Question
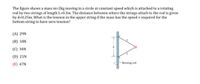
Transcribed Image Text:The figure shows a mass m-2kg moving in a circle at constant speed which is attached to a rotating
rod by two strings of length L=0.3m. The distance between where the strings attach to the rod is given
by d=0.25m. What is the tension in the upper string if the mass has the speed v required for the
bottom string to have zero tension?
(A) 29N
(B) 18N
(C) 34N
(D) 21N
(E) 47N
Rotating rod
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 1.01 kg mass is attached to a spring of force constant 10.4 N/cm and placed on a frictionless surface.By how much will the spring stretch if the mass moves along a circular path of radius 0.520 m at a rate of 1.82 revolutions per second?arrow_forwardAn object on the Earth has a center of gravity that is 6.0 cm above its base. If the same object was taken to the Moon, where the acceleration due to gravity is 1/6th the value on Earth, how far above the base (cm) would the center of gravity be? O 6.0 O 15 O 3.0 O 2.4 O 36 O 8.4 O 3.6 O 1.0arrow_forwardAn object of mass m; = 4.00 kg is tied to an object of mass m2 = 2.80 kg with String 1 of length e = 0.500 m. The combination is swung in a vertical circular path on a second string, String 2, of length e = 0.500 m. During the motion, the two strings are collinear at all times as shown in the figure. At the top of its motion, m, is traveling at v = 5.90 m/s. String 1 e String 2 (a) What is the tension in String 1 at this instant? (b) What is the tension in String 2 at this instant? N (c) Which string will break first if the combination is rotated faster and faster? O string 1 O string 2arrow_forward
- A tetherball is connected to the top of a pole with a rope that is 2.58m long and swings around the pole at an angle of θ = 33.4 degrees between the pole and the rope. Calculate the speed of the tetherball in meters/second, but only enter in the numerical value, do NOT enter units.arrow_forwardThe frame is made from uniform rod which has a mass p per unit length. A smooth recessed slot constrains the small rollers at A and B to travel horizontally. Force P is applied to the frame through a cable attached to an adjustable collar C. Determine the magnitudes and directions of the normal forces which act on the rollers if (a) h = 0.24L, (b) h = 0.50L, and (c) h = 0.91L. The forces will be positive if up, negative if down. Evaluate your results for p = 1.8 kg /m, L = 575 mm, and P = 48 N. What is the acceleration of the frame in each case? (a) Answers: (b) L (c) A h = 0.24L: h = 0.50L: h = 0.91L: L A = A A = B i i i P B N₁ B N, B N, i i N₁ª N,9 N₁9 i i m/s m/s m/sarrow_forwardSand moves without slipping at 6.0 m/sm/s down a conveyer that is tilted at 15∘∘. The sand enters a pipe hhh = 5.0 mm below the end of the conveyer belt, as shown in the figure (Figure 1).arrow_forward
- A speedboat with a mass of 545 kg545 kg (including the driver) is tethered to a fixed buoy by a strong 32.7 m32.7 m cable. The boat's owner loves high speed, but does not really want to go anywhere. So the owner revs up the boat's engine, makes a lot of noise, and runs the boat in circles around the buoy with the cable supplying all the necessary centripetal force. When the tension of the cable is steady at 13700 N,13700 N, with what force is the boat's engine pushing the boat? Different physics textbooks treat drag force somewhat differently and use different formulas. For the present purpose, take the water's drag force on the boat to be (450 kg/m)×?2,(450 kg/m)×v2, where ?v denotes the boat's speed. Ignore any drag force on the cable.arrow_forwardPlease Asaparrow_forwardA 250 g piece of kryptonite is attached to a 90 cm long masless string to form a pendulum. At its highest point (Point A) the string makes an angle of 55 degrees with the vertical. Its lowest point is Point B and Point C is where the string makes an angle of 35 degrees with respect to the vertical. Find the tension in the string and angular acceleration of the rock at (a) Point A, (b) Point B and (c) Point C. (a) Draw a free body diagran of the kryptonite, including all relevant angles and axes at Point A, Point B, and Point C. (Three total FBD) (b) Find the angular speed, angular acceleration and tension in the string at Point A. (c) Find the angular speed, angular acceleration, centripetal force and tension in the string at Point B. (d) Find the angular speed, angular acceleration, centripetal force and tension in the string at Point C.arrow_forward
- An object of mass m₁ = 4.00 kg is tied to an object of mass m₂ = 3.00 kg with String 1 of length 1 = 0.500 m. The combination is swung in a vertical circle on a second string, String 2, of length 1 = 0.500 m. During the motion, the two strings remain in line with one another as shown. At the top of its motion, m₂ is traveling at v = 4.00 m/s. a. Draw the force diagrams for both objects when at the top of the swing. 1 mi String 1 mo String 2 b. Given that m2 is traveling at v₂ = 4.00 m/s at the top, what must be the velocity of m₁ at this point? You should be able to reason it out.arrow_forward2. A 0.99 kg ball is connected by means of two ideal strings to a vertical, rotating rod. The strings are tied to the rod and are taut. The upper string is 24.0 cm long and has a tension of 30.3 N, and it makes an angle 02 = 65.0° with the rod, while the lower string makes an angle 01 N 52.0° with the rod. (a) What is the tension in the lower string? 60 ssf60 ssfo r60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssfóð 0, 60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf60 sf60 ssf60 ssf60 ssf6 160arrow_forwardA 0.900 kg rock is tied to a string and whirled in a vertical circle with a 0.85 m radius and a frequency of rotation of 1.6 Hz. Assuming a constant velocity, determine the tension in the rope at the bottom of the circle. Round up your answer to the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios