
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
1a

Transcribed Image Text:The following cell notation contains two half-reactions.
Pt | Fe2+ (aq), Fe3+ (aq) || Sn4+ (aq), Sn²+ (aq) | Pt
Which of the following statement/equation correctly describes the two half-reactions?
anode: Sn4+ (aq)+2e→Sn²+ (aq); cathode: Fe2+(aq)-e→Fe³+(aq);
O anode: Fe²+ (aq)-e→Fe³+(aq); cathode: Sn²+ (aq)+2e→Sn4+ (aq)
anode: Fe³+ (aq)+e→Fe2+ (aq); cathode: Sn²+ (aq)+2e→Sn³+ (aq)
anode: Pt + e → Fe³+ (aq)+Fe2+ (aq); cathode: Sn4+ (aq)+Sn²+ (aq) +2e→Pt
O anode: Fe²+ (aq)-e→Fe³+ (aq); cathode: Sn4+ (aq)+2e-Sn²+ (aq)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Using data provided in the table of Standard Potentials, calculate standard emf of the cell described in the last question. Please enter your answer with 2 decimals. for example, 1.056 is written as 1.06. Pay attention to the sign.
this is in par to this question thread
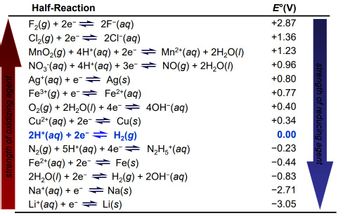
Transcribed Image Text:**Half-Reaction Table and Electrode Potentials**
This table presents various half-reactions along with their standard electrode potentials (E°) measured in volts (V). These potentials indicate the tendency of a chemical species to be reduced—the higher the value, the stronger the oxidizing agent. Conversely, lower values imply stronger reducing agents. The table is organized to show this transition from oxidizing to reducing agents.
### Table Details:
#### Half-Reactions and E° Values:
1. **F₂(g) + 2e⁻ → 2F⁻(aq)**
*E° = +2.87 V*
2. **Cl₂(g) + 2e⁻ → 2Cl⁻(aq)**
*E° = +1.36 V*
3. **MnO₂(g) + 4H⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Mn²⁺(aq) + 2H₂O(l)**
*E° = +1.23 V*
4. **NO₃⁻(aq) + 4H⁺(aq) + 3e⁻ → NO(g) + 2H₂O(l)**
*E° = +0.96 V*
5. **Ag⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Ag(s)**
*E° = +0.80 V*
6. **Fe³⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Fe²⁺(aq)**
*E° = +0.77 V*
7. **O₂(g) + 2H₂O(l) + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻(aq)**
*E° = +0.40 V*
8. **Cu²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Cu(s)**
*E° = +0.34 V*
9. **2H⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → H₂(g)**
*E° = 0.00 V*
10. **N₂(g) + 5H⁺(aq) + 4e⁻ → N₂H₇⁺(aq)**
*E° = −0.23 V*
11. **Fe²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Fe(s)**
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
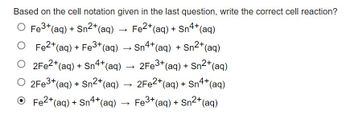
Transcribed Image Text:Based on the cell notation given in the last question, write the correct cell reaction?
O Fe³+ (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)
O Fe²+ (aq) + Fe3+ (aq)
O 2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
O 2Fe3+ (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)
Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
› Sn4+ (aq) + Sn2+ (aq)
2Fe3+ (aq) + Sn2+ (aq)
2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
Fe3+ (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)
O
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Using data provided in the table of Standard Potentials, calculate standard emf of the cell described in the last question. Please enter your answer with 2 decimals. for example, 1.056 is written as 1.06. Pay attention to the sign.
this is in par to this question thread

Transcribed Image Text:**Half-Reaction Table and Electrode Potentials**
This table presents various half-reactions along with their standard electrode potentials (E°) measured in volts (V). These potentials indicate the tendency of a chemical species to be reduced—the higher the value, the stronger the oxidizing agent. Conversely, lower values imply stronger reducing agents. The table is organized to show this transition from oxidizing to reducing agents.
### Table Details:
#### Half-Reactions and E° Values:
1. **F₂(g) + 2e⁻ → 2F⁻(aq)**
*E° = +2.87 V*
2. **Cl₂(g) + 2e⁻ → 2Cl⁻(aq)**
*E° = +1.36 V*
3. **MnO₂(g) + 4H⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Mn²⁺(aq) + 2H₂O(l)**
*E° = +1.23 V*
4. **NO₃⁻(aq) + 4H⁺(aq) + 3e⁻ → NO(g) + 2H₂O(l)**
*E° = +0.96 V*
5. **Ag⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Ag(s)**
*E° = +0.80 V*
6. **Fe³⁺(aq) + e⁻ → Fe²⁺(aq)**
*E° = +0.77 V*
7. **O₂(g) + 2H₂O(l) + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻(aq)**
*E° = +0.40 V*
8. **Cu²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Cu(s)**
*E° = +0.34 V*
9. **2H⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → H₂(g)**
*E° = 0.00 V*
10. **N₂(g) + 5H⁺(aq) + 4e⁻ → N₂H₇⁺(aq)**
*E° = −0.23 V*
11. **Fe²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Fe(s)**
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
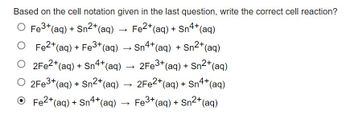
Transcribed Image Text:Based on the cell notation given in the last question, write the correct cell reaction?
O Fe³+ (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)
O Fe²+ (aq) + Fe3+ (aq)
O 2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
O 2Fe3+ (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)
Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
› Sn4+ (aq) + Sn2+ (aq)
2Fe3+ (aq) + Sn2+ (aq)
2Fe2+ (aq) + Sn4+ (aq)
Fe3+ (aq) + Sn²+ (aq)
O
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A tank contains 0.152 lbm of H2 (Hydrogen) and has a volume of 13.6ft^3 at 44.5 Pisa. What is the temperature in Fahrenheit?arrow_forwardThe temperature of a 7.47 × 102 g air sample (density = 1.25 g/L) was lowered, and the density increased to 1.89 g/L. Calculate the new volume of the air sample.arrow_forwardA student calibrated a 10-mL graduated cylinder using water. The empty graduated cylinder weighed 24.378 grams. When it was filled with 9.89 mL of deionized water, it weighed 33.826 grams. The temperature of the water was 21.8oC. What is the density of water, based on these measurements?arrow_forward
- Convert 547.8 Kelvin to celciusarrow_forwardWhat mass of natural gas (CH,) must you burn to emit 327 kJ of heat? CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ΔHxn = −802.3 kJ Express the mass in grams to three significant figures. m= [ΨΕΙ ΑΣΦ Ć ? 80arrow_forwardTo how many significant figures should each answer be rounded (two equations)?arrow_forward
- A salesman on a video recommends a product as a cure for a disease. He states that everyone who used this product felt better immediately. Which of the following responses is in line with scientific methods? O Check all of your neighborhood stores to find this product. "Feeling better" is too vague to be valid in proving a cure, as opposed to something measurable like temperature. If you hoard this product now, you will make a lot of money in a very short time. All of the abovearrow_forwardA sheet of gold weighing 9,6 g and at a temperature of 16.4 °C is placed flat on a sheet of iron weighing 18.5 g and at a temperature of 50.1 "C. What is the final temperature of the combined metals? Assume that no heat is lost to the surroundings Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 0arrow_forwardThe nutritional calorie (Calorie) is equivalent to 1 kilocalorie. One pound of body fat is equivalent to about 4.10 × 103 Calories. Express this quantity of energy in joules and kilojoules. Enter your answers in scientific notation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY