
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The following is an acceleration-time graph of a particle with a starting velocity and the distance traveled at t=10s is -4m/s and 200m respectively. Draw the velocity-time, distance-time graph of the particle and what is the velocity and total distance traveled at t=18s.
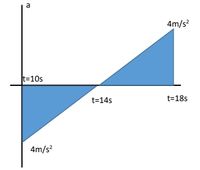
Transcribed Image Text:a
4m/s
t=10s
t=14s
t=18s
4m/s?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Bobby walks north to a convenient store which is 48 m from his house once there he realize he forgot his wallet so he has to hurry home to find it and then walks back to the store if the entire truck takes him 25 minutes what is his average velocity for the trip in m/s?arrow_forwardAssume that an MX missile goes from rest to a suborbital velocity of 3.50 km/s in 90.0 s (the actual speed and time are classified). What is its average acceleration in m/s2? What is its average acceleration in multiples of g?arrow_forwardJohn drops a stone, from rest, at the top of a 40 meter high cliff. His friend Bob throws astone upward from the base of the cliff giving it an initial velocity of 30 m/s. The stones arethrown/dropped at exactly the same instant. Assume Bob’s stone is initially on the ground ata position of 0 meters, while John’s stone starts 40 meters from the ground and that bothstones experience only free fall motion.a) At what time, after he has thrown it, does Bob’s stone to hit the ground?b) At what time, do the two stones pass each other?arrow_forward
- A roly-poly bug moves on the x axis. The bug has a variable velocity which is denoted by 2 v = t² - 2.50t.t is time in seconds and v is meters per second. The origin of the roly-poly bug is at t=0. Your job is to figure out the following after 3s have passed. Be sure to use the correct amount of sig figs! a) Velocity of the bug b) The bugs acceleration c) The bugs position THIS IS How I ROLLarrow_forwardThe Hint The position of a particle moving along the x axis is given by x = (21 +22t+8t²) m, where t is in s. What is the instantaneous velocity of the particle at t= 5.0 s ? a. b. C. e. f. 10.2m/s -2.0 m/s -82.0m/s 331 m/s 102m/s -6.0 m/sarrow_forwardThe position versus time for a certain particle moving along the x-axis is shown in the figure.1. Plot the velocity versus time graph for the time intervals: a. 0 to 2 sb. 2 s to 6 sc. 6 s to 10 s 2. Plot the acceleration versus time graph for the same time intervals.arrow_forward
- Context The position of a peculiar fish as a function of time is given by the following equation. Time is in seconds, position is in meters, and the positive direction is to the right. x(t) = 2t3 + 12t2 - 72t The fish's position, velocity, and acceleration functions are x = 2t3 + 12t2 - 72t, v = 6t2 + 24t - 72, and a = 12t + 24. Question: When, if ever, is the fish at rest? Drag the appropriate label(s) to the correct location(s) on the number line. Remember that it is the circle in the upper left corner of the label that must be in the correct place. Drag the period (.) to denote a single time; for example, t=0. Drag the left bracket ([) to denote the lower end of a range; for example, t>0. Drag the right bracket (]) to denote the upper end of a range; for example, t<0. Drag "none" anywhere near the line if the fish is never at rest. You may place as many of each symbol on the line as needed. See image attached:arrow_forwardQ1) The position of a particle traveling along a straight line is s(t) = (t²-3t²+C) ft, where tis in seconds and C is a constant. If s = 4 ft when t= 0, determine the velocity of the particle when t =4 s. What is the total distance traveled during the time interval t = 0 to t = 4 s? Also, what is the acceleration when t = 2 s?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON