
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
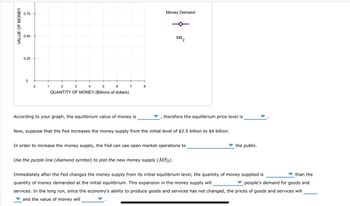
Transcribed Image Text:VALUE OF MONEY
0.75
0.50
0.25
0
1
2
3
4
5
QUANTITY OF MONEY (Billions of dollars)
6
7
According to your graph, the equilibrium value of money is
8
Money Demand
MS,
2
therefore the equilibrium price level is
Now, suppose that the Fed increases the money supply from the initial level of $2.5 billion to $4 billion.
In order to increase the money supply, the Fed can use open market operations to
Use the purple line (diamond symbol) to plot the new money supply (MS2).
the public.
than the
Immediately after the Fed changes the money supply from its initial equilibrium level, the quantity of money supplied is
quantity of money demanded at the initial equilibrium. This expansion in the money supply will
people's demand for goods and
services. In the long run, since the economy's ability to produce goods and services has not changed, the prices of goods and services will
and the value of money will
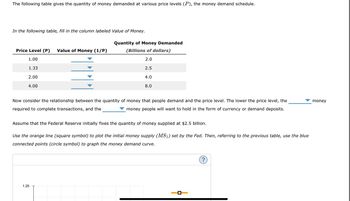
Transcribed Image Text:The following table gives the quantity of money demanded at various price levels (P), the money demand schedule.
In the following table, fill in the column labeled Value of Money.
Price Level (P) Value of Money (1/P)
1.00
1.33
2.00
4.00
Quantity of Money Demanded
(Billions of dollars)
2.0
2.5
4.0
8.0
Now consider the relationship between the quantity of money that people demand and the price level. The lower the price level, the
required to complete transactions, and the
money people will want to hold in the form of currency or demand deposits.
1.25
Assume that the Federal Reserve initially fixes the quantity of money supplied at $2.5 billion.
Use the orange line (square symbol) to plot the initial money supply (MS₁) set by the Fed. Then, referring to the previous table, use the blue
connected points (circle symbol) to graph the money demand curve.
(?)
money
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- TOPIC: A possible break in the Note: everything you need will be in the picturearrow_forwardThe economy of Greatstown produces Oranges, Strawberries, and Peaches. Below are the prices and quantities of these products produced between 1999 and 2001: Year 1999 1999 2000 2000 2001 2001 Price Quantity Price Quantity Price QuantityOranges $0.9 5 $1.4 3 $1.3 2Strawberries $0.7 3 $1.4 5 $1.9 6Peaches $1.7 9 $1.8 8 $0.5 8 Calculate Greatstown’s nominal GDP in 2000. Calculate Greatstown’s real GDP in 2001, using 1999 as the base year.arrow_forwardQ23arrow_forward
- Typed and correct answer please. I ll ratearrow_forwardplease dont make a humungous run on paragraph of an answer/explanation I need to know what I'm reading And answer as soon as possiblearrow_forwardTable: Market for Apartments Rent (per apartment per month) Quantity Demanded (millions of apartments) Quantity Supplied (millions of apartments) $1.400 1.6 2.4 1,300 1.7 2.3 1,200 1,100 1.8 2.2 1.9 2.1 1,000 900 800 2.0 2.0 2.1 1.9 2.2 1.8 700 2.3 1.7 600 2.4 1.6 (Table: Market for Apartments) Look at the table Market for Apartments. If a price ceiling of $700 is imposed on this market, the result will be an inefficiency in the form of a million apartments. O shortage of 0.6 O surplus of 0.6 O None of these options is correct. O shortage of 0.2 O surplus of 0.2arrow_forward
- The market for pizza has the following demand and supply schedules: Price (Dollars) 4 10 5 6 7 8 9 9 Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied Į (Pizzas) 135 115 100 90 60 45 Use the blue points (circle symbol) to graph the demand for pizzas. Then use the orange points (square symbol) to graph the supply of pizza. Finally, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the equilibrium price and quantity in this market. (Pizzas) 15 50 75 90 100 105 ?arrow_forward#38arrow_forward4arrow_forward
- Value of Money 2 1 I MS1 1 19 U MS2 D Money Demand Quantity of Money money supply is MS1 and the value of money is 1, then there is a shortage in Select one: a. supply of money that is represented by the distance between points A and C. b. demand for money that is represented by the distance between points C and D. c. supply of money that is represented by the distance between points C and D. d. demand for money that is represented by the distance between points A and C. Refer to figure. If thearrow_forwardPrice (dollars per pound) 6. 1o Quantity (millions of pounds per day) 14 The graph illustrates the market for British pounds, the currency of the United Kingdom. As the number of buyers of pounds decreases and the number of sellers of pounds increases, the equilibrium price of a pound A) will remain the same. B) will fall. C) will rie. D) might rise, fall, or remain the same but more information is needed. will rise if the magnitude of the effect on the buyers is larger than the E) magnitude of the effect on the sellers.arrow_forwardSuppose there is an increase in money supply, as a result interest rates will Multiple Choice rise and the quantity of money will increases. fall and the quantity of money will remain constant. rise and the quantity of money will decrease. fall and the quantity of money will increases.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education