
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
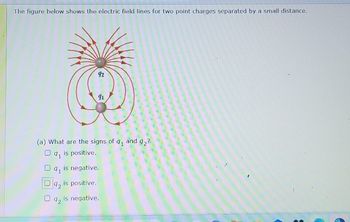
Transcribed Image Text:The figure below shows the electric field lines for two point charges separated by a small distance.
91
(a) What are the signs of q₁ and 92?
is positive.
92
91
Oq2 is positive.
92
91
is negative.
is negative.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. In the figure below, three hollow, concentric spherical conductors are charged as follows: The inner sphere carries a charge +4Q, the middle sphere carries a charge -20. and the outer sphere carries a charge +6Q. What is the charge on the outer surface of the middle sphere? Outer sphere (A) Zero (C) +4Q (E) +2Q (B)-Q (D)-2Q Middle sphere field at a point that is 0.50 m from the center of the sphere is 15x10' N/C and is directed 6. Electric charge is uniformly distributed inside a sphere of radius 0.30 m. The electric radially outward. The maximum magnitude of the electric field in N/C is: +++++ R (A) 25x10 (B) 20x10' (C) 36x10 (D) 42x10² (E) 48x10 7. Electrically neutral objects cannot exert an electrical force on each other, but they can exert a gravitational force on each other. A) True B) False 8. A charge of uniform volume density (40 nC/m3) fills a cube with 8.0-cm edges. What is the total electric flux through the surfaces of this cube in (N.m²/C)? (A) 2.9 (B) 2.0 (C) 2.6 (D)…arrow_forward1. Three identical metallic conducting spheres carry the following charges: 91 = +5.00 μC, q2 = +1.40 µC, and 93 -9.20 μC. The spheres that carry the charges 9₁ and 92 are brought into contact. Then they are separated. After that, one of those two spheres is brought into contact with the third sphere that carries the charge 93; those two are then separated as well. ROJS a) What is the final charge on the third sphere?60 SS μC sf60 s60 s ssf60 ssfo ssf603 60 ssf60 ssiarrow_forward03. The distance between two charges q1 = + 2 μC and q2 = + 6 μC is 15.0 cm. Calculate the distance from charge q1 to the points on the line segment joining the two charges where the electric field is zero. Express your answer in cm with 3 - significant figures.arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON