
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
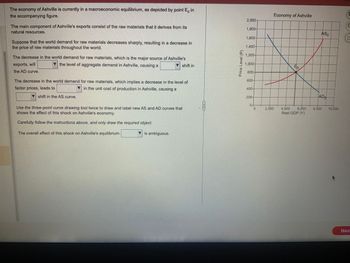
Transcribed Image Text:The economy of Ashville is currently in a macroeconomic equilibrium, as depicted by point E, in
the accompanying figure.
The main component of Ashville's exports consist of the raw materials that it derives from its
natural resources.
Suppose that the world demand for raw materials decreases sharply, resulting in a decrease in
the price of raw materials throughout the world.
The decrease in the world demand for raw materials, which is the major source of Ashville's
exports, will
the level of aggregate demand in Ashville, causing a
▼shift in
the AD curve.
The decrease in the world demand for raw materials, which implies a decrease in the level of
factor prices, leads to
in the unit cost of production in Ashville, causing a
7 shift in the AS curve.
Use the three-point curve drawing tool twice to draw and label new AS and AD curves that
shows the effect of this shock on Ashville's economy.
Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required object.
The overall effect of this shock on Ashville's equilibrium
▼is ambiguous.
#PTT
Price Level (P)
2,000-
1,800-
1.600-
1,400-
1,200-
1.000
800-
600-
200-
0
outl
2.000
Economy of Ashville
Eo
4,000
Real GDP (Y)
ASO
ADO
6,000 8.000 10,000
P
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a demand curve where Q = 20-3P and two supply curves where Q = P + 2 (closed economy) and P = 2 (open economy). a- Draw these three curves on the same captioned graph (add your graph to the appendix) b- What are the price and the equilibrium quantity in a closed economy. c- Evaluate the gains for consumers in an open economy as well as the gains and losses for local and foreign producers. (index: price, quantity consumed, quantity produced locally, imports. Make a comparison between closed economy and open economy.) Calculate the social surplus in an open economy. d- If the government establishes an import quota of 8 units, what will be the changes compared to the previous situation (open economy without protection); calculate the social surplus in this case. e- How much should the price per unit be fixed so that the results are the same as those obtained in question d. f- What should be the price so that the market is distributed one third, two thirds between local…arrow_forwardThe graph below is associated with a hypothetical country. Consider a decrease in aggregate demand (AD). Specifically, aggregate demand shifts to the left from AD₁ to AD2, causing the quantity of output demanded to fall at each price level. For instance, at a price level of 140, output is now $200 billion, where initially it was $300 billion. PRICE LEVEL 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 0 100 +-+ I I 200 300 400 500 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) AD1 AD2 600 700 800 ?arrow_forwardThe U.S. economy relies heavily on international trade. Choose two transactions at random that result from international trade; one where purchases are made from another country and one where the U.S. sends a product to another country. Identify the impact of each of these on imports, exports, net imports, and net exports at the time the transaction takes place. For example, if you purchase a product online that is made in and shipped from Italy to you in the United States what is the effect on the U.S. economy in these four categories at the time of the transaction? In addition, there has been a lot of news in recent years surrounding tariffs. Exactly what is a tariff and what is the impact of tariffs on international trade? Who pays the cost of tarffs?arrow_forward
- Suppose that the U.S. increases its tariffs on all imported goods. Obviously, this will have an impact on the amount of U.S. imports. What indirect effect will this have on U.S. exports – and why?arrow_forwardComplete the following paragraph to explain the effect of multinational enterprises on a host nation's economy. Assume a large pharmaceutical company based in Germany, where the corporate tax is 37% decides to relocate some production of pharmaceuticals to Ecuador, where the corporate tax is 8%. If the parent company from Germany purchases pharmaceuticals from its subsidiary in Ecuador at grossly inflated prices, the result is a neutral impact on Ecuador's economy, and a positive impact on Germany's economy. As a result, the regarding the German subsidiary locating in Ecuador. governments of Germany and Ecuador are likely to experience conflict Now, assume that a major national election takes place in Ecuador. As a result, the Indigo party has come to power. Assume that the Indigo party's main political stance is nationalization of all pharmaceutical facilities. Based on this knowledge of the Indigo party's politics, businesses in Germany are likely to support ▼ the election of the…arrow_forwardImproved methods of inventory control were supposed to reduce fluctuations in inventory stocks. It is clear that these methods have helped reduce the equilibrium inventory/sales ratios in both the manufacturing and trade sectors over the past decade. Yet we find that during the 2001 recession, inventory investment accounted for more than the total decline in real GDP, the first time that had happened since 1949. Explain whether this result is due to a set of odd coincidences, or whether the improved methods of inventory control actually caused bigger fluctuations in inventory investment relative to final sales.arrow_forward
- Consider the following information pertaining to a country's imports, consumption, and production of t-shirts following the removal of Multi Fiber Agreement (MFA) quotas: Under After МFA МFA World Price ($/shirt) Domestic Price (S/shirt) Domestic Consumption (millions of shirts) Domestic Production (millions of shirts) 2.00 2.00 2.50 2.00 100 125 75 50 a. Use the information in the table above to graph the effects of the quota removal on domestic consumption and production. Include a companion graph for the world market like that shown in class. b. The deadweight loss associated with the quota is: c. The quota rents that were earned under the quota are: d. The gain in consumer surplus associated with quota removal is: e. The loss in producer surplus from the removal of the quota is: f. Assuming that the foreign government assigned the quota licenses, the amount the home country gained from removal of the quota is: 4.arrow_forwardQuestion 2 D- i),ii) and iii)arrow_forwardConsider an oil-exporting economy in its long-run equilibrium. Which of the following explains the ultimate short-run effect of a decrease in international oil price on the GDP of this economy? The GDP will ultimately be at potential output. The GDP will ultimately decrease. The GDP will ultimately increase. The effect on GDP will be ambiguous.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education