
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
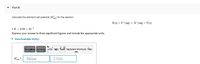
Transcribed Image Text:Part B
Calculate the standard cell potential (E) for the reaction
X(s) + Y*(ag) = X*(ag) + Y(s)
if K = 2.03 x 10
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
> View Available Hint(s)
Pesat
Tempjates Symbols undo redo fesél keyboard shortcuts Help
Value
Units
"cell
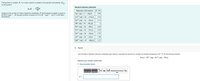
Transcribed Image Text:The equilibrium constant, K, for a redox reaction is related to the standard cell potential, E.
by the equation
Standard reduction potentials
In K
Reduction half-reaction E (V)
Ag (ag) +e
where n is the number of moles of electrons transferred, F (the Faraday's constant) is equal to
98 500 C mol-. R (the gas constant) is equal to 8.314JK
temperature.
+Ag(s)
0.80
and T is the Kelvin
Cu2+ (ag) + 2e-Cu(s)
0.34
Sn+ (ag) + de-→Sn(s)
0.15
2H*(ag) + 2e+H2(g)
Ni+ (ag) + 2e-→Ni(s)
-0.26
Fe2+ (ag) + 20FE(s)
-0.45
Zn2+ (ag) + 2e-+Zn(s)
-0.78
Al3+ (ag) + 3e +Al(s)
-1.66
Mg+ (ag) + 2e →Mg(s) -2.37
• Part A
Use the table of standard reduction potentials given above to calculate the equilibrium constant at standard temperature (25 °C) for the following reaction:
Fe(s) + Ni*+ (ag)→Fe* (ag) + Ni(s)
Express your answer numerically.
> View Available Hint(s)
Templates SymBols undo rego fese keyboard shortcuts help
K =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the cell shown, the measured cell potential, Ecell, is –0.3525 V at 25 °C. Pt(s) | H, (g, 0.851 atm) | H* (aq, ? M) || Cd²+(aq, 1.00 M) | Cd(s) The balanced reduction half-reactions for the cell, and their respective standard reduction potential values, E°, are 2 H* (аq) + 2е H, (g) E° = 0.00 V Cd²+(aq) + 2 e¯ → Cd(s) E° = -0.403 V Calculate the H+ concentration. [H*] =arrow_forwardThe measured cell potential, Ecell, for the cell shown is –0.3549 V at 25 °C. Calculate the Ht concentration. Pt(s) | H, (g, 0.807 bar) | H*(aq, ? M) || Cď²+(aq, 1.00 M) | Cd(s) The balanced reduction half-reactions for the cell and their respective standard reduction potential values, E", are given. 2 H*(aq) + 2 e- Cd2+ (aq) + 2 e- E' = 0.00 V E° = -0.403 V H, (g) Cd(s) %3D [H*] = Marrow_forwardConsider the electrochemical cell reaction of hydrogen gas and chlorine gas to produce 1 mol of HCI in aqueous solution. The molar reaction entropy change is A,S = - 120.6 J K-¹ mol-¹. At 298.15 K the standard cell potential is measured as 1.3583 V. Calculate the cell potential at 482.82 K to 5 sig. fig.arrow_forward
- For the cell shown, the measured cell potential, Ecell, is –0.3521 V at 25 °C. Pt(s) | H,(g, 0.785 atm) | H* (aq, ? M) || Cd²*(aq, 1.00 M) | Cd(s) The balanced reduction half-reactions for the cell, and their respective standard reduction potential values, E°, are 2H* (aq) + 2e- - H, (g) E° = 0.00 V Cd²* (aq) + 2e" - Cd(s) E° = -0.403 V Calculate the H* concentration. [H*] = Marrow_forwardThe net ionic cell reaction for the 'Bunsen cell ' is Zn(s) +2 NO3-(aq) + 4 H+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + 2 H2O(I) + 2 NO2(g). Thestandard cell potential at 25 °C is -0.04 V. Calculate the electricalwork that can be done by the cell.arrow_forwardAn aqueous ScCl3 solution is electrolyzed under 1 bar pressure using platinum electrodes.(a) Write the half-reactions predicted to occur at the anode and cathode, based on the standard cell potentials given below. Standard Reduction Potentials (Volts) at 25 °C Cl2(g) + 2 e- 2 Cl-(aq) 1.360 O2(g) + 4 H3O+(aq) + 4 e- 6 H2O(l) 1.229 2 H2O(l) + 2 e- H2(g) + 2 OH-(aq) -0.828 Sc3+(aq) + 3 e- Sc(s) -2.080 Half-reaction at anode: + + --> + + Half-reaction at cathode: + + --> + + (b) What is the expected decomposition potential? ________Varrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution .....arrow_forwardConsider the following table of standard electrode potentials Standard Electrode Potentials at 25 °C Reduction Half-Reaction E" (V) Au" (ag) + Зе Ag"(aq) + Fe* (aq) + 3e Sn²(aq) v*(aq) + 3e In"(ag) + 3e Eu" (ag) + 3e Cr* (aq) Тa" (ag) + Зе Zn*(aq) Nb* (aq) » Au(s) 1.50 e Ag(s) 0.80 » Fe(s) -0.04 + 2e » Sn(s) -0.14 » V(s) -0.26 » In(s) -0.34 » Eu(s) -0.35 + 3e » Cr(s) -0.42 » Ta(s) -0.60 » Zn(s) » Nb(s) → Ti(s) → Al(s) » Be(s) + 2e -0.76 + 3e -1.10 Ti (aq) + 2e Al" (aq) + 3e Ве (ag) + 2е Am* (ag) + 2e -1.63 -1.66 -1.85 » Am(s) -1.90 Pr* (ag) + 2e" » Pr(s) -2.00 Mg* (aq) + 20 - Mg(s) » Na(s) » Ca(s) -2.37 Na (aq) + Ca*(aq) Sr* (aq) + 2e Ba (aq) e -2.71 2e - 2.87 » Sr(s) -2.90 + 2e + Ba(s) -2.91arrow_forwardA galvanic cell Mn(s)|Mn2+(aq) || Pb2+(aq)|Pb(s) is constructed using a completely immersed Mn electrode that weighs 34.9 g and a Pb electrode immersed in 532 mL of 1.00 M Pb2+(ag) solution. A steady current of 0.0519 A is drawn from the cell as the electrons move from the Mn electrode to the Pb electrode. (a) Which reactant is the limiting reactant in this cell? Enter symbol (b) How long does it take for the cell to be completely discharged? (c) How much mass has the Pb electrode gained when the cell is completely discharged? g (d) What is the concentration of the Pb2+(aq) when the cell is completely discharged? (Assume that the limiting reactant is 100% reacted.) Marrow_forward
- Payalbenarrow_forwardA much-studied cell in electrochemistry has the following cell notation: Ag(s) | AgCI(s) || HCl(aq) | H2(g) | Pt(s) Bearing in mind that HCl(aq) consists of H*(aq) and Cl'(aq), and that this solution is in contact with both electrodes (there is no salt bridge), write down balanced equations for 3. a) the anode half-reaction. b) the cathode half-reaction. c) the cell reaction.arrow_forwardFor the cell shown, the measured cell potential, Ecell, is -0.3587 V at 25 °C. Pt(s) | H, (g, 0.839 atm) | H* (aq, ? M) || Cd²+(aq, 1.00 M) | Cd(s) The balanced reduction half-reactions for the cell, and their respective standard reduction potential values, E°, are 2 H* (aq) + 2 e H, (g) E° = 0.00 V Cd2+ (aq) + 2 e Cd(s) E° = -0.403 V Calculate the Ht concentration. [H*] = %3D rIC ho C TV OLER EEDO DCD 24 4/2 DELL PrtScr Insert Home End F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 F4 F5 F6 F7arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY