
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The diameters of the solid shafts in the gear wheel set shown in the figure are dAB = 20mm, dCD = 25mm, dEF = 40mm. Since the safety shear stress of each shaft is 90MPa, determine the largest T torque that can be applied. Calculate the total angle of rotation in A for the maximum applied torque value.
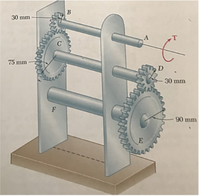
Transcribed Image Text:B.
30 mm
A
T
C
75 mm
30 mm
F
90 mm
E
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2- The motor in the figure applies 50 Nm torsion (torque) to the AB shaft. This torque is transferred to the CD shaft with the help of gears at points E and F. Bearings at B, C and D points provide free rotation to the shafts. Calculate the torque T' on the CD Shaft?arrow_forward3. A steel shaft 60 in. long has applied to it a 10,000 in-lb torque by a pulley located at the center of the shaft. A gear at the left end of the shaft applies 8000 in-lb of torque to the shaft while a gear located 9 in. to the left of the right end of the shaft applies 2000 in-lb of torque. Calculate the angular deflection of the shaft if the shaft is 2 in. in diameter for a length of 36 in. from the left end of the shaft and 1.5 in. in diameter in the remainder of the shaft. Neglect the effect of the keyways in the calculations. Ans. 0.424oarrow_forwardEx. #5] Pinion 2 in the figure runs at 1 750 rpm and transmits 2.5 kW to idler gear 3. The teeth are cut on the 20° full-depth system and have a module of m= 2.5 mm. Draw the free body diagram of gear 3 and shows all the forces acting upon it. Determine the forces acting upon gear 3. The direction of rotation of gear 3, as shown, is counterclockwise. GIVEN: Figure shown N₂ = 1750 rpm $=200 P = 2.5 kW m = 2.5 mm 3 0₂ REQUIRED: CS Draw the freechody distram of gear 3 and compute the forces acting on it.arrow_forward
- In the double-reduction gear train shown (dimensions are in inches), shaft a is driven by a motor attached by a flexible coupling attached to the overhang. The motor provides a torque of 2500 lbf-in at a speed of 1200 rpm. The gears have 20° pressure angles, with diameters shown in the figure. Use an AISI 1020 cold-drawn steel. Design Shaft CD with a design factor of 1.5 by performing the following tasks. (a) Sketch a general shaft layout, including means to locate the gears and bearings, and to transmit the torque. (b) Perform a force analysis to find the bearing reaction forces, and generate shear and bending moment diagrams. (c) Determine potential critical locations for stress design. (d) Determine critical diameters of the shaft based on fatigue and static stresses at the critical locations. (e) Make any other dimensional decisions necessary to specify all diameters and axial dimensions. Sketch the shaft to scale, showing all proposed dimensions. (f) If any of the deflections…arrow_forwardPhoto by Norbert Schnitzler, CC BY-SA 2.0 simple model 36 in bearing bearing fixed support A simplified model of two solid circular shafts connected by two rigid gears is given below. Determine: (1) the torque in shaft c-d to the nearest in-lb and (2) the angle of twist at point a in degrees with two decimal places. b bearing bearing a 62 in Notes: top view (sketch not to scale) - gear b radius= 1.25 in - gear c radius = 4.60 in - shaft ab radius = 1.00 in -shaft cd radius = 0.75 in - shear modulus = 12000 ksi 1100 in-lbarrow_forwardThe four helical gears shown in figure have a module in the normal plane of 4 mm and a pressure angle in the normal plane of 0.35 rad. The motor shaft rotates 550 rpm and transmits 20 kW. Other data are on the drawing. (a) What is the speed ratio between the motor (input) and output shafts? (b) Determine all force components that the 20-tooth pinion applies to the 50-tooth gear. Make a sketch showing these forces applied to the gear. (c) The same as part (b), except for the force components that the 50-tooth gear exerts on the 25- tooth pinion 100 50 teeth 200 125 25 teeth ψ = 0.35 rad right hand Motor 20 teeth ψ = 0.50 rad left hand 50 teeth Outputarrow_forward
- The figure shows a pair of shaft-mounted spur gears having a diametral pitch of 5 teeth/in with an 18-tooth 20° pinion driving a 45-tooth gear. The power input is 28-hp at 1700 rev/min. Find the magnitude of the force acting on bearing D. 3 2 3 in 3 in The magnitude of the force acting on bearing Dis lbf.arrow_forwardThe figure shows a shaft carrying three gears that rotates at 1150 rpm. Gear A delivers power =10kw to a mating gear that drives a mixer. Gear C delivers power =15kw to a different mating gear that drives a circular saw. All power comes into the shaft through gear B. Draw sheardiagramand bending moment diagram. Considering only torsion, compute the body free diagram and shearing stress in each part of the shaft. Consider stress concentrations, assume the Material is 1144 OQT 1300.arrow_forwardThe figure shows a shaft carrying three gears that rotates at 1150 rpm. Gear A delivers power to a mating gear that drives a mixer. Gear C delivers power to a different mating gear that drives a circular saw. All power comes into the shaft through gear B. Draw sheardiagramand bending moment diagram . Considering only torsion, compute the shearing stress in each part of the shaft. Consider stress concentrations, assume the Material is 1144 OQT 1300,And GearA=10kw, Gear C=15kw.arrow_forward
- Oh no! The bearing at the wall on the left has been damaged. It is now acting like another gear that can resist a moment(TW). You estimate the shaft has had torsional loading as follows: TA= 200 Nm TB= 530 Nm TC= 120 Nm TD= 150 Nm TW =? See the diagram for the direction of the torques on the shaft. The shaft diameter is 60 mm. The shaft looks ok but you are checking to see if it has exceeded the allowed shear stress for the shaft. Tw .600 mm 600 mm 600 mm A) Which segment has the maximum Torsion? B) What is the maximum shear stress due to torsion? C) Assume Tallow = 60 MPa did the shaft exceed the allowed shear?arrow_forwardA power transmission mechanism consists of a belt drive and a gear train as shown in the figure. Diameters of pulleys of belt drive and number of teeth (T) on the gears 2 to 7 are indicated in the figure. Find the speed and direction of rotation of gear 7 ? !187 2 N = 2500 rpm 150 mm 250 mm 36T 157 167 337 44Tarrow_forwardIn a gear set, a 36-tooth spur pinion drives a 60-tooth spur gear. The teeth of these gear are cast iron profile. The diametral pitch is 6-teeth/in, the face width si 0.5 inches, and the pressure angle is 20 degrees. Assume that the pinion transmits 10 hp at a speed of 2000 rpm. Find the pitch diameters of the gears. Find the pitch line velocity in ft/min Find the velocity factor Ky Find the tangential load in lbf Find the contact stress in kpsi, assuming CP=1960 psi.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY