
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The following information is available for two samples drawn from independent normally distributed populations.
|
Population A:
|
nA=11
|
S2A=157.8
|
|
Population B:
|
nB=11
|
S2B=107.1
|
What is the value of
F
if you are testing the null hypothesis
H0: σ21−σ22=0?
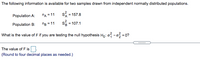
Transcribed Image Text:The following information is available for two samples drawn from independent normally distributed populations.
Population A:
nA = 11 S = 157.8
Population B:
ng = 11
s = 107.1
What is the value of F if you are testing the null hypothesis Họ:o -o = 0?
......
The value of F is
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A simple random sample of size n=15 is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean is found to be x=21.1 and the sample standard deviation is found to be s=6.3. Determine if the population mean is different from 24 at the a=0.01 level of significance. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. (a) Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: H₁B 24 24 Aarrow_forwardThis is a 4 part question.arrow_forward10 for both samples QUESTION 7 A researcher reports t(12) = 2.86, p=.04 for a repeated-measures research study. From this we know: Oa. The researcher would have failed to reject the null if their alpha = .05, and there were 12 participants in the sample. Ob. The researcher would have rejected the null, their alpha = 2.86, and there were 13 participants in the sample. OC. The researcher would have rejected the null if their alpha = .05, and there were 13 participants in the sample. d. The researcher would have failed to reject the null if their alpha = .05, and there were 13 participants in the sample. %3D QUESTION 8 Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answers.arrow_forward
- The following display from a TI-84 Plus calculator presents the results of a hypothesis test for a population mean μ.u=33 t=-1.505947 p=0.069186 x=32.60 Sx=1.89686 n=51How many degrees of freedom are there? Question 20 options: 52 50 33 51arrow_forwardQuestions 1 and 2 1. A sample of n = 4 scores has SS = 60. What is the variance for this sample? 2. True or False? For a one-tailed test evaluating at treatment that is supposed to decrease scores, a researcher obtains t(8) = -1.90. For alpha = .05, the correct decision is to reject the null hypothesis.arrow_forwardQuestion 2: a. Calculate the probability of a Type Il error for the following hypotheses when u = 37: Ho: u=40 H1: µ<40 The significance level is 5%, the population standard deviation is 5, and the sample size is 25. b. Repeat part(a) with a = 15%. c. Describe the effect on ß of increasing a. %3Darrow_forward
- CHALLENGE ACTIVITY 402562.2600368.qx3zqy7 8.2.3: Hypothesis testing for two population proportions (one-tailed z-test). Jump to level 1 A university department chair believes that the afternoon section of a large survey class has a consistently lower proportion of students that pass the class compared to the morning section. The chair checks a random sample of student records from each section. The results of the data collected are shown below. Morning section Afternoon section Successes Observations p-hat_1 346 Successes 400 Observations 0.865 p-hat_2 Confidence level 95% -0.5548 p-value 0.2912 3 2 6 2 P= Ex 1.234 Morning section samples: ₁ Ex: 9 Afternoon section samples: 1₂ Sample proportion for morning section samples: p1 Sample proportion for afternoon section samples: p₂ – O 500 LE E 2 № 7 || ||| Ex: 1.234 D D DOarrow_forwardThe NAEP considers that a national average of 283 is an acceptable performance. Using α = .05, run a two-tail t-test for one sample to test Ho: µ=283 for the 2019 scores. Report the t-obt, df, and p-values. Would you reject the null hypothesis that the 2019 scores come from a population with average 283? If this is the case, does it come from a population from larger or smaller average?arrow_forwardQuestion 16 Match the p-values with the appropriate conclusion: I. 0.00001 II. 0.0297 III. 0.0721 IV. 0.4490(a) The evidence against the null hypothesis is significant, but only at the 10% level. (b) The evidence against the null and in favor of the alternative is very strong. (c) There is not enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis, even at the 10% level. (d) The result is significant at a 5% level but not at a 1% level.arrow_forward
- Question 15 A random sample of 450 shoppers at FSK Mall found that 125 favored longer shopping hours. Is this sufficient evidence to conclude that less than 30% of the shoppers at FSK Mall favor longer hours? Let alpha= 0.05. Show all 6 steps to hypothesis testing.arrow_forwardQUESTION 6 Which of the following P-values will lead us to reject the null hypothesis at the .05 level? O.10 O .025 O.075 O.15 O Any P-value greater than .05 QUESTION 7 Suppose that when data from an experiment was analyzed, the P-value for testing HO mu=50 versus H1 mu > 50 was calculated as 0.0244. Which of the following statements are true? O HO is rejected at .10 level. O HO is not rejected at .05 level. O HO is not rejected at .025 level. H0 is rejected at any level o O All of the above statements are true. wwww..arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman