
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
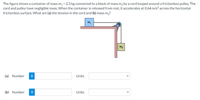
Transcribed Image Text:The figure shows a container of mass m1 = 2.3 kg connected toa block of mass m2 by a cord looped around a frictionless pulley. The
cord and pulley have negligible mass. When the container is released from rest, it accelerates at 0.64 m/s? across the horizontal
frictionless surface. What are (a) the tension in the cord and (b) mass m2?
(a) Number
Units
(b) Number
i
Units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are out on a hike and come across an unfortunate scene: a fellow hiker has fallen off a ledge. You happen to be carrying a long rope, and bravely decide to help. You tie the rope to a rock of mass mR=500 kgmR=500 kg and make your way over the ledge (see figure). If the coefficient of static friction between the rock and the ground is μS=0.355μS=0.355, and your mass is mH=70.5 kgmH=70.5 kg, what is the maximum mass of the fallen hiker (mFmF) that the rock can hold so that you two can make it back up from the ledge? Assume that where the rope passes the ledge is frictionless and that the rope is parallel to the ground.arrow_forwardSally wants to hang up some decorations on the side of her house, so she props up a ladder of length L = 3m against a wall at an angle of θ = 50° with respect to the horizontal. The ground is somewhat icy, where the coefficient of static friction between the ground and the ladder’s feet is µ = 0.55; while the wall of her house can be considered frictionless. If Sally has a mass of 60kg and the ladder has a mass of 80kg, what is the max distance that she can climb up the length of the ladder without it slipping? You may assume the ground is perfectly flat, and the wall is perpendicular to the ground.arrow_forwardm F 0 You are pressing a box against a sloped ceiling, perpendicular to the ceiling itself, as shown in the figure. The mass of the box is m=3.3 kg, the angle of the ceiling is 0=37°, and the coefficients of friction are μs-0.31 and μk=0.2. (a) What is the minimum force needed from you to keep the box at rest? N (b) Choosing up the sloping ceiling to be the positive direction, suppose you push with a force 4 N smaller than your answer to the previous part. What will be the acceleration of the box? m/s²arrow_forward
- Two constant forces act on an object of mass m = 4.30 kg object moving in the xy plane as shown in the figure below. Force F, is 26.5 N at 35.0°, and force F, is 48.0 N at 150°. At time t = 0, the object is at the origin and has velocity (3.50î + 2.15j) m/s. 150° 35.0° (a) Express the two forces in unit-vector notation. F, - N (b) Find the total force exerted on the object. N (c) Find the object's acceleration. m/s2 Now, consider the instant t = 3.00 s. (d) Find the object's velocity. m/s (e) Find its position. (f) Find its kinetic energy from V½mv2. kJ (g) Find its kinetic energy from 2mv,2 + EF · AF. kJarrow_forwardTwo horizontal forces, P and Q, are acting on a block that is placed on a table. We know that P is directed to the left but the direction of Q is unknown; it could either be directed to the right or to the left. The object moves along the x-axis. Assume there is no friction between the object and the table. Here P = -6.1 N and the mass of the block is 3.8 kg. P (a) What is the magnitudeand direction of Q (in N) when the block moves with constant velocity? (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) 6.1 N (b) What is the magnitude and direction of Q (in N) when the acceleration of the block is +7.5 m/s2. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) X 22.4 The acceleration given here is due to the net force acting on the object. N (c) Find the magnitude and direction of Q (in N) when the acceleration of the block is -7.5 m/s2. (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) X -34.6 What is the direction of motion of the object when the acceleration is…arrow_forwardA sphere of mass 1.5 × 10-4 kg is suspended from a cord.arrow_forward
- An empty pail and a 34 kg wooden mass are tied together by a very light string which passes over a massless and frictionless pulley. There is a force of friction between the mass and the table and there is a coefficient of static friction of 0.76 and a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.46. Water is added to the bucket one drop at a time until the system just begins to move. When the system just begins to move, what will the acceleration be? (Answer to 1 decimal place, use g = 9.8m/s2)arrow_forward(a) A flatbed truck moving at 28 m/s carries a steel girder that rests on its wooden floor. The girder is not strapped down, in violation with USDOT regulations. If the coefficient of static friction between steel and wood is 0.52, what is the minimum distance over which the truck can come to a stop without the girder sliding toward the cab of the truck? (answer: 77 m) (b) What is the minimum time over which the truck can accelerate forward from 0 m/s to 28 m/s with a constant acceleration without the girder sliding off the back? (answer: 5.5 s) FNET = ma fs.max = μsn W = mg v² = v₁² + 2aAx V = Vo+ at g=9.81 m/s²arrow_forwardA stacked pair of books with masses m1= 2.0 kg (bottom book) and m2 = 1.5 kg (top book) are tossed onto a table. The books strike the table with no vertical velocity and their common horizontal speed is ?o = 0.75 m/s. The kinetic friction coefficient between the bottom book and the table is ?k1=0.45; the kinetic and static friction coefficients between the two books are ?k2=0.3 and ?s2= 0.4. Find the final horizontal position of each book relative to the spot where the stack hits the table.arrow_forward
- Tarzan, who weighs 777 N, swings from a cliff at the end of a 16.5 m vine that hangs from a high tree limb and initially makes an angle of 21.9° with the vertical. Assume that an x axis points horizontally away from the cliff edge and a y axis extends upward. Immediately after Tarzan steps off the cliff, the tension in the vine is 721 N. Just then, what are (a) the force from the vine on Tarzan in unit-vector notation, and (b) the net force acting on Tarzan in unit-vector notation? What are (c) the magnitude and (d) the direction (measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis) of the net force acting on Tarzan? What are (e) the magnitude and (f) the direction of Tarzan's acceleration just then?arrow_forwardThe figure shows a container of mass m₁ = 1.7 kg connected to a block of mass m₂ by a cord looped around a frictionless pulley. The cord and pulley have negligible mass. When the container is released from rest, it accelerates at 1.0 m/s² across the horizontal frictionless surface. What are (a) the tension in the cord and (b) mass m₂? (a) Number (b) Number i Units Units m₁ mq >arrow_forwarda 1.34 kg ball is connected by means of two massless strings, each of length L = 1.70 m, to a vertical, rotating rod. The strings are tied to the rod with separation d = 1.70 m and are taut. The tension in the upper string is 35 N. What are the (a) tension in the lower string, (b) magnitude of the net force on the ball, and (c) speed of the ball? (d) What is the direction of the net force?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON