
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
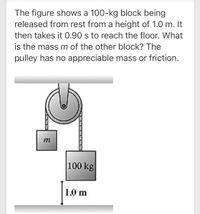
Transcribed Image Text:The figure shows a 100-kg block being
released from rest from a height of 1.0 m. It
then takes it 0.90 s to reach the floor. What
is the massm of the other block? The
pulley has no appreciable mass or friction.
m
100 kg
1.0 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If you push a box across the floor its "physics work" but if you push on the wall it's not. Which of the following choices best explains why? Question 12 options: The direction of the force on the box is not the same direction as the motion. You're applying a force to the box but you are not applying a force to the wall. You're not applying a force to the box but you are applying a force to the wall. The box is moving but the wall is not.arrow_forwardIn the figure, two blocks are connected over a pulley. The mass of block A is 14.0 kg and the coefficient of kinetic friction between A and the incline is 0.140. Angle 0 of the incline is 42.0°. Block A slides down the incline at constant speed. What is the mass of block B? Frictionless, massless pulley A B Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA stockroom worker pushes a box with mass 11.6 kg on a horizontal surface with a constant speed of 3.40 m/s. The coefficient of kinetic Part A friction between the box and the surface is 0.21. What horizontal force must the worker apply to maintain the motion? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA ? F = Value Units Submit Request Answerarrow_forward
- Below are six crates at rest on level surfaces. The crates have different masses and the frictional coefficients between the crates and the surfaces differ. The same external force is applied to each crate, but none of the crates move. Rank the crates on the basis of the frictional force acting on them. Largest to smallestarrow_forwardThe figure shows the configuration of two identical bricks. In case 1 the bricks are placed end to end. In case 2 the bricks are stack on top of each other. What can you say about the kinetic friction when the bricks are pushed across a tabletop with constant speed?arrow_forwardThe diagram shows all the forces on an object with mass m = magnitude of the acceleration of the object? 89 kg. What is the 480 N Select one: O 9.4 m/s? 30° O 6.0 m/s? 3.0 m/s? 120 N O 4.5 m/s sine and cosine reversed. Check that you didn't get 11.5 m/s? 240 Narrow_forward
- Power As shown in the picture below, you and a friend are pushing a box horizontally. You can assume that you and your friend are both pushing completely horizontally in this case. Your combined push force (from you and your friend) is Push = 46.0 N. The box has a mass of 20.0 kg. You and your friend push the box a horizontal distance of 6.50 m. There is a force of friction between the ground and the box with a value of f = 28.0 N. Assume that initially the box is at rest when you and your friend start pushing it. What is the rate at which all of the forces do work on the box? This is another way of asking about Power. You'll need acceleration to find the time - but you have enough information to calculate the acceleration. Motion Воx Your answer should include the following: 2 Decimal Places Correct SI Units Appropriate sign (only needed for negative answers) Answers must be in the following format: Written out and NOT in scientific notation Acceptable: 278.40 Not Acceptable: 2.784 x…arrow_forwardThe two masses shown in the figure are each initially 1.8 m above the ground, and the massless frictionless pulley is 4.8 m above the ground. 1.8 m 4.8 m 2.2 kg 3.6 kgarrow_forwardved 161 A single cable is wrapped from the center of pulley A, around pulley B, and around pulley A. This cable is pulled downward at 2 m/s. At what speed does pulley B move upward? V = 1 S L= take a time derivitive 0-2 VAB+ VAC dB C WEIGHT 2 m/s dearrow_forward
- Multiple-object systems without friction: The figure shows a 100-kg block being released from rest from a height of 1.0 m. It then takes it 0.90's to reach the floor. What is the mass m of the other block? The pulley has no appreciable mass or friction. (60 kg) m ------- 100 kg 1.0 marrow_forwardAfter being release from rest, the objects move. When the blocks have moved 1 meter, calculate the speed of the blocks. 2.6 m/s 1.7 m/s 4.4 m/s 2.9 m/s 3.6 m/sarrow_forwardA 1490 N crate is resting on a table connected to a 400 N block through a frictionless pulley system as shown. Friction between the crate and the table is enough to keep the system at rest. The arrows show the forces that act on the crate and the block.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON