
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Determine:
(a) the magnitude of the pump power, in kW.
Wev
CV
kW
(b) the mass flow rate of steam, in kg/s, that flows through the turbine.
m3
=
kg/s
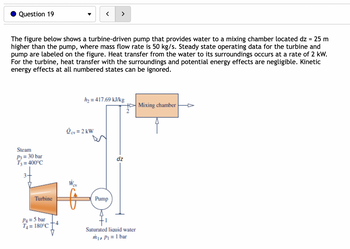
Transcribed Image Text:Question 19
The figure below shows a turbine-driven pump that provides water to a mixing chamber located dz = 25 m
higher than the pump, where mass flow rate is 50 kg/s. Steady state operating data for the turbine and
pump are labeled on the figure. Heat transfer from the water to its surroundings occurs at a rate of 2 kW.
For the turbine, heat transfer with the surroundings and potential energy effects are negligible. Kinetic
energy effects at all numbered states can be ignored.
Steam
P3 = 30 bar
T3 = 400°C
3
Turbine
▼
P4= 5 bar
T₁ = 180°C
h₂ = 417.69 kJ/kg
Ocv = 2 kW
Pump
dz
+Mixing chamber
Saturated liquid water
m₁, P₁ = 1 bar
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Determine:
(a) the magnitude of the pump power, in kW.
Wev
= 23.7625
x KW
(b) the mass flow rate of steam, in kg/s, that flows through the turbine.
m3
0.0589275
x kg/s
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Determine:
(a) the magnitude of the pump power, in kW.
Wev
= 23.7625
x KW
(b) the mass flow rate of steam, in kg/s, that flows through the turbine.
m3
0.0589275
x kg/s
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An oil pump operating at steady state delivers oil at a rate of 10 lb/s through a 1-in.-diameter exit pipe. The oil, which can be modeled as incompressible, has a density of 70 lb/ft3 and experiences a pressure rise from inlet to exit of 40 lb/in². There is no significant elevation difference between inlet and exit, and the inlet kinetic energy is negligible. Heat transfer between the pump and its surroundings is negligible, and there is no significant change in temperature as the oil passes through the pump. Determine the velocity of the oil at the exit of the pump, in ft/s, and the power required for the pump, in hp. Determine the power required for the pump, in hp.arrow_forwardLooking for velocity at the exit and mass flow rate. Show step by step solution please thank youuarrow_forward12arrow_forward
- T-12arrow_forwardThe figure shows data for a portion of the ducting in a ventilation system operating at steady state. The ducts are well insulated and the pressure is very nearly 1 atm throughout. The volumetric flow rate entering at state 2 is AV₂2 = 4400 ft3/min. Assume the ideal gas model for air with cp = 0.24 Btu/lb-ºR and ignore kinetic and potential energy effects. 1 (AV)1 = 5000 ft³/min T₁ = 80°F (AV)₂ T₂ = 40°F ft³/min Air, Cp=0.24 Btu/lb R p=1 atm -Insulation 3 V3=400 ft/min T3 = ? Determine the temperature of the air at the exit, in °F, and the rate of entropy production within the ducts, in Btu/min.°R.arrow_forwardIn an air conditioning system running at steady-state, m ̇ = 0.7 kg/s of refrigerant 3 134a in saturated liquid state at 48◦C flow through a throttling valve reducing its pressure to a value of p4 = 4 bars. The system is shown in Fig. 1. Then the refrigerant flows through the internal side of a heat exchanger exiting at saturated vapor with p5 = p4. Air enters the external side of the heat exchanger at T1 = 300 K and exits at T2 = 295 K moved by a fan ̇ Figure 1: Problem 1 that consumes WCV = 0.15 kW. Determine the mass flow rate of the air, in kg/sarrow_forward
- Q. The velocity of steam leaving a nozzle of Turbine is 896 m/s and the nozzle angle is 20°. The blade velocity is 300 m/s and the blade coefficient is 0.79. Assuming the mass flow rate as 1 kg/s and the runner blades are symmetric. Determine the power developed in kWarrow_forwardThermodynamicsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY