demand for the peaches industry should be perfectly elastic.arrow_forward
- Draw a graph of a typical firm and an industry market (with supply and demand). Illustrate and explain what happens in the market if at the initial price, the typical firm is earning an economic profit. Show and explain how the two graphs will adjust toward market equilibrium.arrow_forwardConsider the weekly market for.gyros in a popular neighborhood close to campus. Suppose this market is operating in long-run competitive equilibrium with many gyro vendors in the neighborhood, each offering basically the same gyros. Due to the structure of the market, the vendors act as price takers and each individual vendor has no market power. The following graph displays the supply (SMC) and demand (D) curves in the weekly market for gyros. Place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the market price and quantity that will result from competition. PRICE (Dollars per gyro) 5.0 4.5 4.0 Competitive Market 3.5 S=MC 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 D 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 PC Outcome (?)arrow_forwardQuestion 35 Suppose all firms in a perfectly competitive industry have marginal cost of producing q units is MC = 8 + 16q. The industry demand curve is given by P = 488 – Q. The price of the good is $200. What is this firm’s optimal short-run quantity and how many firms produce this good in the short run? 12 units and 12 firms 48 units and 24 firms 192 units and 24 firms 12 units and 24 firmsarrow_forward
- Consider a perfectly competitive market where all firms produce using the same technology. In the long run the equilibrium price equals (Need help? Read chapter 4.6 of the textbook, here: https://playconomics.com/textbooks/view/playconomics4-2019t3/part2/ch4/s6) the Fixed Cost. the minimum Marginal Cost. the minimum Average Total Cost. the maximum Average Variable Cost. None of these.arrow_forwardCalculate the consumer surplus if the industry is perfectly competitive according to this diagram in the image.arrow_forwardIn competitive markets, there are many small firms with each firm unable to influence the market price. Suppose company ABX operates in the wheat market. The company produces and markets wheats at a Price = $20 per container. The firm’s total costs are given as: TC = 50 +2Q + 3Q2 What is the firm’s demand curve? Show it on a graph and label the axes showing P and Qarrow_forward
- Which of the following is an example of a perfectly competitive market structure? a) The market for smartphones b) The market for agricultural products c) The market for electricity in a regulated market d) The market for luxury carsarrow_forwardThe graph below shows a perfectly competitive firm in short run equilibrium, where the firm has chosen the output level maximizing its profit. Consider the level of profits being earned here, and what will happen over time. What will happen in the long run? Note that the horizontal demand curve, D1, is also equivalent to marginal revenue and price. Group of answer choices The market price will increase causing economic profits to increase Demand will increase causing economic profits to increase The market price will decrease until economic profit is zeroarrow_forwardIf there were 20 firms in this market, the short-run equilibrium price of ruthenium would be per pound. At that price, firms in this industry would . Therefore, in the long run, firms would the ruthenium market. Because you know that competitive firms earn economic profit in the long run, you know the long-run equilibrium price must be per pound. From the graph, you can see that this means there will be firms operating in the ruthenium industry in long-run equilibrium. True or False: Assuming implicit costs are positive, each of the firms operating in this industry in the long run earns negative accounting profit. True Falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education