
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
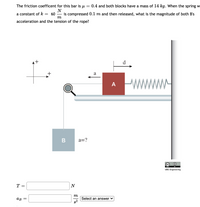
Transcribed Image Text:The friction coefficent for this bar is u
0.4 and both blocks have a mass of 14 kg. When the spring w
N
a constant of k
60
is compressed 0.1 m and then released, what is the magnitude of both B's
m
acceleration and the tension of the rope?
it
d
+
a
A
a=?
cc
UBC Engineering
T =
N
m
Select an answer v
g2
ав
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!arrow_forwardFirst, consider the cane where the surface is flat, as ahown below. Pick the comect free-body diagram for the block on the flat surface, where f - force of friction, N- normal force. W- weight, F.- force of spring 13 13 1Z 13 14 12arrow_forwardQ4: The slider block B is confined to move within the smooth slot. It is connected to two springs, each of which has a stiffness of k = 30 N/m. They are originally stretched 0.5 m when s = 0 as shown. Determine the maximum %3D distance, smax, block B moves after it is hit by block A which is originally traveling at (vA) = 8 m/s. Take e = 0.4 and the mass of each block to be 1.5 kg. Ans.: Smas. = 1.53 m 2 m - 30 N/m (VAh-8 m/s 2m k - 30 N/marrow_forward
- A roofer pulls a 25.0 kg bundle of shingles up the side of a roof that has a 29.0 ̊pitch. She applies a force to the shingles, counteracting the 18.5 N of friction, toaccelerate the shingles at a rate of 0.50 m/s2. Calculate the force she applied tothe shingles.arrow_forwardwn ot ei tedw,8 Jiog o lniog leiini ali moil og ol abnoos2 01 19j250 Jill (3 SaieWi nouoril gt oub 1ot2soa ordt yd boonsins a2ol 3. A box, initially at rest, is placed on the top of the frictionless incline shown. onob how 1ot Inuooos o boon Jon 20ob ono aoilsluolso ni vdw nislg (1 6 m A) Using a free body diagram and Newton's second law, find the box's acceleration in m/s². 8 m B) Use the constant acceleration equations to find the speed se 12 moil 2hc of the box when in reaches the bottom of the incline. S wold S lo noitoi to Insioifiooo oitonl o (A C) Find the work done by the constant net force on the box as it slides from the top of the incline to the bottom. Use the work-kinetic energy theorem to find the speed of the box when it reaches the bottom of the incline and check that your answer with B). 1 nde waainge o lliw doum woH (8 6ol 2omoo (viisinomom) loold odl nordw a20m marrow_forwardI Review | Constants A 2.00-kg package is released on a 53.1° incline, 4.00 m from a long spring with force constant 120 N/m that is attached at the bottom of the incline (Figure 1). The coefficients of friction between the package and the incline are us = 0.40 and µk the spring is negligible. Part A 0.20. The mass of What is the speed of the package just before it reaches the spring? V ΑΣφ m/s Figure 1 of 1 Request Answer Submit m = 2.00 kg Part B 4.00 m What is the maximum compression of the spring? V ΑΣφ 53.1° d = m Suhmit Request Answer II wwwwwwwwarrow_forward
- I hang a 83-kg weight on a force spring, which registers 183.07 Newtons. With what acceleration does it pull down the spring in m/s2? Round to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardDont use chatgpt plzarrow_forwardA mass of 5.0 kg will stretch a vertical spring 3.25 cm. Draw a free body diagram (include all relevant forces and values) and calculate the spring constant.arrow_forward
- L. Fo A block of mass 3.00 kg is moving in the positive x direction, across a rough surface (UK=0.11) with an initial velocity of 6.00 m/s and is acted upon by a force Fo=4.00 N, applied in the negative x direction. Select the correct FBD for the mass.arrow_forward4. Show that the acceleration of any object down an incline where friction behaves simply (that is, where F* = Hk FN) is a = g(sin 0 – Hk Cos 0). Note that the acceleration is independent of mass and reduces to a = g sin ở when friction becomes negligibly small (4k = 0).arrow_forwardA.2042 N/m B.1042 N/m C.3042 N/marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON