
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Find the momentum of the propellant gases in a coordinate system attached to the earth as they leave the muzzle of the rifle. p=

Transcribed Image Text:The expanding gases that leave the muzzle of a rifle also
contribute to the recoil. A.30 caliber bullet has mass
7.20×10-³ kg and a speed of 601 m/s relative to the muzzle
when fired from a rifle that has mass 3.00 kg . The loosely
held rifle recoils at a speed of 2.05 m/s relative to the earth.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
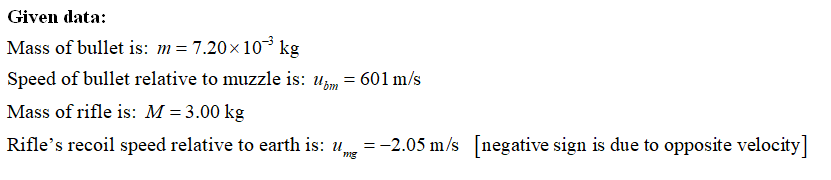
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For a ballistic pendulum, if the length L = 1.64 meter, angle of deflection from vertical θ = 20.8 degree, the mass of the bullet m = 12.1 gram, and the mass of the catcher M = 646 gram, the velocity (m/s) of the bullet isarrow_forwardAn object, with mass 88 kg and speed 18 m/s relative to an observer, explodes into two pieces, one 4 times as massive as the other; the explosion takes place in deep space. The less massive piece stops relative to the observer. How much kinetic energy is added to the system during the explosion, as measured in the observer's reference frame?arrow_forwardAn object has a kinetic energy of 310 J and a momentum of magnitude 28.1 kg · m/s. (a) Find the speed of the object.(b) Find the mass of the object.arrow_forward
- A ball with a mass of 275 g is dropped from rest, hits the floor and rebounds upward. If the ball hits the floor with a speed of 3.50 m/s and rebounds with a speed of 1.50 m/s, determine the following. (a) Magnitude of the change in the ball's momentum in kg · m/s (Let up be in the positive direction.) (b) Change in the magnitude of the ball's momentum in kg · m/s (Let negative values indicate a decrease in magnitude.) (c) Which of the two quantities calculated in parts (a) and (b) is more directly related to the net force acting on the ball during its collision with the floor? 1. The magnitude of the change in the ball's momentum2. Neither are related to the net force acting on the ball. 3. They both are equally related to the net force acting on the ball.4. The change in the magnitude of the ball's momentumarrow_forwardProblem 9: A baseball of mass mj = 0.39 kg is thrown at another ball hanging from the ceiling by a length of string L = 1.35 m. The second ball m2 = 0.79 kg is initially at rest while the baseball has an initial horizontal velocity of V, = 3.5 m/s. After the collision the first baseball falls straight down (no horizontal velocity). Randomized Variables V, m1 = 0.39 kg m2 = 0.79 kg L= 1.35 m V1 = 3.5 m/s m, m,arrow_forwardNeeds Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forward
- An object A moving with velocity v collides with a stationary object B. After the collision, A is moving with velocity 2 1 v and B with velocity 3 2 v. Find the ratio of their masses. If, instead of bouncing apart, the two bodies stuck together after the collision, with what velocity would they then move?arrow_forwardA ball of mass 179 g is thrown with an initial velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 30° with the horizontal direction. Ignore air resistance. What is the momentum of the ball after 0.8 s? (Do this problem by finding the components of the momentum first and then constructing the magnitude and direction of the momentum vector from the components. Find the magnitude in kg · m/s and the direction in degrees counterclockwise from the +x-axis. Assume the +x-axis points horizontally to the right.) magnitude _____ kg · m/s direction ______ ° counterclockwise from the +x-axisarrow_forwardA ball of mass 191 g is thrown with an initial velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 30° with the horizontal direction. Ignore air resistance. What is the momentum of the ball after 0.6 s? (Do this problem by finding the components of the momentum first and then constructing the magnitude and direction of the momentum vector from the components. Find the magnitude in kg · m/s and the direction in degrees counterclockwise from the +x-axis. Assume the +x-axis points horizontally to the right.) V = (25 m/s)û 30° magnitude kg · m/s direction ° counterclockwise from the +x-axisarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON