
Concept explainers
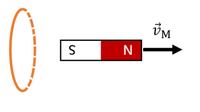
The figure below shows a ring whose plane is perpendicular to your screen (the dashed parts are behind the screen and the solid parts are in front of the screen). A bar magnet is moved away from the ring in the direction show with vM .
Choose the correct direction for external flux through the ring (\PhiΦ), the change in external flux through the ring (\Delta\PhiΔΦ) and the direction of the induced magnetic field (B_{ind}Bind) caused by the current induced in the ring.
a.Φ: right
\Delta\PhiΔΦ: increasing (or pointing right)
B_{ind}Bind: right
B.\PhiΦ: right
\Delta\PhiΔΦ: increasing (or pointing right)
B_{ind}Bind: left
C.\PhiΦ: right
\Delta\PhiΔΦ: decreasing (or pointing left)
B_{ind}Bind: right
D.\PhiΦ: left
\Delta\PhiΔΦ: decreasing (or pointing right)
B_{ind}Bind: right
E.\PhiΦ: left
\Delta\PhiΔΦ: decreasing (or pointing right)
B_{ind}Bind: left
F\PhiΦ: right
\Delta\PhiΔΦ: decreasing (or pointing left)
B_{ind}Bind: left
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- Following conventional current flow, what would be the direction of the induced magnetic field and the direction of the current for the two situations, a) right after the switch is closed b) the switch has been closed for a long time and now right after the switch has been opened? See figure below. The figure on the left is a battery connected to a coil. The figure on the right is a coil connected to an amp meter. Determine which direction the amp meter shows current for each situation.arrow_forward(a) Find the magnetic field at the center of a square loop, which carries a steady current I. Let R be the distance from center to side. (b) Find the magnetic field at point P for the steady current configurations shown in the Figure below. Rarrow_forwardA loop of wire in the shape of a rectangle of width w and length L and a long, straight wire carrying a current I lie on a tabletop as shown in the figure below. (a) Determine the magnetic flux through the loop due to the current I. (Use any variable stated above along with the following as necessary: Mo.) ФВ (b) Suppose the current is changing with time according to I = a + bt, where a and b are constants. Determine the magnitude of the emf (in V) that is induced in the loop if b = 20.0 A/s, h = 1.00 cm, w = 20.0 cm, and L = 1.20 m. v (c) What is the direction of the induced current in the rectangle? O clockwise O counterclockwise O The magnitude is zero. What If? Suppose a constant current of I = 6.00 A flows in the straight wire and the loop moves from an initial position ho = 1.00 cm toward the bottom of the figure at a constant speed of v = 16.0 cm/s. (d) What is the magnitude of the induced emf (in V) in the loop 1.00 s after it begins to move? V (e) What is the direction of the…arrow_forward
- Show all your calculations while explaining why you do each step.An electron enters a region of uniform 0.10T magnetic field (into the page) with a kinetic energy of 100 keV. Can you calculate the radius of the curved path that it will take? (And include a diagram that shows which way the path curves).arrow_forwardA loop of wire in the shape of a rectangle of width w and length L and a long, straight wire carrying a current I lie on a tabletop as shown in the figure below. (a) Determine the magnetic flux through the loop due to the current I. (Use any variable stated above along with the following as necessary: H. and r.) (b) Suppose the current is changing with time according to I = a + bt, where a and b are constants. Determine the magnitude of the emf that is induced in the loop if b = 17.0 A/s, h = 1.00 cm, w = 19.0 cm, and L = 1.25 m. V (c) What is the direction of the induced current in the rectangle? O clockwise O counterclockwise O The magnitude is zero.arrow_forwardDon't use chatgptarrow_forward
- An aluminum rod with a mass m slides on parallel horizontal brass rails, a distance L apart, and carries a current of I. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the rod and rails is ?. What vertical, uniform magnetic field is needed to keep the rod moving at a constant speed? (Enter the magnitude. Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: g.)arrow_forwardA square loop (each side is 10 cm) of wire with Resistance 100Ω is moved at a constant speed of 30cm/s across a uniform magnetic field 2 T, confined in a square region (Each side of the square is 20cm). (a) Graph the force needed to move the loop at a constant speed from -20 cm to 20cm (as shown in the figure). What will be the maximum force required? Assume that the force pointing to the right as positive (b) Graph the current induced in the loop as a function of distance from -20cm to 20cm. Assume clockwise current to be positive. What will be the maximum value of current? Hint: The figure is drawn not to scalearrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





