
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
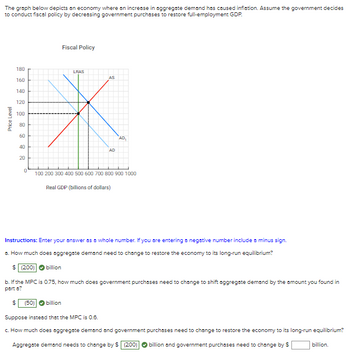
Transcribed Image Text:The graph below depicts an economy where an increase in aggregate demand has caused inflation. Assume the government decides
to conduct fiscal policy by decreasing government purchases to restore full-employment GDP.
Price Level
180
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
Fiscal Policy
LRAS
AS
AD
AD,
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
Real GDP (billions of dollars)
Instructions: Enter your answer as a whole number. If you are entering a negative number include a minus sign.
a. How much does aggregate demand need to change to restore the economy to its long-run equilibrium?
$ (200) billion
b. If the MPC is 0.75, how much does government purchases need to change to shift aggregate demand by the amount you found in
part a?
$ (50) → billion
Suppose instead that the MPC is 0.6.
c. How much does aggregate demand and government purchases need to change to restore the economy to its long-run equilibrium?
Aggregate demand needs to change by $ (200) billion and government purchases need to change by $
billion.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand show the relationship between economic output (GDP) and price levels in the macro-economy at a given point in time. Define the terms ‘Aggregate Demand’ and ‘Aggregate Supply.’ State TWO (2) monetary and TWO (2) fiscal policies that government can adopt, to effect change in Aggregate Demand.arrow_forwardDraw an AS-AD model of an economy dealing with an inflationary gap. What is one fiscal policy that can be implemented to close this gap? Draw the effect of that policy. Explain how the model returns to long run equilibrium if the government does not intervene.arrow_forwardAssuming that the economy shown in the figure below is in equilibrium, calculate the recessionary or inflationary gap in each case below. AS 350 AD 300 250 200 150 100 50 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Real GDP a. Potential GDP (LAS) is $300 then there is a(n) (Click to select) ♥ gap of $ (Click to select) b. Potential GDP (LAS) is $600 then there is a(n) inflationary recessionary Įgap of $ c. Potential GDP (LAS) is $750 then there is a(n) (Click to select) v gap of $ Price indexarrow_forward
- The graph below depicts an economy where an increase in aggregate demand has caused Inflation. Assume the government decides to conduct fiscal policy by changing taxes to bring Inflation under control. Price Level 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 Fiscal Policy LRAS AS Real GDP (billions of dollars) AD₁ AD 40 80 160 240 320 400 480 560 640 720 800 Instructions: Round your answers to 2 decimal places. If you are entering a negative number include a minus sign. a. How much does aggregate demand need to change to restore the economy to its long-run equilibrium? billion b. If the MPC is 0.75, how much do taxes need to change to shift aggregate demand by the amount you found in part a? $ billion Suppose Instead that the MPC is 0.5. c. How much does aggregate demand and taxes need to change to restore the economy to its long-run equilibrium? Aggregate demand needs to change by $ billion and taxes need to change by $ billion.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardIf the equilibrium real GDP were higher than potential GDP, then a contractionary fiscal policy would cause the inflation rate to be ________ and real GDP to be ________. a. higher; higher b. higher; lower c. lower; higher d. lower; lowerarrow_forward
- Show effect of expansionary fiscal policy in the short run and medium run. AS AD model using ISLM model.arrow_forwardWhat is the appropriate fiscal policy to lower the unemployment rate? Group of answer choices decrease the money supply increase the money supply increase taxes decrease government spending increase government spending do nothingarrow_forwardpols Homework (Ch 15) 4. Using fiscal policy to fight inflation Consider the hypothetical economy depicted on the graph. Initially, the economy operates below full-employment output at a price level of 105 and real GDP of $480 billion. Then aggregate demand (AD) increases from AD₁ to AD₂, moving the economy up along the intermediate and classical ranges of the aggregate supply (AS) curve. Real GDP increases to the full-employment output level of $540 billion, and the price level increases to 120. PRICE LEVEL (CPI) 130 125 120 115 110 100 95 90 85 80 400 420 440 AS AD₂ 460 REAL GDP (Billions of dollars) AD₁ 480 500 520 540 560 580 600 MacBook Pro (?) Xarrow_forward
- Which fiscal policy will increase aggregate supply? increasing tax rates on businesses O increasing tax rates on consumers instituting more regulations on businesses allocating more money for federal student loansarrow_forwardConfused not sure how to answerarrow_forwardThe graph below depicts an economy where a decline in aggregate demand has caused a recession. Assume the government decides to conduct fiscal policy by increasing government purchases to reduce the burden of this recession. Price Level 160 140 LA 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 Fiscal Policy LRAS AD₁ Real GDP (billions of dollars) billion AS 80 160 240 320 400 480 560 640 720 800 AD O Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. a. How much does aggregate demand need to change to restore the economy to its long-run equilibrium? billion B b. If the MPC is 0.6, how much does government purchases need to change to shift aggregate demand by the amount you found in part a? Suppose instead that the MPC is 0.75. c. How much does aggregate demand and government purchases need to change to restore the economy to its long-run equilibrium? Aggregate demand needs to change by $ billion and government purchases need to change by $ billion.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education