
Concept explainers
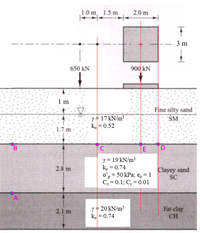
The following picture depicts a soil profile that has two sources of above-ground loading: (1) a point load of 650 kN and (2) a rectangular footing that support a loading of 900 kN. Calculate the following:
-
Vertical effective stress (σ’v ) at point A. Assume free field condition (i.e., no effect from the above-ground point load and rectangular footing).
-
Horizontal total stress (σh ) at point A. Assume free field condition.
-
Vertical effective stress (σ’v ) at point B. Assume free field condition.
-
Vertical effective stress (σ’v ) at point C. Consider the effect from the point load only.
-
Vertical effective stress (σ’v ) at point D. Consider the effect from the rectangular footing only. Use the DM 7.01 method. Approximate method is not allowed.
-
Vertical effective stress (σ’v ) at point E. Consider the effect from the rectangular footing only. Use the DM 7.01 method. Approximate method is not allowed.
-
Vertical effective stress (σ’v ) at point E. Consider the effects from the rectangular footing AND point load
-
Settlement on the Lean clay layer resulted from the rectangular footing AND point load. State all assumptions you have made. Express your answer in cm.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- Figure 5 summarizes the loading on two footings. What will be the increase in thevertical stress (Licrv) at point A which is located in the middle of two foundations and is 2meters deep from the ground surface? Calculation should be performed using twodifferent methods.arrow_forwardShear Stress 3. Please provide proper discussion and illustration. Clear and complete solution please thank you. It is known that the angle of internal friction for the soil comprising a granular deposit is 37°. At one depth in the deposit, the lateral pressure is 45 kPa, and this is considered the value of the minor principal stress. Use the Mohr’s circle analysis to determine the maximum verticalp ressure (major principal stress) that can be applied (i.e. the vertical pressure for incipient shear)arrow_forwardA 1.8 m square, 2 m deep and 1 m high footing supports a column load of 570 kN. It is supported on a clayey sand. There is no water present at the site. Use unit weight for the concrete 24 kN/m³. A dilatometer test run at the site has returned the following constrained modulus profile: Depth (m) M (MPa) 2 7.7 3 8.8 4 5 10.2 14.8 6 15.4 Plot the modulus distribution with depth considering both the strain distribution with depth and the soil moduli, and divide soil into 5 layers, then determine the average modulus for each soil layer.arrow_forward
- A 3 ft square footing carries a sustained load of 10.6kips. It is placed on the surface of a 30 ft thick saturated overconsolidated clay underlain by dense sand. Based on laboratory tests, the clay can be adequately modeled using the e-log-p method. The laboratory tests provide the following compressibility information for the clay: y = 123.4lb/ft³ Cc = 0.064 1+eo Cr 1+eo Aom = 920lb/ft² The groundwater table is located at the ground surface. Estimate the primary consolidation occurred in the clay layer. Solution: Preliminary Calculations: 1). It should be adequate to compute the compressibility to a depth of = 0.0024 2). Layer thickness = ft; 2). Bearing pressure at the bottom of the footing: q = Primary consolidation for each layer: a). Layer 1: 1). depth to layer midpoint = 2). Total vertical stress at midpoint: Oz ft; 3). Pore water pressure at midpoint: u = 4). Effective vertical stress at minpoint: Oz! 6). Induced vertial stress: Az = = = 9). The type of this layer of soil is :…arrow_forwardA 4m x 5m rectangular footing resting at ground level carries a uniform load of 550 kPa. Compute the vertical stress increment at a depth of 8.0m below the ground surface. a. Use 2:1 Approximation Method (70.51) b. Use 60 Approximation Method (58.36)arrow_forwardA soil element is subject to an overburden pressure equal to 100 kPa. The maximum shear stress develops within the element without failing is equal to 30 kPa. Find the lateral earth pressure coefficient at rest? (Acceptable tolerance = 2%).arrow_forward
- For the stressed soil element shown, determine: 1. The major principal stress 2. The minor principal stress 3. The normal and shear stresses on the plane AE 4. The orientation of the major principal plane 150 Ib/in? 60 lb/in? D E 90 Ib/in? 60 Ib/in? 45°arrow_forwardA cohesive soil with an angle of shearing resistance of 28.08°has cohesion of 32.14 Kpa. The shear stress at failure is 64 Kpaa) Compute the normal stressb) Calculate the confining pressurec) Calculate the maximum principal stressarrow_forwardDetermine the effective stress increase, rate of increase of effective stress in the soil at depth of 4 meters below the footing. The water table is 5 meter below the footing. Soil below has the following properties in laboratory: wet mass=44g, dry mass=30.1g, wet volume=24.6cc, dry volume=15.9cc, SR=1.893, void ratio=1.3 (assume soil above WT is dry)arrow_forward
- A footing of size 2m×2m transferring a pressure of 200 kN/m², is placed at a depth of 1.5 m below the ground as shown in the figure (not drawn to the scale). The clay stratum is normally consolidated. The clay has specific gravity of 2.65 and compression index of 0.3. 1.5m 1m 1.5 m 200 kN/m² Silty sand Clay Ya =15kN/m³ Y sat = 18kN/m³ Y sat = 17 kN/m³ GWT $0.5 m Dense sand Considering 2:1 (vertical to horizontal) method of load distribution and Y₁ = 10kN/m³, the primary consolida- tion settlement (in mm, round off to two decimal places) of the clay stratum isarrow_forwardWater table at a site was lowered from depth of 4 ft to depth of 15 ft to allow for excavation of a building foundation. The soil is mainly consist of silty sand deposit. Assuming that the soil above the water table remained saturated at a moisture content of 28 percent, estimate the increase in effective stress at a depth of 16 ft. Soil specific gravity is given at 2.68.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 a) In a geotechnical laboratory an oedometer test on a saturated clay soil was conducted. The results in the laboratory report stated that the Ce= 0.2, C, -0.04 and OCR = 4.5. The existing vertical effective stress in the field was 130 kPa. A shallow foundation was designed to construct above the soil condition. This will increase the vertical stress at the center of the clay by 50 kPa. The thickness of the clay layer is 2 m and its water content is 28%. Solve the primary consolidation settlement and determine the difference in the settlement if OCR value were 1.5 instead 4.5.arrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





