
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Vinubhai
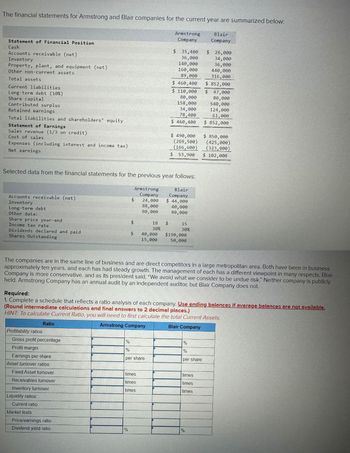
Transcribed Image Text:The financial statements for Armstrong and Blair companies for the current year are summarized below:
Blair
Company
Statement of Financial Position
Cash
Accounts receivable (net)
Inventory
Property, plant, and equipment (net)
Other non-current assets
Total assets
Current liabilities
Long-term debt (10%)
Share capital
Contributed surplus
Retained earnings
Total liabilities and shareholders' equity
Statement of Earnings
revenue (1/3 on credit)
Cost of sales
Expenses (including interest and income tax)
Net earnings
Accounts receivable (net)
Inventory
Long-term debt
Other data:
Share price year-end
Income tax rate
Dividends declared and paid
Shares Outstanding
Selected data from the financial statements for the previous year follows:
Blair
Company
Armstrong
Company
24,000
88,000
80,000
$ 44,000
40,000
80,000
Profitability ratios:
Ratio
Gross profit percentage
Profit margin
Earnings per share
Asset turnover ratios:
Fixed Asset turnover
Receivables turnover
Inventory turnover
Liquidity ratios:
Current ratio
Market tests:
$
Price/earnings ratio
Dividend yield ratio
$
$
%
18
30%
40,000
15,000
%
%
per share
times
times
times
Armstrong
Company
$
$ 35,400
36,000
The companies are in the same line of business and are direct competitors in a large metropolitan area. Both have been in business
approximately ten years, and each has had steady growth. The management of each has a different viewpoint in many respects. Blair
Company is more conservative, and as its president said, "We avoid what we consider to be undue risk." Neither company is publicly
held. Armstrong Company has an annual audit by an independent auditor, but Blair Company does not.
140,000
160,000
89,000
Required:
1. Complete a schedule that reflects a ratio analysis of each company. Use ending balances if average balances are not available.
(Round intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.)
HINT: To calculate Current Ratio, you will need to first calculate the total Current Assets.
Armstrong Company
Blair Company
$ 460,400
$ 110,000
80,000
158,000
34,000
78,400
$ 460,400
$ 490,000
(269,500)
(166,600)
$ 53,900
15
30%
$190,000
50,000
%
%
per share
$ 26,000
34,000
36,000
440,000
316,000
$ 852,000
times
times
times
$ 47,000
80,000
540,000
124,000
61,000
$ 852,000
%
$ 850,000
(425,000)
(323,000)
$ 102,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education