
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![The formation of tert-butanol is described by the following chemical equation:
\[
(\text{CH}_3)_3\text{CBr (aq)} + \text{OH}^- \text{(aq)} \rightarrow \text{Br}^- \text{(aq)} + (\text{CH}_3)_3\text{COH (aq)}
\]
Suppose a two-step mechanism is proposed for this reaction, beginning with this elementary reaction:
\[
(\text{CH}_3)_3\text{CBr (aq)} \rightarrow (\text{CH}_3)_3\text{C}^+ \text{(aq)} + \text{Br}^- \text{(aq)}
\]
Suppose also that the second step of the mechanism should be bimolecular.
Suggest a reasonable second step. That is, write the balanced chemical equation of a bimolecular elementary reaction that would complete the proposed mechanism.
[ ]
There are no graphs or diagrams present in the image.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/a60cc6ce-11de-444a-af29-e9eb1b50e640/ba7e46ba-65f4-4999-b38c-63e6f216af78/rg8litb_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:The formation of tert-butanol is described by the following chemical equation:
\[
(\text{CH}_3)_3\text{CBr (aq)} + \text{OH}^- \text{(aq)} \rightarrow \text{Br}^- \text{(aq)} + (\text{CH}_3)_3\text{COH (aq)}
\]
Suppose a two-step mechanism is proposed for this reaction, beginning with this elementary reaction:
\[
(\text{CH}_3)_3\text{CBr (aq)} \rightarrow (\text{CH}_3)_3\text{C}^+ \text{(aq)} + \text{Br}^- \text{(aq)}
\]
Suppose also that the second step of the mechanism should be bimolecular.
Suggest a reasonable second step. That is, write the balanced chemical equation of a bimolecular elementary reaction that would complete the proposed mechanism.
[ ]
There are no graphs or diagrams present in the image.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Given reaction
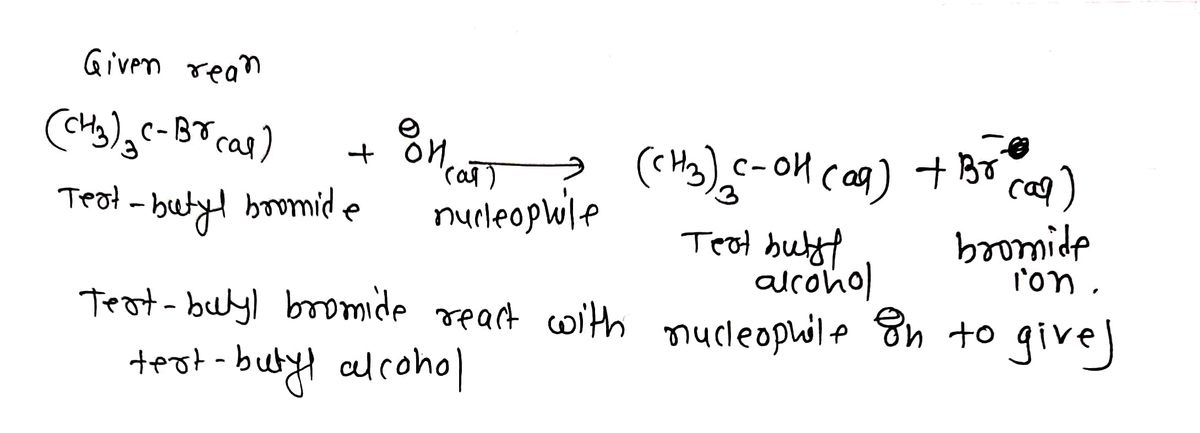
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the reaction 5B1¯ (aq) + Br0, (aq) + 6H† (aq)→3B12 (aq) + 3H2O(1) The average rate of consumption of Br is 1.16×10-4 M/s over the first two minutes. What is the average rate of formation of Br2 during the same time interval? Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardThe formation of iodine is described by the following chemical equation: H, (g) + 2IC1 (g) → 2HC1 (g) +Iz (g) Suppose a two-step mechanism is proposed for this reaction, beginning with this elementary reaction: H, (g) + IC1 (g) НI (g) + HCI (g) Suppose also that the second step of the mechanism should be bimolecular. Suggest a reasonable second step. That is, write the balanced chemical equation of a bimolecular elementary reaction that would complete the proposed mechanism.arrow_forwarda)A nickel catalyst is commonly used in the hydrogenation of ethylene. If the initial concentration of ethylene is 2.75 mol·L−1 and the rate constant for the reaction is 0.0018 mol·L−1·s−1, what is the rate of reaction if it follows a zero-order reaction mechanism? Express your answer to two significant figures. b)Determine the half-life for the reaction in Part B. Express your answer to two significant figures.arrow_forward
- [4] Consider the following mechanism for the reaction of nitric oxide and hydrogen: kı 2NO(g)+ H2(g) → N;O(g) + H¿O(g) slow k2 N,0(g) + H2(g) → N2(g) + H2O(g) fast (a) Write an equation for the overall reaction. (b) Write the theoretical rate law for the above mechanism. (c) Is a catalyst involved in the above mechanism? If so, what is it? (d) Are there any reaction intermediates? If so, list them.arrow_forwardConsider the mechanism. 2 A = B В +С — D Step 1: equilibrium Step 2: slow Overall: 2A +С — D Determine the rate law for the overall reaction, where the overall rate constant is represented as k. rate =arrow_forwardConsider the following proposed reaction mechanism: (1) CIO (aq) + H,O(1)= HCIO(aq) + OH (aq) [fast] (2)I (aq) + HCIO(aq) → HIO(aq) + Cl¯(aq) [slow] (3) OH (aq) + HIO(aq) → H,O() + 10 (aq) [fast] Ignoring water, how many reaction intermediates are present? O 3 O 1 O 2arrow_forward
- Chlorine dioxide, Cl02, is a reddish-yellow gas that is soluble in water. In basic solution it gives Cl03- and CIO2 ions. 2C1O:(aq) + 20н (ад) —> СIО3 (aд) + CIO, (aq) + H;0(1) To obtain the rate law for this reaction, the following experiments were run and, for each, the initial rate of reaction of ClO2 was determined. Initial Concentration Initial Concentration Initial Rate of Cl02 (mol/L) of OH (mol/L) (mol(L's) Exp. 1 0.21 1.6 x 10-2 0.162 Exp. 2 7.0 x 10-2 1.6 x 10-2 1.80 x 10-2 Exp. 3 7.0 x 10-2 4.8 x 10-2 5.39 х 10-2 a Obtain the rate law. (Use k for the rate constant.) Rate law =arrow_forwardIdentify each of the following elementary reactions as unimolecular, bimolecular, or termolecular, and write the rate expression. Reaction Molecularity Rate expression (a) NO2 + NO2→2 NO + 02 rate = (b) BrONO- ЭBro + NOz rate = (c) 0+ 02 + M 03 + M rate = unimolecular bimolecular termoleculararrow_forwardFor the first-order reaction N2O5( g) 2 NO2 g) + → t1/2= 20.5 h at 20°C and 3.5h at 40°C. (a) Calculate the activation energy of this reaction. (b) If the Arrhenius constant A = 2.5 x 105 s', determine the value of k at 50°C.arrow_forward
- Suppose the formation of nitryl fluoride proceeds by the following mechanism: step elementary reaction 1 NO₂ (g) +F₂ (g) → NO₂F (g)+F (g) 2 F (g) + NO₂ (g) → NO₂F (g) Suppose also k₁ << k₂. That is, the first step is much slower than the second. Write the balanced chemical equation for the overall chemical reaction. Write the experimentally- observable rate law for the overall chemical reaction. Note: your answer should not contain the concentrations of any intermediates. 0 rate = & rate constant k₁ k₂arrow_forwardSuppose the reaction between nitric oxide and bromine proceeds by the following mechanism: step elementary reaction 1 NO (g) + Br₂ (g) → NOBr₂ (g) k₁ k₂ 2 NOBr₂ (g) + NO (g) → 2NOBr (g) Suppose also k₁ « k₂ . That is, the first step is much slower than the second. Write the balanced chemical equation for the overall chemical reaction. Write the experimentally- observable rate law for the overall chemical reaction. Note: your answer should not contain the concentrations of any intermediates. 0 rate = k rate constant 010 X Śarrow_forwardSuppose the reaction between nitric oxide and oxygen proceeds by the following mechanism: step elementary reaction rate constant 1 NO(g) + O,(g) –→ NO2(g) + O(g) k1 NO(g) + O(g) → NO2(g) Suppose also k,«k,. That is, the first step is much slower than the second. Write the balanced chemical equation for the overall chemical reaction: Write the experimentally- observable rate law for the overall chemical reaction. rate = k || Note: your answer should not contain the concentrations of any intermediates. Express the rate constant k for the overall chemical reaction in terms of k1, k2, and (if necessary) the rate constants k.1 and k-2 for k = | %3D the reverse of the two elementary reactions in the mechanism.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY