Question
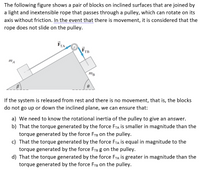
Transcribed Image Text:The following figure shows a pair of blocks on inclined surfaces that are joined by
a light and inextensible rope that passes through a pulley, which can rotate on its
axis without friction. In the event that there is movement, it is considered that the
rope does not slide on the pulley.
FTA
FTB
mA
mB
If the system is released from rest and there is no movement, that is, the blocks
do not go up or down the inclined plane, we can ensure that:
a) We need to know the rotational inertia of the pulley to give an answer.
b) That the torque generated by the force FTA is smaller in magnitude than the
torque generated by the force FrB on the pulley.
c) That the torque generated by the force FTA is equal in magnitude to the
torque generated by the force FTB g on the pulley.
d) That the torque generated by the force FTA is greater in magnitude than the
torque generated by the force FTB on the pulley.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- how much does the cat increase the kinetic energy of the cat-ring system if the cat crawls to the inner edge at radius R?arrow_forwardrrrA solid spherical jewel rolls smoothly from rest down a ramp. The jewel descends a vertical height of 1.2m to reach the bottom of the ramp. The previous question asked "What is the jewel's speed at the bottom of the ramp?" Hint: This problem has nothing to do with elasticity as we did not formally cover that topic. All elastic energy terms are zero. List all terms that had a value of zeroarrow_forwardThe orienting track of a bowl feeder consists of one device (X). The part has four natural resting positions. The device efficiency matrix and the initial distribution matrix are below. Parts enter the track at the rate of 170 min. How many parts exit device-X in position 3 per minute? (One place of decimal) INITIAL DISTRIBUTION MATRIX Position P1 P2 P3 P4 Bowl 0.41 0.18 0.29 0.120 DEVICE-X TRANSITION MATRIX 0.50 P13 0.49 P23 0.19 0.29 P33 0.18 0.37 P43 0.15 1 Note: Each row must sum to 1. Therefore P13, P23, P33 AND P43 ARE 1-Sum(All other row cells)arrow_forward
- A Block-Spring System A block of mass 1.0 kg is attached to horizontal spring that has a force constant of 2,000 N/m as shown in figure (a). The spring is compressed 3.0 cm and then released from rest as in figure (b). (a) A block attached to a spring is pushed inward from an initial position x -0 by an external agent. (b) At position x, the block is released from rest and the spring pushes it to the right. x = 0 (For the following, when entering a mathematical expression, do not substitute numerical values; use variables only.) (a) Calculate the speed of the block as it passes through the equilibrium positio x = 0 if the surface is frictionle SOLUTION Conceptualize This situation has been discussed before, and it is easy to visualize the block being pushed to the right by the spring and moving with some speed at x = 0. Categorize We identify the system as the block and model the block as [--Select-- Vsystem. Analyze In this situation, the block starts with v, = 0 at x, = -3.0 cm, and…arrow_forwardA ball of mass m is attached to a string of length L. It is being swung in a vertical circle with enough speed so that the string remains taut throughout the ball's motion. (Figure 1)Assume that the ball travels freely in this vertical circle with negligible loss of total mechanical energy. At the top and bottom of the vertical circle, the ball's speeds are vt and vb, and the corresponding tensions in the string are T⃗ t and T⃗ b. T⃗ t and T⃗ b have magnitudes Tt and Tb. Find Tb−Tt, the difference between the magnitude of the tension in the string at the bottom relative to that at the top of the circle. Express the difference in tension in terms of m and g. The quantities vt and vb should not appear in your final answer.arrow_forwardFind 0(theta) and W in the figure below where w1 = 15.0 N, w2 = 31.0 N, and ? = 64.0°, assuming that the arrangement is at rest. 0(theta)= W =arrow_forward
- A vertical spring stretches by 0.15 m to its new equilibrium length when a 3.0 N weight is attached. What is the spring constant?arrow_forwardThe coefficient of static friction between mass mA and the table is 0.48, whereas the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.27. Ignore masses of the cord and the (frictionless) pulley. What minimum value of mA will keep the system from starting to move? What value of mA will keep the system moving at constant speed?arrow_forwardTrue or Falsearrow_forward
- 7. A car of mass 1500kg is pulling a trailer of mass 750 kg up a straight hill of length 800 m inclined at an angle of arcsin(0.08) to the horizontal. The resistances to the motion of the car and trailer ure 400 N and 200 N respectively. The car and trailer are connected by a light rigid tow-bar. The car and trailer have speed 30m * s ^ - 1 at the bottom of the hill and 20m * s ^ - 1 at the top of the hill, After reaching the top of the hill the system consisting of the car and trailer travels along a straight level road. The driving force of the car's engine is 2400 N Find the acceleration of the system and the tension in 8. and the resistances to motion are unchanged. the tow-bar.arrow_forwardA 1.15 kg mass is attached to a 1.86 m string that is anchored to the ceiling. The mass is pulled back to an initial angle of theta = 65.1 degrees and released from rest. (a) How fast is the ball moving at the bottom of its swing — the position indicated in the figure? (b) What is the tension in the string at the bottom of the swing — the position indicated in the figure?arrow_forwardA car with a mass of 1020 kg is traveling in a mountainous area with a constant speed of 64.9 km/h. The road is horizontal and flat at point A, horizontal and curved at points B and C. A B IC IB The radii of curvatures at B and C are: rg = 130 m and rc = 120 m. Calculate the normal force exerted by the road on the car at point A. Submit Answer Tries 0/12 Now calculate the normal force exerted by the road on the car at point B. Submit Answer Tries 0/12 And finally calculate the normal force exerted by the road on the car at point C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios