
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
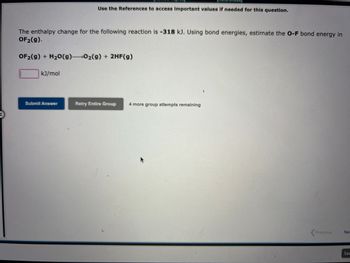
Transcribed Image Text:The enthalpy change for the following reaction is -318 kJ. Using bond energies, estimate the O-F bond energy in
OF₂(g).
OF₂(g) + H₂O(g) 0₂(g) + 2HF(g)
kJ/mol
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group 4 more group attempts remaining
Previous
Nex
Sav
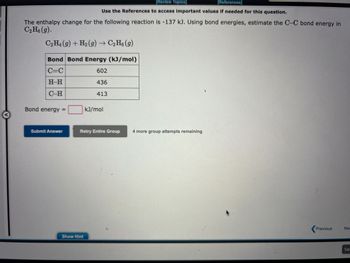
Transcribed Image Text:The enthalpy change for the following reaction is -318 kJ. Using bond energies, estimate the O-F bond energy in
OF₂(g).
OF₂(g) + H₂O(g) 0₂(g) + 2HF(g)
kJ/mol
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group 4 more group attempts remaining
Previous
Nex
Sav
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Write the steps (reactions) for the Born-Haber cycle for MgCl2(s). Use the Born-Haber cycle to calculate the lattice energy of MgCl2(s). Some useful data to work with: For Mg: ΔΔHsub = 147 kJ/mol, IE1 and IE2 are 738 kJ/mol and 1450 kJ/mol, respectively. For chlorine: Bond energy = 243 kJ/mol, EA1 = -349 kJ/mol, respectively. The enthalpy of formation of magnesium chloride is -748.8 kJ/mol.arrow_forwardUse the bond energy to calculate an approximate value of AH for the following reaction. Which is the more stable form of FNO2? 0=N-0-F:arrow_forwardThe enthalpy change for the following reaction is 206 kJ. Using bond energies, estimate the C-H bond energy in CH4(g). CH4(g) + H₂O(g)-3H₂(g) + CO(g) kJ/molarrow_forward
- What energy change is associated with the reaction to obtain one mole of H2 from one mole of water vapor? The balanced equation is 2 H20(g)2H2(g) + O2(g) and the relevant bond energies are: HH = 436 kJ/mol; H- O 467 kJ/mol; O - O 146 kJ/mol; O O = 498 kJ/mol.arrow_forwardCalculate the ΔHrxn using bond enthalpies for the balanced equation below (Lewis structures also provided). Bond Enthalpy Values: Bond ΔH (kJ/mol) C=C 611 C–H 414 H–H 436 C–C 347 Group of answer choices -219 kJ -128 kJ 286 kJ -564 kJarrow_forwardCalculate the lattice energy for the formation of Mg+2(g) + S -2 (g) → MgS (s) ΔH= ?arrow_forward
- 2. Use the data provided below to calculate the lattice energy of calcium chloride. Electron affinity of Cl = -348.7 kJ/mol 1st ionization energy of Ca = 590.0 kJ/mol 2nd ionization energy of Ca = 1145.0 kJ/mol Bond energy of Cl2 = 242.6 kJ/mol Sublimation energy of Ca = 178.0 kJ/mol AH¡ [CaCl. (s)] =-795.0 kJ/molarrow_forwardIf the bond energy for the N−HN−H bond is 391 kJ/molkJ/mol, how much energy is released when 1 molmol ammonia gas is formed?arrow_forward-U * USing average bond enthalpies (linked above), Estimate the enthalpy change for the following reaction: 2 HCI (g) + Brz (g) → 2 HBr (g) + C/₂ (g) KJarrow_forward
- Use bond energies to determine the energy change for the following reaction (-) indicates exothermic and (+) indicates endothermic energy change: H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)arrow_forwardExplain how you would get an enthalpy of formation that is greater than zero using the magnitudes of the bond enthalpies and equation 9.3 (given in the image attached)arrow_forwardKBr has a lattice energy -671 kJ/mol. Consider a hypothetical salt XY. X3+ has the same radius of K+ and Y3− has the same radius as Br−. Estimate the lattice energy of XYXY.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY