
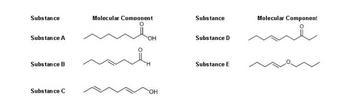
Concept explainers
The DIAGRAM below contains FIVE PURE SUBSTANCES with the molecular component
shown per substance. Using this DIAGRAM answer the questions.
1. Which substance CANNOT decolorize bromine water?
Substance A
Substance B
Substance C
Substance D
2. Which substance is expected to turn blue litmus paper into red color?
Substance A
Substance B
Substance C
Substance D
3. Which substance has the greatest tendency to participate in a
reaction
Substance A
Substance B
Substance D
Substance E
4. Which substance has the highest solubility to hexadecane?
Substance A
Substance C
Substance D
Substance E
5. Which substances can react with potassium borohydride, converting the
product into
Substance A and B
Substance B and D
Substance C and D
Substance D and E
6. Aside from London dispersion forces, which substance do you expect dipole
interactions to be effective?
Substance A and B
Substance B and D
Substance A and C
Substance B and E
7. Which substance is expected to have the lowest boiling point?
Substance A
Substance C
Substance D
Substance E
8. The presence of trans pi bonds can influence molecular stacking due to the
limitation of bond rotation. Based on this information, which substance is
characterized by molecules that have effective molecular stacking?
Substance B
Substance C
Substance D
Substance E
9. The physical properties of the substances are influenced by intermolecular
forces of attraction. Which substance(s) are predominantly influenced by the
intermolecular association of the molecules via hydrogen bonding?
Substance A only
Substance A and C
Substance A, B, and C
Substance A, B, C, and D
10. Which substance will exhibit the lowest melting point?
Substance A
Substance B
Substance D
Substance E
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- Help with the following questionarrow_forwardBased on the table below, which sample has the lowest melting point? Fat or oil Palmitic A 24.6 B 14.6 C 8.5 D 6.0 Sample A Sample B Sample C Sample D % Fatty acid by weight Stearic Oleic Linoleic 15.0 50.4 10.0 75.4 10.0 6.00 51.6 26.0 2.0 44.0 48.0arrow_forwardIn chem lab when creating aspirin, how does a melting point range for pure aspirin compound differ from impure? Explain the meaning of value and range of melting point. How does the meaning of value melting point and range of melting pointarrow_forward
- Rank these substances in order of increasing solubility in water. Solubility Substances (4 items) (Drag and drop into the appropriate area) Most soluble CH3CH2CH2OH 1 CH3(CH2)5OH CH3(CH2)3OH 2 CH3CH2OH 3. 4 Least solublearrow_forwardIn comparing a reaction run under reflux versus distillation, distillation will remove the product, as it's formed. Are we using thermodynamics or kinetics to drive the reaction? Only kinetics because the raised temperature makes the reaction occur faster Only thermodynamics because we're removing products, Le Chatlier would describe this as a way to favor products Both kinetics and thermodynamics are favored Neither kinetics or thermodynamics are favoredarrow_forwardCircle the FOUR fat soluble substances.arrow_forward
- Please answer subparts to question 4. A,B, and C 4. For each substance described below, indicate whether it is a solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature. 4a. A clear substance that takes the shape of its container but does not fill it up completely 4b. A green colored substance with a melting point of 234 °C. 4c. A substance that maintains its shape when you remove it from the box that held it.arrow_forwardWhat do you think are the chemical reactions involved in breathalyzer test administered to potentially drunk drivers? Provide the reactants and products of the reaction and explain what observations would indicate if the person was drunkarrow_forward12. Normal boiling point of ethanol (C2H5OH) is 78 °C, and of propanol (C3H;OH) is 97 °C. a. Explain the reason for the difference in boiling points of these two alcohols. b. When the underline methyl group in propanol, CH3CH2CH2OH, is replaced with a hydroxyl group (HOCH2CH2OH), boiling point of the molecule increases to 197 °C. Explain the reason for observed increase in the boiling point.arrow_forward
- Constants Periodic Table A sample of a liquid substance called jojane- named after the narcissitic scientist Dr. Joey Negdirf who discovered the substance- was brought back to Earth following a five year mission exploring the Andromeda galaxy. In their lab on earth, Dr. Negdirf's team conducted a number of experiments to determine the physical properties of the substance. Part A Using the Dumas method to determine the molar mass of a volatile liquid, a sample of jojane was vaporized in a 2.000 L vessel and heated to 401.6 K at 1.150 bar. The mass of the vapour in the vessel was 5.106 g. Determine the the molar mass of the compound. 60.10 g mol-1 O 88.14 g mol-1 O 72.09 g mol-1 O 74.12 g mol-1arrow_forwardChemistry HW need help, how to do these caculation and answer these questions?arrow_forwardAspirin has a higher molar mass compared to salicylic acid, however aspirin melts at a lower temperature than salicylic acid. Provide a brief explanation for this observation. Table 1 Compound: Formula: Salicylic Acid C;H6O3 Aspirin C9H3O4 Molar Mass: 138.12 Melting point: Ka 158-160°C 1.08 x 10³ 180.15 140-142°C 2.72 x 10$ pKa Solubility (g/100ML) 2.99 4.57 0.18 0.25arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





