
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
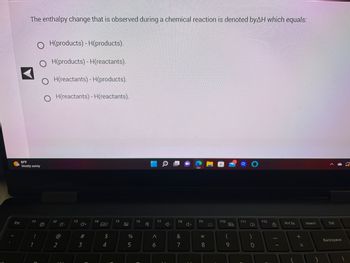
Transcribed Image Text:**Understanding Enthalpy Change in Chemical Reactions**
The enthalpy change observed during a chemical reaction is denoted by ΔH, which equals:
- ○ H(products) - H(products)
- ○ H(products) - H(reactants)
- ○ H(reactants) - H(products)
- ○ H(reactants) - H(reactants)
**Explanation:**
The concept of enthalpy change (ΔH) in a chemical reaction is crucial for understanding energy flow. Enthalpy measures the total heat content of a system, and changes occur when reactants are converted into products. To calculate the enthalpy change, subtract the enthalpy of the reactants from that of the products:
ΔH = H(products) - H(reactants)
This calculation helps determine if a reaction is exothermic (releases heat) or endothermic (absorbs heat).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Air in an inflated balloon (system) is cooled and loses 203. J of heat. The surroundings also compress it, doing 79.8 J of work. What is the change in internal energy for the system?arrow_forwardience ChemistryQ&A Libraryn the laboratory a "coffee cup" calorimeter, or constant pressure calorimeter, is frequently used to determine the specific heat of a solid, or to measure the energy of a solution phase reaction. A student heats 62.86 grams of copper to 97.81 °C and then drops it into a cup containing 84.35 grams of water at 23.05 °C. She measures the final temperature to be 28.02 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (sometimes referred to as the calorimeter constant) was determined in a separate experiment to be 1.77 J/°C. Assuming that no heat is lost to the surroundings calculate the specific heat of copper. Specific Heat (Cu) = ___________J/g °C n the laboratory a "coffee cup" calorimeter, or constant pressure calorimeter, is frequently used to determine the specific heat of a solid, or to measure the energy of a solution phase reaction. A student heats 62.86 grams of copper to 97.81 °C and then drops it into a cup containing 84.35 grams of water at 23.05 °C.…arrow_forwardfor this question. In the laboratory a "coffee cup" calorimeter, or constant pressure calorimeter, is frequently used to determine the specific heat of a solid, or to measure the energy of a solution phase reaction. Thermometer Stirring rod Since the cup itself can absorb energy, a separate experiment is needed to determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter. This is known as calibrating the calorimeter and the value determined is called the calorimeter constant. One way to do this is to use a common metal of known heat capacity. In the laboratory a student heats 93.58 grams of nickel to 99.47 °C and then drops it into a cup containing 82.02 grams of water at 21.76 °C. She measures the final temperature to be 30.12 °C. Using the accepted value for the specific heat of nickel (See the References tool), calculate the calorimeter constant. Metal sample Cole Calorimeter Constant = J/°C. Submit Answer Try Another Version 3 item attempts remaining Previous Next Save and Ex Cengage Learning…arrow_forward
- A chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction: Cl2(9)+H2(g) → 2 HCl(g) AH=-184. kJ Use the information to answer the following questions. endothermic. This reaction is... x10 exothermic. Suppose 39.8 g of Cl, react. Yes, absorbed. Yes, released. Will any heat be released or absorbed? No. If you said heat will be released or absorbed in the second part of this question, calculate how much heat will be released or absorbed. kJ Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardA student runs two experiments with a constant-volume "bomb" calorimeter containing 1300. g of water (see sketch at right). thermometer stim First, a 6.500 g tablet of benzoic acid (C,H,CO,H) is put into the "bomb" and burned completely in an excess of oxygen. (Benzoic acid is known to have a heat of combustion of 26.454 k/g.) The temperature of the water is observed to rise from 21.00 "C to 51.76 °C over a time of 12.3 minutes. water insulation Next, 5.880 g of ethanol (C,H,OH) are put into the "bomb" and similarly completely burned in an excess of oxygen. This time the temperature of the water rises from 21.00 °C to 46.93 °C. chemical reaction Use this information, and any other information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions below about this reaction: "bomb A "bomb" calorimeter. C,H,OH() + 30,2) - 200,2) + 3H,0 (g) Be sure any of your answers that are calculated from measured data are rounded to the correct number of significant digits. Note for advanced…arrow_forwardof 1. Magnesium solid reacts with aqueous hydrochloric acid to form the Mg2+ ion in solution. In an experiment, 60.0 mL of aqueous HCl was mixed with 0.1297 g magnesium solid in a double Styrofoam cup calorimeter. The reaction caused the temperature of the substances in the calorimeter to rise 10.02°C. Assume the density and specific heat of the HCl solution is that of water, 1.00 g/mL and 4.184 J/g °C, respectively. The specific heat of magnesium is 1.02 J/g °C. a. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. b. Calculate the heat of this reaction, AHrxn, in kJ. c. Calculate the heat of this reaction per mole of Mg2+ formed, AHxn/mole Mg2+. d. The literature value of this reaction is -466.85 kJ/mole. Calculate the percent deviation of the experimental value from the literature value.arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution ...arrow_forwardReactions are classified as either exothermic or endothermic. Exothermic reactions feel hot (e.g., a burning campfire), whereas endothermic reactions feel cool (e.g. squeezing an instant cold pack). A thermometer measures the temperature of the surroundings in a calorimeter to determine the amount of energy being transferred by the system. Water molecules speed up when they gain heat and slow down when they lose heat; note that you can track both the cold and hot water molecules in the simulation based on the shade of red of the larger central oxygen atom by checking the box labeled Show microscopic view. Select the Experiment tab in the simulation, and then click Run Demonstration. When observing the simulation, pay particular attention to the temperature change and movement of the molecules by clicking Show microscopic view when HCl and NaOH neutralize each other in the fourth experiment. Use your observations to complete the following sentences. Match the words in the left column to…arrow_forwardWhen thermal energy is transferred from the system to its surroundings, heat (q) is:arrow_forward
- A chemist measures the energy change AH during the following reaction: 2 Fe,O3(s) → 4 FeO(s)+O,(g) AH=560. kJ Use the information to answer the following questions. endothermic. This reaction is... х10 exothermic. Suppose 17.3 g of Fe,O, react. Yes, absorbed. Yes, released. Will any heat be released or absorbed? No. If you said heat will be released or absorbed in the second part of this question, calculate how much heat will be released or absorbed. kJ Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardAccording to the following thermochemical equation, what mass of HF (in g) must react in order to produce 487. kJ of energy? Enter your answer as an integer. SiO,(s) +4 HF(g- SIFale) + 2H,O1) AH--184 k/mol Type your answer. Next Previousarrow_forwardThe heat capacity of a substance can be obtained by multiplying its mass by its specific heat. Specific heat is defined as the amount of heat that must be supplied to the unit mass of the substance to raise its temperature by one unit. According to this, indicate the units in which the heat capacity is measured.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY