
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
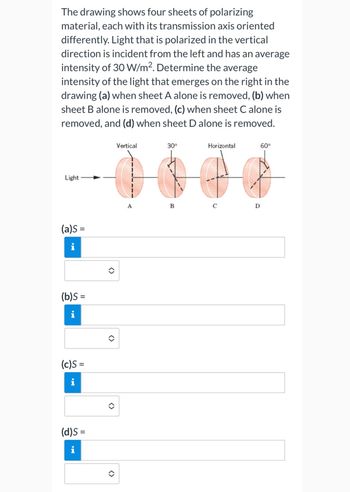
Transcribed Image Text:The drawing shows four sheets of polarizing
material, each with its transmission axis oriented
differently. Light that is polarized in the vertical
direction is incident from the left and has an average
intensity of 30 W/m². Determine the average
intensity of the light that emerges on the right in the
drawing (a) when sheet A alone is removed, (b) when
sheet B alone is removed, (c) when sheet C alone is
removed, and (d) when sheet D alone is removed.
Light
(a)s =
i
(b)S =
(c)S =
HI
(d)s=
i
()
<>
()
Vertical
A
30°
B
Horizontal
с
D
60°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The electric component of a beam of polarized light is Ey=(5.21 V/m) sin((1.08 x 106 m ¹)z + wt]. (a) Write an expression for the magnetic field component of the wave, including a value for w. What are the (b) wavelength, (c) period, and (d) intensity of this light? (e) Parallel to which axis does the magnetic field oscillate? (f) In which region of the electromagnetic spectrum is this wave? (a) B=(i i (b) Number i (c) Number i )t] ✓) sin[(i si Units Units ×106 ✓ )2 + (arrow_forwardA wave is passing through two polarizers. It is an unpolarized electromagnetic wave, and it initially has a max electric field magnitude of 20000N/C. The 1st polarizer, polarizes at an angle of 20 degrees vertical. The 2nd polarizer, polarizes at an angle of 30 degrees horizontal. What would be the intensity of a light wave that passes through the two polarizers?arrow_forwardFrom a local TV station transmitter, a sinusoidal, plane electromagnetic wave is normally incident on an open window that has an area of 0.510m2. The wave travels to the right in the positive x-direction at the speed of light c and the window is thus perpendicular to the x-axis. See the schematic. Suppose the three electric field components have wave functions: EX = 0 EY = Emsin(kx-ωt) EZ = 0 See the axes below. At the moment shown the electric field - indicated by the vertically upward arrow - points in the positive y direction. Assume the field magnitude Em = 0.01000 V/m. The Erms (root mean square) of the electric field would thus be Erms = 0.00707 V/m. (a) At the moment shown above, in what direction does the magnetic field point? Indicate this direction by drawing a symbol near the z-axis. (b) Compute the numerical value of amplitude Bm of the magnetic field component pointing in the direction you found.arrow_forward
- A plane electromagnetic wave varies sinusoidally at 90.0 MHz as it travels through vacuum along the positive x direction. The peak value of the electric field is 2.00 mV/m, and it is directed along the positive y direction. Find (a) the wavelength, (b) the period, and (c) the maximum value of the magnetic field. (d) Write expressions in SI units for the space and time variations of the electric field and of the magnetic field. Include both numerical values and unit vectors to indicate directions. (e) Find the average power per unit area this wave carries through space. (f) Find theaverage energy density in the radiation (in joules per cubic meter). (g) What radiation pressure would this wave exert upon a perfectly reflecting surface at normal incidence?arrow_forwardThe electric component of a beam of polarized light is Ey = (5.08 V/m) sin[(1.10 × 10° m-4)z + wt). (a) Write an expression for the magnetic field component of the wave, including a value for w. What are the (b) wavelength, (c) period, and (d) intensity of this light? (e) Parallel to which axis does the magnetic field oscillate? (f) In which region of the electromagnetic spectrum is this wave? (a) Bx = ( i ) sin[( i x106 v )z +( i )t] (b) Number i Units (c) Number i Units (d) Number i Units (e) (f) > >arrow_forwardThe average intensity of light emerging from a polarizing sheet is 0.789 W/m2, and that of the horizontally polarized light incident on the sheet is 0.865 W/m2. Determine the angle that the transmission axis of the polarizing sheet makes with the horizontal.arrow_forward
- A linearly polarized sinusoidal electromagnetic wave moving in the positive x direction has a wavelength of 7.60 mm. The magnetic field of the wave oscillates in the xz plane and has an amplitude of 6.90 µT. The magnitude of the electric field vector for this wave can be written as E = Emax sin(kx – øt). What are the following? (a) the value of Emax 2070 V/m (b) the wave number k 826.73 m-1 (c) the angular frequency w 2.48e11 rad/s (d) the plane in which the electric field oscillates the xz plane the yz plane the xy plane (e) the average Poynting vector (Express your answer in vector form.) Sav 11.37 · 10°i X W/m² (f) the radiation pressure exerted by this wave on a perfectly reflecting lightweight solar sail 3.79e-5 Pa (g) the acceleration of the solar sail if its dimensions are 5.00 m x 8.00 m and its mass is 40.0 g 0.038 m/s²arrow_forwardWe want to rotate the direction of polarization of a beam of polarized light through 90° by sending the beam through one or more polarizing sheets. (a) What is the minimum number of sheets required? (b) What is the minimum number of sheets required if the transmitted intensity is to be more than 83% of the original intensity?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON