
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
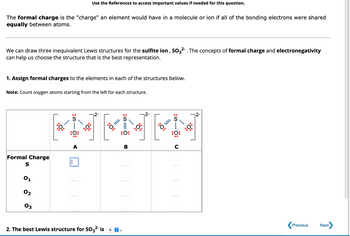
Transcribed Image Text:The content discusses the concept of formal charge in chemistry, emphasizing its role in understanding bonding in molecules or ions. Specifically, it addresses the formal charge as the hypothetical charge an element would have if bonding electrons were shared equally.
### Explanation:
We are considering the sulfite ion, \( \text{SO}_3^{2-} \). The discussion focuses on using formal charge and electronegativity to determine the most accurate Lewis structure representation.
**Task: Assign Formal Charges**
1. **Objective:** Assign formal charges to the elements in the given Lewis structures.
2. **Instructions:** Count oxygen atoms starting from the left for each structure.
### Diagram Description:
There are three structures labeled A, B, and C.
- **Structure A:**
- Central sulfur (S) atom is bonded to three oxygen (O) atoms. Double bonds and lone pairs are depicted.
- **Structure B and C:**
- Similar layout with variation in double bonds and lone pairs, affecting formal charge distribution.
**Table for Formal Charges:**
This section provides a systematic way to specify formal charges for sulfur (S) and each oxygen atom (\( O_1, O_2, O_3 \)) in structures A, B, and C.
### Selection:
2. **Result:** Determination of the best Lewis structure for \( \text{SO}_3^{2-} \) which is indicated by selecting one of the options (A, B, or C).
This educational content helps students practice calculating formal charges and applying theoretical principles to practical scenarios in molecular chemistry.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the best Lewis Structure for SOCl2 based on overall formal charges. Answer the questions below based on that structure. How many (total) bonding electron pairs are in the molecule? How many (total) non-bonding electron pairs are in the molecule? How many non-bonding electron pairs are on the central atom?arrow_forwardWrite a Lewis structure for each of the following polyatomic ions. Show all bonding valenceelectron pairs as lines and all nonbonding valence electron pairs as dots. For those ions thatexhibit resonance, draw the various possible resonance forms.a. phosphate ion, PO4 3-b. chlorate ion, ClO3-arrow_forwardAn incomplete Lewis structure is shown below. The structure only shows the atoms and how they are connected. The molecule has a net charge of zero. H I H-C-C-N-O | H Complete the Lewis structure giving all atoms full octets. If there is more than one way to do this, draw resonance structures showing all possibilities. If not, just draw one Lewis structure. Be sure to write in any non-zero formal charges.arrow_forward
- Draw Lewis structure(s) for the carbonate lon (CO₂). If there are equivalent resonance structures, draw all of them. n D co₂2: 0 . Draw one structure per sketcher box, and separate added sketcher boxes with the symbol. Do not include overall lon charges or formal charges in your drawing. Do not draw double bonds to oxygen unless they are needed in order for the central atom to obey the octet rule. ● 6 # H Ⓒ CH, CHO: 0 Y Chemic b Draw Lewis structure(s) for the acetaldehyde molecule (CH₂CHO). If there are equivalent resonance structures, draw all of the POLICE 81 MEDITE HARA (4) Y Draw one structure per sketcher box, and separate added sketcher boxes with the symbol. Do not include overall ion charges or formal charges in your drawing. Do not draw double bonds to oxygen unless they are needed in order for the central atom to obey the octet rule. ARQQA 000-ZIF www HEADING Chartlkoodn MES DE A V Ja remove 000-n [ MacBook Airarrow_forwardDraw three resonance structures for N3-. This species has its three atoms bonded sequentially in the following fashion: N-N-N. Draw your resonance structures so that the atoms in them are bonded together in this order. Select the most important resonance structure for this species based on the formal charges on the atoms of the three resonance structures you have drawn. Now select the statement from the multiple choices which is true about this most important resonance structure.In the most important resonance structure of N3- : a) The leftmost bond (between N and N) is a single bond.b) The rightmost bond (between N and N) is a single bond.c) The formal charge on the leftmost (N) atom is -1.d) The number of nonbonding pairs (lone pairs) of electrons on the leftmost (N) atom is 4.e) The number of nonbonding (lone) pairs of electrons on the rightmost (N) atom is 4.arrow_forwardUse the figure to find the electronegativity difference between each of the following pairs of elements, then use the table below to classify the bonds that occur between them as pure covalent, polar covalent, or ionic. Electronegativity Difference (ΔENΔEN) Bond Type Example zero (0−0.40−0.4) pure covalent Cl2Cl2 intermediate (0.4−2.00.4−2.0) polar covalent HFHF large (2.0+2.0+) ionic NaClNaCl Find the electronegativity difference between K and Cl. Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forward
- Draw the best Lewis Structure for ClO4– based on overall formal charges. Answer the questions below based on that structure. How many (total) bonding electron pairs are in the molecule? _______ How many (total) non-bonding electron pairs are in the molecule? _______ How many non-bonding electron pairs are on the central atom? _______arrow_forward9. Draw all the possible resonance structures for the iodate ion. How many resonance structures can you have in total for iodate?arrow_forwardA newly discovered element Lm has 3 valence electrons. How many total valence electrons are in LmF3 molecule, a molecule that Lm forms with fluorine? Draw a valid Lewis Structure for the molecule LmF3 that Lm forms with fluorine and use your Lewis structure to determine the number of lone pairs of electrons around the central Lm atom in this molecule. What is the formal charge of Lm in LmF3? (Number and sign of formal charge) What is the hybridization of Lm according to the hybrid orbital model?arrow_forward
- The formal charge is the "charge" an element would have in a molecule or ion if all of the bonding electrons were shared equally between atoms. Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. We can draw three inequivalent Lewis structures for dinitrogen monoxide, N₂O . The concepts of formal charge and electronegativity can help us choose the structure that is the most significant representation. 1. Assign formal charges to the elements in each of the structures below. Formal Charge N₁ N₂ :N,=N,-O: || A N=N,=Ô N-N,=O: C 2. The structure that contributes most significantly to the overall electronic structure of N₂O is ↑ Formal Chargearrow_forwardng and lear X G The element in period 5 that has X C Solved The following Lewis diagr. X nt/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator-assignment-take The formal charge is the "charge" an element would have in a molecule or ion if all of the bonding electrons were shared equally between atoms. Formal Charge 01 We can draw three inequivalent Lewis structures for carbon dioxide, CO₂. The concepts of formal charge and electronegativity can help us choose the structure that is the most significant representation. 1. Assign formal charges to the elements in each of the structures below. C [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. 02 :0₁-C=0₂: A 0,=C=0₂ :0,=C-0₂: + B 999 C *** 2. The structure that contributes most significantly to the overall electronic structure of CO₂ is. AG ENG neme Next 11:52 AM 11/28/2022 [arrow_forwarda. Write a Lewis structure that obeys the octet rule for the following species. Assign the formal charge for the central atom of XeO4. If multiple resonance structures exist, use one that does not involve an expanded valence. Formal charge: b. Write a Lewis structure that obeys the octet rule for the following species. Assign the formal charge for the central atom of clO3¯. If multiple resonance structures exist, use one that does not involve an expanded valence. Formal charge:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY