
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
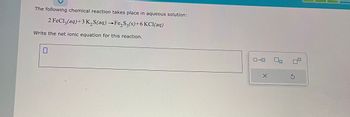
Transcribed Image Text:The following chemical reaction takes place in aqueous solution:
2 FeCl3(aq) +3 K₂S(aq) →Fe₂S3(s)+6 KCl(aq)
Write the net ionic equation for this reaction.
0
0-0
X
S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- One way in which the useful metal copper is produced is by dissolving the mineral azurite, which contains copper(II) carbonate, in concentrated sulfuric acid. The sulfuric acid reacts with the copper(II) carbonate to produce a blue solution of copper(II) sulfate. Scrap iron is then added to this solution, and pure copper metal precipitates out because of the following chemical reaction: Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq) Suppose an industrial quality-control chemist analyzes a sample from a copper processing plant in the following way. He adds powdered iron to a 200. mL copper(II) sulfate sample from the plant until no more copper will precipitate. He then washes, dries, and weighs the precipitate, and finds that it has a mass of 107. mg. Calculate the original concentration of copper(II) sulfate in the sample. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 0 x10 х §arrow_forwardNa+(aq)+OH−(aq)+H+(aq)+Cl−(aq)→ Write the net ionic equation for the reaction. Express your answer as a chemical equation.arrow_forwardConsider the following precipitation reaction: 5 Fe2+(aq) + MnO4-(aq) + 8 H+(aq) → 5 Fe3+(aq) + Mn2+(aq) + 4 H2O(l) An iron sample weighing 0.276 g is converted into Fe2+(aq) and requires 31.57 mL of MnO4-(aq) according to the equation above. What is the Molarity of the MnO4-(aq) solution?arrow_forward
- The amount of nitrogen in an organic substance can be determined by an analytical method called the Kjeldahl method, in which all the nitrogen in the organic substance is converted to ammonia. The ammonia, which is a weak base, can be neutralized with hydrochloric acid, as described by the equation NH, (aq) + HCl(aq) → NH₂Cl(aq) If 46.0 mL of 0.150 M HCl(aq) is needed to neutralize all the NH, (g) from a 2.25 g sample of organic material, calculate the mass percentage of nitrogen in the sample. mass percentage:arrow_forwardGive the complete ionic equation for the reaction (if any) that occurs when aqueous solutions of H2SO4 and KOH are mixed. OH(aq) + OH¯(aq) → H₂O(l) O H+ (aq) + OH(aq) + 2 K+ (aq) + SO4²-(aq) → H+ (aq) + OH¯(aq) + K₂SO4(s) O No reaction occurs. O 2 K+ (aq) + SO4²- (aq) → K₂SO4(s) H+ (aq) + OH Taq) + 2 K+ (aq) + SO42 (aq) → H₂O(l) + 2K+ (aq) + SO4²- (aq)arrow_forward5.00 mL of 2.5 M NaCl(aq) is diluted with water to the calibration line in a 100.00 mL volumetric flask. What is the concentration of the new solution?arrow_forward
- One way to determine the hardness of a water sample is to precipitate the calcium out of solution as a carbonate. The net ionic reaction for this precipitation is: Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → CaCO3 (s) A 1.00 L sample of water is drawn from a Phoenix, AZ well and 0.534 g of calcium carbonate is recovered using the above reaction. What was the Ca2+ concentration of the original water sample in ppm? Show your work and include units. Hint: ppm stands for parts per million, and in the case of an aqueous solution, this is equivalent to mg/L.arrow_forwardTo measure the amount of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) in a seashell, an analytical chemist crushes a 4.30 g sample of the shell to a fine powder and titrates it to the endpoint with 233. mL of 0.2700M hydrogen chloride (HCI) solution. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is: 2HCl(aq) + CO3(aq) → H₂CO3(aq) + 2Cl(aq) 19 0 What kind of reaction is this? O precipitation O acid-base redox X olo If you said this was a precipitation reaction, enter the chemical formula of the precipitate. 0 Ar If you said this was an acid-base reaction, enter the chemical formula of the reactant that is acting as the base. If you said this was a redox reaction, enter the chemical symbol of the element that is oxidized. Calculate the mass percent of CaCO3 in the sample. Be sure your answer has 3 significant digits. П 0 0% S ?arrow_forwardBalance and write the net ionic equation for the following reaction Mg(s) + AgNO3(aq) → Mg(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s) Balanced Equation: Complete Ionic Equation: Net Ionic Equation:arrow_forward
- For each of the following reactions, suggest two soluble ionic compounds that, when mixed together in water, result in the net ionic equation given: (a) 2 Ag+ (aq) + CO3²¯ (aq) → Ag₂CO3(s) (b) Mg²+ (aq) + 2 OH¯(aq) → Mg(OH)₂(s), the suspension present in milk of magnesia 3+ (c) 3 Ca³+ (aq) + 2 PO2 (aq) → Ca3(PO4)2(s), gypsum, a component of concretearrow_forwardA 0.124 M NaOH(aq) solution was used to titrate 20.00 mL of an acetic acid (CH3COOH) solution that has an unknown concentration. The equivalence point is reached after adding 15.34 mL of NaOH(aq). a) Write out the complete balanced equation for the reaction that occurs in this titration. b) How man moles of NaOH were added to the acetic acid solution? c) How many moles of acetic acid were in the original 20.00 mL solution? d) What was the concentration of acetic acid in the orignial 20.00 mL solution?arrow_forwardAs shown in the following Figure, an aqueous solution of Nal is poured into an aqueous solution of Pb(NO3)2 which results in the formation of a yellow precipitate. Assuming stoichiometric amounts of Nal and Pb(NO3)2 are reacted, give the chemical formula of the yellow precipitate and the chemical formula of all molecules and/or ions that are present in the solution (You may use the solubility matrix to answer this question). (b)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY