
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Assume Sam dislikes doing chores and likes watching TV. Given these preferences, increasing Sam's time spent watching TV while holding time spent doing chores constant Sam's utility. Decreasing Sam's time spent doing chores while holding time spent watching TV constant his utility.
The following graphs depict two sets of indifference
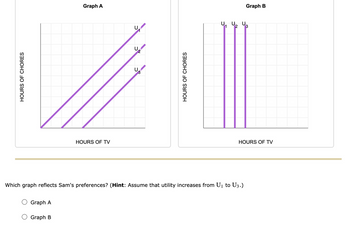
Transcribed Image Text:HOURS OF CHORES
Graph A
Graph A
Graph B
HOURS OF TV
U
U
HOURS OF CHORES
~
Which graph reflects Sam's preferences? (Hint: Assume that utility increases from U₁ to U3.)
Graph B
3
HOURS OF TV
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Emily is a utility maximizer. Her income is $100, which she can spend on cafeteria meals and on notepads. Each meal costs $5 and each notepad costs $2. At these prices Emily chooses to buy 16 cafeteria meals and 10 notepads. a) Draw a diagram that shows Emily’s choice using an indifference curve and her budget line, placing notepads on the vertical axis and cafeteria meals on the horizontal axis. Label the indifference curve, I1, and the budget line BL1. Make sure you calculate the endpoints of the budget constraint. b) The price of notepads falls to $1; the price of cafeteria meals remains the same. On the same diagram, draw Emily’s budget line with the new prices and label it BL2. c) Lastly, Emily’s income falls to $90. On the same diagram, draw his budget line with this income and the new prices and label it BL3. Is she worse off, better off, or equally as well off with these new prices and lower income than compared to the original prices and higher income?arrow_forwardLisa consumes only two goods, pizzas and burritos. In equilibrium, her marginal utility per slice of pizza is 10 and her marginal utility per burrito is 8. Instructions: Enter your answer rounded to two decimal places. If a slice of pizza costs $3, then the price of a burrito must be $arrow_forward5arrow_forward
- A consumer currently spends a given budget on two goods, X and Y, in such quantities that the marginal utility of X is 10 and the marginal utility of Y is 8. The unit price of X is $5 and the unit price of Y is $2. The utility-maximizing rule suggests that this consumer shouldarrow_forwardWhich of the following statement is TRUE Group of answer choices As the consumption of a good increases, marginal utility rises, but total utility falls. As the consumption of a good increases, total utility falls and marginal utility falls. As the consumption of a good increases, total utility rises, but marginal utility falls.arrow_forwardThere are two shows on Netflix that Jeff can watch, Show 1 and Show 2. Where x₁ measures the number of episodes watched of Show 1 and x2 measures the number of episodes watched of Show 2, Jeff's preferences can be represented by u(x₁, x₂) = x² + ax. Jeff has 8 hours available for watching Netflix today. Each episode of Show 1 lasts 30 minutes, while each episode of Show 2 lasts one hour. Draw an indifference curve for Jeff, then answer the following questions. If rounding is needed, please round to 3 decimal places. a) When a = 2, Jeff optimally watches_ episodes of Show 1..... (fill in the blank) b)... and he watches episodes of Show 2. (fill in the blank) c) When a = 6, Jeff optimally watches_ episodes of Show 1..... (fill in the blank) d) ... and he watches. episodes of Show 2. (fill in the blank)arrow_forward
- please helparrow_forwardTessa likes both ice-creams and pies. However, if she eats too much of them, she gets sick. That is, cating ice-creams or pics beyond a certain amount lowers Tessa's utility. Draw a set of indifference curve which might represent Tessa's preferences for ice-creams and pies.arrow_forwardThe marginal utility for shoes and coffee is given below for five individuals. A pair of shoes costs $2, and a cup of coffee costs $1. Which of these consumers are optimizing over their choices? Explain For those who are not, how should they adjust their spending? Explain “Pasta is Miguel’s favorite meal therefore the law of diminishing marginal utility does not apply”. Do you agree with this statement? It is known that the indifference curve is convex. What does this tell you about the relationship between the goods? The income effect and the substitution effect work in the same direction for a normal good. Explain how this differs for an inferior good.arrow_forward
- Question 11 Marcus spends his income on movies and concerts. At his optimum, Marcus’ Group of answer choices marginal rate of substitution is equal to 1. marginal utility per dollar spent on movies equals his marginal utility per dollar spent on concerts. utility from consuming movies is equal to his utility from consuming concerts. marginal utility of movies is equal to his marginal utility of concerts.arrow_forwardLorenzo enjoys going to the theater to see plays, and he also enjoys going to rock concerts. The following diagram shows two of Lorenzo's indifference curves for going to plays and concerts. With Lorenzo's initial budget constraint (BC1), he chose to go to five concerts and three plays per month (point X). Then his budget constraint shifted to BC2, and he chose to go to four concerts and six plays per month (point Y). PLAYS 10 0 4 5 CONCERTS BC 8 Show Transcribed Text BC 10 C Of the following choices, which could have shifted Lorenzo's budget constraint from BC₁ to BC₂? Check all that apply. The price of theater tickets increased while his income and the price of concert tickets stayed the same. His income decreased while the prices of theater and concert tickets stayed the same. His income increased while the prices of theater and concert tickets stayed the same. The prices of both theater and concert tickets decreased while his income stayed the same. Based on Lorenzo's consumption…arrow_forwardCharlie has the utility function U(xA, xB) = xAxB. His indifference curve passing through 35 apples and 18 bananas will also pass through the point where he consumes 5 apples and Select onearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education