
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
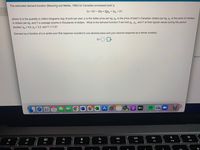
Transcribed Image Text:The estimated demand function (Moschini and Meilke, 1992) for Canadian processed pork is
Q = 161 - 20p + 20p, + 3pc + 2Y,
where Q is the quantity in million kilograms (kg) of pork per year, p is the dollar price per kg, p, is the price of beef in Canadian dollars per kg, Pe is the price of chicken
in dollars per kg, and Y is average income in thousands of dollars. What is the demand function if we hold ph, Per and Y at their typical values during the period
studied: ph = 4.6, p. = 3.2, and Y = 11.5?
Demand as a function of p is (enter your first response rounded to one decimal place and your second response as a whole number):
Incor
tv
30
MacBook Ai
DII
80
F9
F10
F11
F6
F7
F8
FI
F2
F3
F4
F5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose the demand function for a product is given by the function: D(q) = -0.018q+50.4 Find the Consumer's Surplus corresponding to q = 1,550 units. (Do no rounding of results until the very end of your calculations. At that point, round to the nearest tenth, if necessary. It may help you to sketch the demand curve, which crosses the horizontal at q = 2,800.) dollars Answer:arrow_forwardExample 2: In fall of 2011, the National Christmas Tree Association decided to impose a fee/tax of $0.15 per tree sold.² They claimed the tax revenue raised would fund a new marketing campaign for Christmas tree growers in response to growing plastic tree imports. The proposal quickly drew controversy: some argued that the fee/tax would be passed along in higher prices to consumers, but the National Christmas Tree Association says no. How does the answer to this question depend on the assumption about the price elasticity of demand? a. Consider two graphs of the market for Christmas trees. The supply curve in each market is assumed to be the same. In the left graph, assume the price elasticity of demand is relatively inelastic and in the right graph, assume the price elasticity of demand is relatively elastic. Add labels on your diagram to identify the equilibrium price and quantity of trees before the tax. b. Now, suppose retailers are assessed a tax of amount for each tree sold.…arrow_forwardThe coconut oil demand function (Bushena and Perloff, 1991) is Q=1,200-9.5p+16.2pp +0.2Y, where Q is the quantity of coconut oil demanded in thousands of metric tons per year, p is the price of coconut oil in cents per pound, pp is the price of palm oil in cents per pound, and Y is the income of consumers. Assume that p is initially 65 cents per pound, p, is 31 cents per pound, and Q is 1,275 thousand metric tons per year. Calculate the price elasticity of demand for coconut oil and the cross-price elasticity of demand (with respect to the price of palm oil). The price elasticity of demand is (Enter your response rounded to three decimal places and include a minus sign.) e=arrow_forward
- The coconut oil demand function (Buschena and Perloff, 1991) is Q = 1,200 -9.5p + 16.2pp +0.2Y, where Q is the quantity of coconut oil demanded in thousands of metric tons per year, p is the price of coconut oil in cents per pound, pp is the price of palm oil in cents per pound, and Y is the income of consumers. Assume that p is initially 45¢ per pound, pp is 31¢ per pound, and Q is 1,322 thousand metric tons per year. Calculate the income elasticity of demand for coconut oil. The income elasticity of demand for coconut oil is (Enter a numeric response using a real number rounded to three decimal places.)arrow_forwardThe domestic demand (Qpp) for wheat in the United States is estimated to be QDD=1430-55P, where the quantity of wheat is measured in millions of bushels per year. Suppose China also demands U.S. wheat (Qpc) and that its demand is given by QDc=1920-60P. What is the total demand for U.S. wheat, assuming the only two sources of demand are domestic and Chinese? The total demand for U.S. wheat is OA. Qp =3350-115P for all P. O B. Q =3350-115P for P≤ $26 and Qp = 1920-60P for P> $26. OC. Q=1920-60P for all P. O D. Q =3350-115P for P ≤ $32 and Qp =1430-55P for P> $32 E. Q =3350-115P for P≤ $26 and Qp =1430-55P for P> $26.arrow_forwardThe coconut oil demand function (Buschena and Perloff, 1991) is Q = 1,200 - 9.5p + 16.2 pp + 0.2Y, where Q is the quantity of coconut oil demanded in thousands of metric tons per year, p is the price of coconut oil in cents per pound, Pp is the price of palm oil in cents per pound, and Y is the income of consumers. Assume that p is initially 45 ¢ per pound, Pp is 31 ¢ per pound, and Q is 1,275 thousand metric tons per year. Calculate the income elasticity of demand for coconut oil. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- M8arrow_forwardSuppose that the inverse demand curve for a product is given by: P = 100-Qd+ 2M, where M is the average income in 1000 USD. The inverse supply is P = 0.5Q - 20. If M = 15 the equilibrium price is equal to and the equilibrium quantity is equal to 40, 60 100,30 30,100 60.40arrow_forwardSuppose consumers will demand 40 units of a product when the price is RM12.75 per unit and 25 units when the price is RM18.75 each. Find: The demand function. i) ii) 1) iv) Price per unit when 37 units are demanded Quantity (units) demanded when the price is RM20.00. The equilibrium point if the supply equation is p = q - 0.75arrow_forward
- You are an economist for the City Subway Commission. Presently, the price of a subway ride is 80 cents, and 250000 seats are filled weekly. The price elasticity of demand for subway rides is -0.40, and the income elasticity of demand is -0.60. (A) If a recession lowered area incomes by 5%, how many additional seats per week would the subway need?arrow_forwardAssume that the demand curve D(p) given below is the market demand for widgets: Q = D(p) = 1183-12p, p > 0 Let the market supply of widgets be given by: Q = S(p) = -5 + 10p, p > 0 where p is the price and Q is the quantity. The functions D(p) and S(p) give the number of widgets demanded and supplied at a given price. What is the equilibrium price? Please round your answer to the nearest hundredth. What is the equilibrium quantity? Please round your answer to the nearest integer. What is the total revenue at equilibrium? Please round your answer to the nearest integerarrow_forwardGasoline for cars is produced in a market. There are equations for the Supply and Inverse Demand of car gasoline that model its Supply and Demand graph. These equations are (for supply), P = 20 + Qs, and (for Inverse Demand), P = 80 - Qd. Due to gasoline shortages, some sellers may be able to get access to more gasoline and produce it better than others. As a result, the federal government placed a quantity restriction of 15 units on the sellers. (Part I) Draw the market equilibrium with the government intervention (Q** and P**) of the quantity restriction. Please label the graph for slopes, the equilibrium point, etc. (Part II) What is the market equilibrium without the intervention of the government? (Part III) The government decided that the previous quantity restriction was not sufficient. So, it increased the restriction from 15 units to 20 units. Consequently, what is the new market equilibrium point with this new intervention? It is not necessary to label this point on the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education