
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
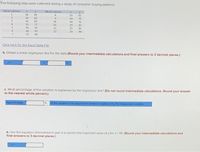
Transcribed Image Text:The following data were collected during a study of consumer buying patterns:
Observation
Observation
y.
69
y.
18
19
81
2
26
81
9
14
75
41
85
10
10
76
4
35
77
11
25
83
56
95
12
21
86
46
93
13
29
90
33
86
Click here for the Excel Data File
b. Obtain a linear regression line for the data (Round your intermediote calculations and final answers to 3 decimal places.)
y3=
c. What percentage of the variation is explained by the regression line? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer
to the nearest whole percent.)
Approximately
of the varlation in the dependent varlable is explainud by the independent variable
d. Use the equation determined in part b to predict the expected value of y for x 44. (Round your intermediate calculations and
final answers to 3 decimal places.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How do I code this in MATLAB?arrow_forwardA split at the $3200 income point creates a top and bottom partition. Compute the overall(weighted) Gini index given an income split of 32000. income is 0, 10,000, 20,000, 30,000, 40,000, 50,000, 60,000, 70,000, 80,000, and age is 0,10,20,30,40,50 (Please give correct answer with explanction)arrow_forwardHow to solve this Use the fastfood.csv file to complete the following assignment. Create a file, fastfood.py, that loads the .csv file and runs a regression predicting calories from total_fat, sat_fat, cholesterol, and sodium, in that order. Add a constant using sm.add_constant(data). Then, print the following to two decimals print(model.mse_total.round(2)) print(model.rsquared.round(2)) print(model.params.round(2)) print(model.pvalues.round(2))arrow_forward
- Analysts at a start-up company are analyzing 35 months of sales data. They partition the data (the first 20 observations are assigned to the training set; the most recent 15 months are in the test set). The only independent variable is T (month number, ranging from 1 to 35). Five models (polynomials of order 1 - 5) are fit to the data. The first order is just the linear model; the 2nd order polynomial is the quadratic model; order 3 is the cubic model, etc. In each case the model is fit on the training data, and scored on both the training and test data sets. The results are below. Based on this output, which is the best predictive model? Metrics AE RMSE MAE SSE Metrics AE RMSE MAE SSE Model 2 Model 3 Model 5 Model 4 Model 1 1 <0.000001 0.955978 0.792802 18.277907 1 -1.034550 1.424155 1.208991 30.423248 Training Data Scoring Models (Polynomial of order 1-5) 4 2 <0.000001 0.928791 0.759583 17.253086 3 <0.000001 <0.000001 0.928295 0.855568 0.761951 0.652212 17.234646 14.639962 Test Data…arrow_forwardWe use the Breast Cancer Wisconsin dataset from UCI machine learning repository: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Breast+Cancer+Wisconsin+%28Diagnostic%29 Data File: breast-cancer-wisconsin.data (class: 2 for benign, 4 for malignant) Data Metafile: breast-cancer-wisconsin.names Please implement this algorithm for logistic regression (i.e., to minimize the cross-entropy loss as discussed in class), and run it over the Breast Cancer Wisconsin dataset. Please randomly sample 80% of the training instances to train a classifier and then testing it on the remaining 20%. Ten such random data splits should be performed and the average over these 10 trials is used to estimate the generalization performance. You are expected to do the implementation all by yourself so you will gain a better understanding of the method. Please submit: (1) your source code (or Jupyter notebook file) that TA should be able to (compile and) run, and the…arrow_forwardA Ridge Linear Regression adds the sum of the squared values of the coefficients to the loss function to penalize large coefficients. Group of answer choices True Falsearrow_forward
- In the simple linear regression equation ŷ = bo + b₁x, how is b₁ interpreted? it is the change in that occurs with a one-unit change in y O It is the estimated value of ŷ when x = 0 O It is the change in ŷ that occurs when bo increases O it is the change in ŷ that occurs with a one-unit change inarrow_forwardThe first principal component is a normalized linear combination of the original variables with the largest varianceTrueFalsearrow_forwardAssume the following simple regression model, Y = β0 + β1X + ϵ ϵ ∼ N(0, σ^2 ) Now run the following R-code to generate values of σ^2 = sig2, β1 = beta1 and β0 = beta0. Simulate the parameters using the following codes: Code: # Simulation ## set.seed("12345") beta0 <- rnorm(1, mean = 0, sd = 1) ## The true beta0 beta1 <- runif(n = 1, min = 1, max = 3) ## The true beta1 sig2 <- rchisq(n = 1, df = 25) ## The true value of the error variance sigmaˆ2 ## Multiple simulation will require loops ## nsample <- 10 ## Sample size n.sim <- 100 ## The number of simulations sigX <- 0.2 ## The variances of X # # Simulate the predictor variable ## X <- rnorm(nsample, mean = 0, sd = sqrt(sigX)) Q1 Fix the sample size nsample = 10 . Here, the values of X are fixed. You just need to generate ϵ and Y . Execute 100 simulations (i.e., n.sim = 100). For each simulation, estimate the regression coefficients (β0, β1) and the error variance (σ 2 ). Calculate the mean of…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education