
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
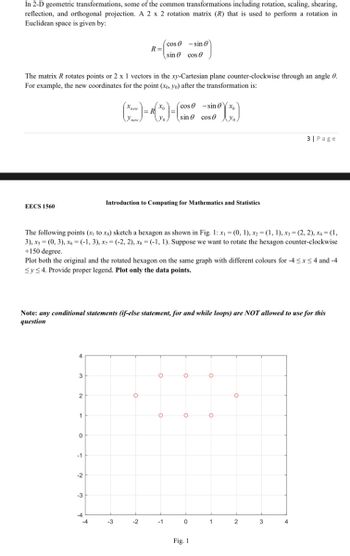
Transcribed Image Text:In 2-D geometric transformations, some of the common transformations including rotation, scaling, shearing,
reflection, and orthogonal projection. A 2 x 2 rotation matrix (R) that is used to perform a rotation in
Euclidean space is given by:
EECS 1560
The matrix R rotates points or 2 x 1 vectors in the xy-Cartesian plane counter-clockwise through an angle 0.
For example, the new coordinates for the point (xo, yo) after the transformation is:
4
3
2
1
0
-1
-2
-3
X new
The following points (x₁ to xg) sketch a hexagon as shown in Fig. 1: x₁ = (0, 1), x2 = (1, 1), x3 = (2, 2), X4 = (1,
3), x5 = (0, 3), x6 = (-1,3), x7= (-2, 2), xs = (-1, 1). Suppose we want to rotate the hexagon counter-clockwise
+150 degree.
-4
y new.
Plot both the original and the rotated hexagon on the same graph with different colours for -4≤x≤4 and -4
Sy≤ 4. Provide proper legend. Plot only the data points.
-4
Note: any conditional statements (if-else statement, for and while loops) are NOT allowed to use for this
question
R=
-3
= R
R(x) = (
(1
O
-2
cos
sin
Introduction to Computing for Mathematics and Statistics
cos
O
cos
sin0x₂
sinᎾ cose yo
()
Yo
O
-1
sin 0
O
O
0
Fig. 1
O
O
1
O
3| Page
2
3
4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 15 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 18.) Which is not a point on the equation -2x - 3y + 5z = 7? a. (1,2,3) b. (-2,-3,5) c. (-2,4,3) d. (-4,2,1)arrow_forward19) Find the distance between these two points (-8, 5) and (15, -9) Use the formula: d = square root of [(x2– x1)² + (y2 - yı)²]arrow_forwardThere are exactly two values of y that make the points A = (0,1), B = (4, –10) and C = (-15, y) form a right triangle. The two values are (Enter exact values - integers or fractions of integers - with a comma between them.)arrow_forward
- §B: Determine which of the following points are contained by the circle (x – 4)² + (y + 1)² = 16 10. (1, 4) 11. (4, 3) 12. (-2, 3) 13. (5, 3) 14. (0, -1)arrow_forwardFind all values of x so that the triangle with vertices A=(5, x,-2), B-(7,-7, 0), and C-(5, -7,-5) has a right angle at A.arrow_forwardShow that the points P(9,-4) Q(8,6) and R(-1,5) lie on a circle with Centre C(4,1)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

