
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
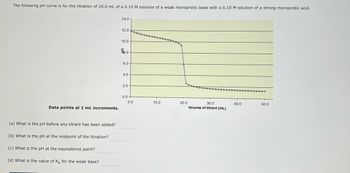
Transcribed Image Text:The following pH curve is for the titration of 20.0 mL of a 0.10 M solution of a weak monoprotic base with a 0.10 M solution of a strong monoprotic acid.
**Graph Details:**
- **Title:** pH vs. Volume of Titrant
- **X-axis:** Volume of titrant (mL), ranging from 0 to 50 mL.
- **Y-axis:** pH, ranging from 0 to 14.
- **Curve Characteristics:**
- The curve starts at a high pH (around 11.5) and decreases gradually.
- A more rapid pH drop occurs between approximately 20 mL and 25 mL of titrant, indicating the equivalence point.
- The curve flattens out around a pH of 2 after the equivalence point.
**Data points at 1 mL increments.**
**Questions:**
(a) What is the pH before any titrant has been added?
(b) What is the pH at the midpoint of the titration?
(c) What is the pH at the equivalence point?
(d) What is the value of \( K_b \) for the weak base?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given,
pH curve .
Volume of monoprotic base =20.0 mL
concentration of strong acid = 0.1 M
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Weak Base + Strong Acid Titration - Example Problem: Titration of 25 mL of .1 M NH3 With .1 M HCl: a. 0 mL. b. 12.5 mL. c. 20 mL. d. 25 mL. e. 30 mL.arrow_forwardIf you are given sodium acetate and asked to make a 250 mM acetate buffer and titrate it to a final pH of 4.76, will you have to add acid, base, or nothing in order to achieve the proper pH? Why? Please explain the “why” part of the question. Please type answer note write by hend.arrow_forwardA 1:2 molar ratio of 0.015L buffer prepared using sodium acetate (0.5 M) and acetic acid (1.0 M) is prepared. Determine the pH of the buffer at the 5 specied points as 0.50 M strong acid and strong base are added. a) 18 mL strong acid b) 14 mL strong acid c) 0 mL strong acid/base d) 24 mL strong base e) 38 mL strong basearrow_forward
- Which type of titration will be the pH be acidic at the equivalence point? a) strong acid vs strong base b) strong acid vs weak base c) weak acid vs strong base d) weak acid vs weak base e) none of thesearrow_forwardWeak Acid + Strong Acid Base Titration - Example Problem: Consider Titration of 25 mL of .1 M CH3CO2H With .1 M NaOH. Calculate The pH After Adding The Following Volumes of NaOH: a. 0 mL b. 12.5 mL c. 25 mL d. 37.5 mL - I know that the correct the answer for letter d. is 12.28. I just don't know how to get to this answer.arrow_forwardConsider the titration of a 35.0 mL sample of 0.175 M HBr with 0.200 M KOH. Determine each of thefollowing. e) the pH after adding 5.0 mL of base beyond the equivalence pointarrow_forward
- Solve only D ... Don't provide handwriting solutions....arrow_forwardBuild a titration curve for the following scenarios. Make sure to label your accesses and anyother appropriate pieces of data. Each curve should have a minimum of 4 data points, but youcan use the following to help structure your curvea) Initial pHb) pH at Veqc) pH=pka (if applicable)d) pH when excess titrant is addede) Additional pH point near Veq for Strong Acid/Strong Base titrations (in order to see thesteepness of the slope) OR additional pH point in buffer zone for titrations with a Weakcompound.arrow_forwardFor which of the following aqueous solutions will a decrease of pH increase the solubility? A) CaCO₃ B) PbCl₂ C) CuBr D) AgClarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY